Abstract
Objective: To observe the effect of warm-unblocking acupuncture plus fluticasone propionate nasal spray on the pulmonary ventilation, level of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and sleep quality in patients with allergic rhinitis (AR).
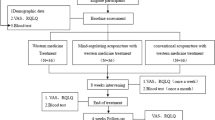
Methods: A total of 112 AR patients were enrolled between January 2013 and August 2018 and were divided into an observation group and a control group by the random number table method, with 56 cases in each group. Patients in the observation group received warm-unblocking acupuncture plus fluticasone propionate nasal spray, and patients in the control group only received fluticasone propionate nasal spray. The nasal symptom score, pulmonary function indexes, the levels of IFN-γ and interleukin (IL)-4 in serum, and sleep quality in the two groups were compared.
Results: After treatment, the total effective rate in the observation group was higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). The nasal symptom score dropped in both groups after treatment (both P<0.05), and the score in the observation group was lower than that in the control group (P<0.05). The pulmonary ventilation indexes all increased significantly after treatment in the observation group (all P<0.05); the forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity (FVC) ratio (FEV1/FVC) and the forced expiratory flow at 50%, 75% and 25%-75% of the vital capacity (FEF50%, FEF75%, FEF25%-75%) increased after treatment in the control group (all P<0.05); the pulmonary ventilation indexes were higher in the observation group than those in the control group (all P<0.05). The level of IFN-y increased significantly after treatment in the two groups (both P<0.05) and the level of IL-4 dropped significantly (both P<0.05); the observation group had a higher IFN-γ level (P<0.05) and a lower IL-4 level (P<0.05) compared with the control group. Regarding the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI), the scores of subjective sleep quality, habitual sleep efficiency and sleep disturbances and the general PSQI score decreased significantly after treatment in both groups (all P<0.05), and the scores in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: Warm-unblocking acupuncture plus fluticasone propionate nasal spray can effectively control the clinical symptoms and improve pulmonary function in the treatment of AR; this approach can regulate the levels of IFN-γ and IL-4 towards the normal range in AR patients; it can also improve patient’s sleep quality. This method can produce more significant efficacy than fluticasone propionate nasal spray used alone.
摘要
目的: 观察温通针法联合丙酸氟替卡松鼻喷雾剂对变应性鼻炎(AR)患者肺通气功能、γ-干扰素(IFN-γ)水平及睡眠质量的影响。
方法: 选取2013年1月至2018年8月就诊的112例AR患者, 依据随机数字表法分为观察组和对照组, 每组56例。观察组患者接受温通针法联合丙酸氟替卡松鼻喷雾剂治疗, 对照组患者仅接受与观察组相同的丙酸氟替卡松鼻喷雾剂治疗。比较两组鼻部症状评分、肺功能指标、血清IFN-γ与白细胞介素(IL)-4水平以及睡眠质量情况。
结果: 治疗后, 观察组总有效率高于对照组(P<0.05); 两组鼻部症状评分均低于治疗前(P<0.05), 且观察组评分低于对照组(P<0.05); 观察组肺功能各项指标均较治疗前明显上升(P<0.05), 对照组第一秒用力呼气容积占用力肺活量的百分比(FEV1/FVC)、用力呼出50%、75%及25%~75%肺活量的呼气流速占预计值的百分比(FEF50%, FEF75%, FEF25%-75%)较治疗前上升(P<0.05), 且观察组肺功能各项指标均明显高于对照组(均P<0.05); 两组IFN-γ水平均较治疗前明显升高(P<0.05), IL-4水平明显降低(P<0.05), 且观察组IFN-γ水平高于对照组(P<0.05), IL-4水平低于对照组(P<0.05); 两组匹兹堡睡眠质量指数(PSQI)中睡眠质量评分、睡眠效率评分、睡眠障碍评分及PSQI总分均较治疗前明显降低(P<0.05), 且观察组各项评分明显低于对照组(P<0.05)。
结论: 温通针法联合丙酸氟替卡松鼻喷雾剂治疗AR在控制临床症状与改善肺功能方面效果可靠, 可改变患者的IFN-γ和IL-4水平, 使之接近正常范围; 同时可改善患者睡眠, 其效果优于单独使用丙酸氟替卡松鼻喷雾剂。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie Q, Fu WY. Exploration on the treatment of allergic rhinitis by Chinese medicine. Xibu Zhongyiyao, 2015, 28(3): 140–142.
Chen WB. Therapeutic observation of montelukast plus fluticasone propionate nasal spray for allergic rhinitis. Zhongguo Xiangcun Yiyao, 2018, 25(10): 25, 50.
Zheng XL, Tian YP, Luo HY, Zhao YD, Liu XY, Jiang Y, Ma CX, Wang MJ, Liu M. Effect of warm acupuncture on the levels of serum immunoglobulin E, interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α in rats with allergic rhinitis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2018, 43(1): 34–37.
Editorial Board of the Chinese Journal of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis. Zhongguo Linchuang Yisheng, 2010, 38(6): 67–68.
State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 2009: 107–108.
Smyth C. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI). Medsurg Nurs, 2003, 12(4): 261.
Qian JF. Curative effect of fexofenadine hydrochloride tablets? Combined with fluticasone propionate in treatment of allergic rhinitis and effect on IFN-γ and IL-4 of patients. Zhong Wai Yiliao, 2016, 35(7): 125–126.
Feng J, Li YM, Wei M, Kang Q. Efficacy of fluticasone propionate nasal spray combined with electroacupuncture in treatment of patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Linchuang Wuzhen Wuzhi, 2017, 30(11): 101–105.
Muganurmath CS, Curry AL, Schindzielorz AH. Causality assessment of olfactory and gustatory dysfunction associated with intranasal fluticasone propionate: application of the Bradford Hill criteria. Adv Ther, 2018, 35(2): 173–190.
Liu T, Zhu L. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Zhongyiyao Linchuang Zazhi, 2017, 29(3): 436–439.
Wang MY, Lu YF. Experience of Lu Yan-fang in treating allergic rhinitis in kids. Hubei Zhongyi Zazhi, 2016, 38(2): 23–25.
Sun L, Yu ZX, Ma Y. Clinical observation of combining Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of allergic rhinitis of children. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2016, 34(5): 135–137.
Shi J, Liu Y. Clinical observation of Yiqi Tuomin Tang for allergic rhinitis of invasion of cold and lung deficiency type. Xin Zhongyi, 2017, 49(12): 110–112.
Tian YP, Zhao YD, Bi AP, Han DY. Observation on effects of ’warming-promotion acupuncture’ in treating allergic rhinitis of pulmonary deficiency & invasion of cold type. Xibu Zhongyiyao, 2012, 25(5): 82–84.
Pu YL, Su CH, Zhang YJ, Yang CG, Fang XL. Clinical and experimental research progress of Zheng’s warmunblocking acupuncture method. Gansu Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2017, 34(1): 86–90.
Sheng XY, Xing JM, Han YD, Zhang YF, Zhang XL, Yan XK. Summary of the theoretical foundation and clinical application of Prof. Zheng Kui-shan’s ’warming-dredging needling technique’. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2016, 14(2): 115–121.
Xu WL. Clinical analysis of acupuncture in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Zhongguo Weisheng Biaozhun Guanli, 2015, 6(8): 67–68.
Zhang CH, Hong J, Wu LX, Liu J, Ma XP, Hou SY, Xie C. Clinical observation of Zhen’ai needling method in Nei Jing (Classic of Internal Medicine) on improving quality of life in patients with allergic rhinitis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2018, 16(5): 349–354.
Shen F, Peng YJ, Zhu BM, Lu SF, Shi J, Chen X. Principles of acupoint selection in treatment of allergic rhinitis based on data mining. Jilin Zhongyiyao, 2017, 37(2): 198–201.
Liu P, Zhang BM, Zong L, Hu ZH, Shou Y, Li BR, Yuan L, Xu SW, Yang Y, Zhang KY, Jiang HR. Therapeutic efficacy observation on acupuncture for persistent allergic rhinitis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2018, 16(4): 271–275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the individual participants recruited in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Hy., Wei, Ql., Tian, Yp. et al. Effect of acupuncture plus medication on the pulmonary ventilation, IFN-γ level and sleep quality in allergic rhinitis patients. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 402–408 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1142-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1142-7
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Acupuncture Medication Combined
- Rhinitis, Allergic
- Fluticasone Propionate
- Nasal Sprays
- Pulmonary Ventilation
- Interferons
- Sleep