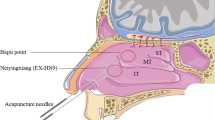
Abstract
Objective: To observe the therapeutic effect of acupuncture-moxibustion at different intervals on persistent allergic rhinitis.
Methods: A total of 90 patients conforming to the inclusion criteria were randomized into three groups named A, B and C by randomized block method. Patients in all three groups received the same treatment of acupuncture and herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion at the same acupoints, while the treatment frequency was different. Patients in group A received the treatment once a week, group B twice a week and group C three times a week, and all the treatment lasted for 4 weeks. The total nasal symptom score (TNSS), total ocular symptom score (TOSS) and Sino-nasal outcome test-20 (SNOT-20) were evaluated before and after treatment. The self-rating score of symptoms was evaluated during treatment and 2 weeks after treatment.
Results: The total effective rate was 80.0% in group A, 93.3% in group B, and 100.0% in group C. The total effective rate in group A was statistically different from that in group B and group C (both P<0.05), but there was no significant inter-group difference in total effective rate between group B and group C (P>0.05). After treatment, scores of TNSS, TOSS and SNOT-20 in all three groups dropped significantly, and statistically different from those before treatment (all P<0.05); between-group comparison showed group B and group C decreased more obvious than group A (all P<0.05). In self-rating score of symptoms, there were no inter-group statistically significant differences in the first 3-week treatment (all P>0.05); after 4-week treatment, the score in group A was higher than that in group B and group C, and showed statistical significant (both P<0.05); at 2 weeks after treatment, the score in group A was higher than that in group B and group C based on an everyday record, showing statistical significance (both P<0.05). At the 11th day after treatment, the score in group B was higher than that in group C (P<0.05). There were no significant differences between group B and group C at other time points (all P>0.05).
Conclusion: All three protocols are effective for allergic rhinitis. With the increase of treatment frequency, the therapeutic efficacy with a treatment frequency of twice a week and three times a week is superior to that of once a week. Frequency of three times a week has a better long-term effect than once and twice a week, together with the least fluctuation of symptoms.
摘要
目的: 观察不同频次针灸治疗持续性变应性鼻炎的临床疗效。
方法: 将符合纳入标准的90例患者, 采用 随机区组法分为A组、B组和C组。三组治疗方法相同, 均采用相同穴位进行针刺和隔药饼灸, 但三组治疗频次不 同, A组每周治疗1次, B组每周治疗2次, C组每周治疗3次。三组均治疗4周。观察三组治疗后鼻部症状总评分(TNSS)、 眼部症状总评分(TOSS)和鼻腔鼻窦结局评分(SNOT-20)的变化。观察治疗期间及治疗结束后2周患者症状自主评分 变化。
结果: A组总有效率80.0%, B组总有效率93.3%, C组总有效率100.0%; A组总有效率与B、C组的差异均有统计 学意义(均P<0.05), B组和C组总有效率无统计学差异(P>0.05)。TNSS, TOSS和SNOT-20评分方面, 治疗后, 三组评分 均较同组治疗前降低, 组内差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05); 组间比较, B、 C两组评分较A组降低更明显(均P<0.05)。 症状自主评分方面, 治疗前3周三组评分无统计学差异(均P>0.05); 第4周时A组评分高于B组和C组, 组间差异有 统计学意义(均P<0.05); 治疗结束后2周A组每天的评分均高于B组和C组, 组间差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05); 治 疗结束后第11天B组高于C组(P<0.05), 其余时间B组和C组差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。
结论: 三种治疗频次对 于持续性变应性鼻炎患者均有效, 且随着治疗时间的累计, 每周2次及每周3次治疗的疗效优于每周1次。每周3次 较每周1次及每周2次更能维持疗效, 且治疗结束后患者症状波动最小。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association of Otolaryngology, Chinese Medical Association, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Otolaryngology. Attachment: clinical classification and staging of chronic sinusitis and nasal polyps and evaluation criteria of endoscopic sinusitis surgery (Haikou, 1997). Zhonghua Erbiyanhouke Zazhi, 1998, 33(3): 134–135.
Zheng M, Wang X, Zhang L. Distinctive prevalence of allergic rhinitis among adults in urban and rural areas of China: a population-based cross-sectional survey. J Allerg Clin Immunol, 2015, 135(2): 148–157.
Department of Rhino logy, Society of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis (Tianjin, 2015). Zhonghua Erbi Yanhou Toujing Waike Zazhi, 2016, 51(1): 6–24.
Wang DJ, Wang SZ. Otolaryngology of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2008.
Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Diagnostic and treatment principle for allergic rhinitis and a recommended scheme (2004, Lanzhou). Zhonghua Erbi Yanhou Toujing Waike Zazhi, 2005, 40(3): 166–167.
Wang Q, Liu ZB, Niu WM, Yang XH, Wang Y, Zhu XW, Liu SY, Wang WG. Effects of electroacupuncture of Yingxiang (LI 20) on expression of Ki-67 and IGF-1R of olfactory mucosa and IGF-1 of olfactory bulb in rats with olfactory dysfunction. Shaanxi Zhongyi, 2016, 37(11): 1547–1550.
Liu ZB, Niu WM, Yang XH, Zhu XW, Wang Y, Wang Q, Liu SY, Wang WG. Influence of stimulating Yingxiang (LI 4) on the expression of bFGF in rats with olfactory dysfunction. Xiandai Zhongyiyao, 2016, 36(5): 97–101.
Cui LH, Xing X. Clinical study on paralleling puncturing Yingxiang (LI 20) with electroacupuncture for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Hebei Zhongyiyao Xuebao, 2014, 29(2): 36–37.
Han W A multi-center study on the effectiveness of Yintang (GV 29) during allergic rhinitis treatment. Zhongyiyao Linchuang Zazhi, 2007, 19(4): 392–394.
He YT, Li HQ, Zhao YD, Gao HY Treatment of 60 cases of allergic rhinitis mainly with point-through-point method. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2006, 26(2): 110–112.
Zhao LJ, Yin JY, Sun HF, Shi C, Wang PP, Liu Y. Analysis of acupuncture and moxibustion treatment of allergic rhinitis. Zhejiang Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2017, 41(7): 624–628.
Shen F, Peng YJ, Zhu BM, Lu SF, Shi J, Chen X. Principles of acupoint selection in treatment of allergic rhinitis based on data mining. Jilin Zhongyiyao, 2017, 37(2): 198–201.
Tai HQ, Jiang WF. Experimental research on treating allergic rhinitis with Xiaguan (ST 7). Zhejiang Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2008, 18(2): 747–748.
Zhang LW Fifty-seven cases of allergic rhinitis patients treated with Xiaguan (ST 7). Linchuang Yixue Yanjiu Yu Shijian, 2016, 18): 62.
Zhu GX. Treatment of allergic rhinitis with Shangxing (GV23). Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 1993, 13(1): 25–26.
Yu B, Wang C, Zhang YC. Analysis Hegu (LI 4) point in Zhen Jiu Da Cheng. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2016, 32(6): 61–64.
Jia XJ, Xiong YQ, Wang JY. Therapeutic effect of acupuncture and moxibustion on allergic rhinitis and its influence on the patients’ quality of life. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2019, 38(2): 202–205.
Zhang CH, Hong J, Wu LX, Liu J, Ma XP, Hou SY, Xie C. Clinical observation of Zhen’ai needling method in Nei Jing (Classic of Internal Medicine) on improving quality of life in patients with allergic rhinitis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2018, 15(5): 349–354.
Zhao S, Gu ME, Li S, Li J, Wu HG, Fan J. Research advances in the mechanism of action of acupuncture-moxibustion prevention and treatment of allergic rhinitis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2018, 37(6): 720–724.
Liu P, Zhang BM, Zong L, Hu ZH, Shou Y, Li BR, Yuan L, Xu SW, Yang Y, Zhang KY, Jiang HR. Therapeutic efficacy observation on acupuncture for persistent allergic rhinitis. J AcupunctTuinaSci, 2018, 16(4): 271–275.
Zhou GT. On the relationship between time and acupuncture treatment. Tianjin Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao, 2002, 21(4): 23–24.
Xue XJ, Liu ZB, Wang YY, Yang JS. Correlations of curative effect with time interval of acupuncture and moxibustion. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2018, 34(1): 1–4.
Zhang TJ, Liu LA. Review on the acupuncture interval for the treatment effect. Heilongjiang Zhongyiyao, 2013, 42(1): 59–61.
Pan L, Zhou L, Hu H. Relationship between acupuncture frequency and curative effect: a research on ancient literature. Beijing Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao (Zhongyi Linchuang Ban), 2013, 20(5): 33–35.
Zhong YT, Huang DL, Gao M. Research on the effect that frequency on the curative effect of acupuncture. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2012, 14(10): 132–133.
Zheng TL, Zhang W. Observations on the effects of different frequencies of acupuncture treatments on early idiopathic facial neuritis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2013, 32(3): 185–186.
Dai Z, Liu HS, Wang SJ, Bai W, Yang JY, Li H, Sun Y, Liu Q. Efficacy analysis on patients with knee osteoarthritis receiving acupuncture treatment with different frequencies. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi, 2014, 41(7): 1496–1498.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shanghai Special Diagnosis and Treatment Project of Acupuncture-moxibustion (上海 市针灸特色诊疗项目, No. ZJ2016022); Construction Project of Acupuncture-moxibustion Specialty Alliance [针 灸专科联盟建设项目, No. ZY(2018-2020)-FWTX-4008].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Fan, Q., Qin, Ml. et al. Therapeutic observation on acupuncture-moxibustion at different intervals for persistent allergic rhinitis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 409–415 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1143-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1143-6
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Acupuncture-moxibustion Therapy
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Herbal Cake Separated Moxibustion
- Rhinitis
- Allergic
- Frequency