Abstract
Objective: To observe the effects of moxibustion on serum levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and to explore the effects of moxibustion on inflammatory damaging factors in experimental rheumatoid arthritis (RA) model rats; the relationship between the therapeutic effect of moxibustion on RA and the change in the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway was analyzed using Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) antagonists and agonists.
Methods: Fifty Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided into a normal group, a model group, a moxibustion group, a moxibustion plus TLR4 agonist group (agonist group) and a moxibustion plus TLR4 antagonist group (antagonist group) according to the random number table, with 10 rats in each group. Except the normal group, rats in the other four groups were subjected to model preparation with the wind, cold and wet environmental factors plus Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA). Rats in the normal and model groups were not treated; rats in the moxibustion, agonist and antagonist groups started to be treated with the moxibustion (cigarette-type moxa) at bilateral Shenshu (BL 23) and Zusanli (ST 36) from the 4th day after the successful modeling, for 20 min each time with a total of 10 d. Rats in the agonist and the antagonist groups were injected with TLR4 agonist or antagonist [0.1 mg/(kg•bw)] via the tail vein 30 min before moxibustion. The concentrations of serum IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in each group were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
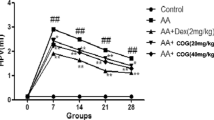
Results: Compared with the normal group, in the model group, the rat’s right hind paw swelling was significantly obvious (P<0.01), there was a lot of inflammatory infiltration in the synovial tissues, the surface of the synovial membrane was unsmooth, the synovial membrane was hyperplasia and thicker, and the serum IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α concentrations increased significantly (P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the paw swelling degrees of the rats in the moxibustion, the agonist and the antagonist groups reduced significantly (all P<0.01); the swelling degree in the antagonist group was milder than that in the agonist group, but the between-group difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05); inflammatory infiltration and synovial membrane hyperplasia in the synovial tissues of the moxibustion group and the antagonist group were all relieved differently; the decrease of synovial layer number in the moxibustion group was more obvious, and there were no obvious improvements in inflammatory infiltration and synovial thickness in the agonist group; the concentrations of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in the moxibustion group were decreased, and the differences in the IL-6 and TNF-α concentrations were statistically significant (all P<0.01); there was no significant between-group difference in the IL-8 concentration (P>0.05); the concentrations of serum IL-8 and TNF-α in the agonist group increased significantly (both P<0.01), while the IL-6 concentration decreased without significant difference (P>0.05); the concentrations of IL-6 and IL-8 in the antagonist group decreased but the between-group differences were statistically insignificant (both P>0.05), and the TNF-α concentration significantly increased (P<0.05). Compared with the moxibustion group, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α concentrations increased in the agonist group, and the differences in the IL-8 and TNF-α concentrations were statistically significant (both P<0.01); the concentrations of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α increased in the antagonist group, and the differences in the IL-6 and TNF-α concentrations were statistically significant (both P<0.01); there was no significant difference in the IL-8 concentration between the groups (P>0.05). The serum levels of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in the antagonist group were lower than those in the agonist group (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: Moxibustion at Shenshu (BL 23) and Zusanli (ST 36) can reduce the joint swelling degree and inflammation in synovial tissue of RA model rats, decrease the serum levels of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in RA model rats; the decreases of IL-6 and TNF-α are more significant than the decrease of IL-8; TLR4 agonist and antagonist can significantly attenuate the effect of moxibustion in inhibiting releases of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α, so that the change in TLR signaling pathway affects the effect of moxibustion in inhibiting the releases of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α.
摘要
目的:观察艾灸对实验性类风湿性关节炎(RA)模型大鼠血清中白细胞介素(IL)-6、IL-8和肿瘤坏死因子α (TNF-α)含量的变化, 探讨艾灸对RA模型大鼠相关炎性致损因子的干预作用; 通过应用Toll样受体4(TLR4)拮抗剂和 激动剂, 分析艾灸对RA的治疗作用与Toll样受体信号通路变化之间的关系。方法:将50只Sprague-Dawley(SD)大鼠 根据随机数字表分为正常组、模型组、艾灸组、艾灸加TLR4激动剂组(激动剂组)和艾灸加TLR4拮抗剂组(拮抗剂组), 每组10只。除正常组外, 其余4组大鼠采用风、寒、湿环境因素+弗氏完全佐剂(FCA)复合造模。正常组和模型组不 作治疗; 艾灸组、激动剂组和拮抗剂组于造模成功后第4天开始用香烟型艾条灸双侧肾俞和足三里, 每穴每次灸 20 min, 共灸10 d。激动剂组和拮抗剂组分别在艾灸前30 min经尾静脉注射TLR4激动剂或拮抗剂 [0.1 mg/(kg·bw)]。 采用酶联免疫吸附(ELISA)法测定各组大鼠血清IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α的浓度。结果:与正常组比较, 模型组大鼠右后 肢肿胀明显(P<0.01), 滑膜组织中有大量炎性浸润表现, 滑膜表面不整齐, 滑膜增生变厚; 血清IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α 浓度均显著升高(均P<0.05)。与模型组比较, 艾灸组、激动剂组和拮抗剂组大鼠的足趾肿胀程度均明显减轻 (P<0.01), 拮抗剂组肿胀程度轻于激动剂组, 但组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 艾灸组和拮抗剂组滑膜组织中 炎性浸润和滑膜增生变厚现象不同程度缓解, 其中艾灸组滑膜层数减少最明显, 激动剂组的炎性浸润和滑膜厚 度缓解不明显。艾灸组IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α浓度均下降, 其中IL-6和TNF-α浓度的组间差异有统计学意义(均P<0.01), IL-8浓度的组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 激动剂组大鼠血清IL-8和TNF-α的浓度均显著上升(均P<0.01), 而IL-6 下降, 但组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 拮抗剂组IL-6和IL-8浓度均降低, 但组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), TNF-α浓度升高, 组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。与艾灸组比较, 激动剂组IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α均升高, 其中IL-8和 TNF-α浓度的组间差异有统计学意义(均P<0.01); 拮抗剂组IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α浓度均升高, 其中IL-6和TNF-α浓度的 组间差异有统计学意义(均P<0.01), IL-8浓度的组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。拮抗剂组大鼠血清IL-6、IL-8和 TNF-α浓度均低于激动剂组(均P<0.05)。结论:艾灸肾俞和足三里可减轻RA模型大鼠足趾肿胀和滑膜炎症, 降低 血清中IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α浓度, 且IL-6和TNF-α的浓度下降较IL-8更为显著; TLR4激动剂和拮抗剂介入艾灸治疗能显 著减弱艾灸抑制IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α释放的作用, TLR信号通路的变化影响艾灸抑制IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α释放的作用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He W, Rebello O, Savino R, Terracciano R, Schuster-Klein C, Guardiola B, Maedler K. TLR4 triggered complex inflammation in human pancreatic islets. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2019, 1865(1): 86–97.
Huffman KM, Jessee R, Andonian B, Davis BN, Narowski R, Huebner JL, Kraus VB, McCracken J, Gilmore BF, Tune KN, Campbell M, Koves TR, Muoio DM, Hubal MJ, Kraus WE. Molecular alterations in skeletal muscle in rheumatoid arthritis are related to disease activity, physical inactivity, and disability. Arthritis Res Ther, 2017, 19(1): 12–29.
Li YY, Zhang WT. IL-6: the next key target for rheumatoid arthritis after TNF-α. Shengwu Gongcheng Xuebao, 2017, 33(1): 36–43.
Li P, Cao JP, Zhao LJ. Serum levels of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their significance. Zhonghua Fengshibingxue Zazhi, 1998, 2(4): 59–61.
Ye RG, Lu Z Y. Internal Medicine. 6th Edition. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2004: 885.
Hu L, Hao F, Zhong F, Qin LH, Xia XH, Chu HR, Luo L, Cai RL. Multicenter randomized controlled clinical study on rheumatoid arthritis with moxibustion. Huanqiu Zhongyiyao, 2011, 4(6): 401–405.
Ni ZZ. Health Statistics. 4th Edition. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2002: 267.
Hu L, Lars DH, Song XG, Tang ZL, Cai RL, He L, Luo L. Effect of moxibustion on IL-1β and IL-2 in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2010, 8(3): 149–153.
Yu SG, Guo Y. Experimental Acupuncture Science. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2014: 147–148.
Ding F. Moxibustion alone in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2007, 23(10): 40–41.
Zhang H, Ma XP, Wu HG, Wu SB, Su SS, Hu YC, Li ZF, Zhang L, Xie MY. Effect of moxibustion on tumor necrosis factor-α and nuclear transcription factor kappa B in ankle joints of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(3): 171–176.
Cai RL, Hu L, Song XG, Xia XH, Li M. A survey of clinical and experimental research on moxibustion for arthritis. Zhongyiyao Linchuang Zazhi, 2008, 20(4): 427–429.
Zhang LX, Wu J, Lan Y, Lu P, Liu M, Zhang YH, Hu YP. Research progress in the clinical and mechanism of acupuncture treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Heilongjiang Zhongyiyao, 2013, 42(1): 51–52.
Luo L, Hu L, Song XG, Tang ZL, He L, Cai RL, Hao F. Effect of moxibustion on the metatarsal joint cytokine in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Huanqiu Zhongyiyao, 2011, 4(6): 416–419.
Chen KH, Li RB, Li K, Qin L, Qin SJ, Lai YH, Zhong QN, Liang TW. Clinical effects of moxibustion treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and a study of its blood IL-6 and CRP levels. Zhongyao Yaoli Yu Linchuang, 2015, 31(1): 303–304.
Can CX, Yang QW, Lü FL, Cui J, Fu HB, Wang JZ. Reduced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in Toll-like receptor 4 deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2007, 353(2): 509–514.
Teng JY. Study on the Correlation of TLR4 Gene Polymorphism with the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Xiamen: Master Thesis of Huaqiao University, 2017.
Zhu XK, Yang RF, Meng YQ. Research progress in ligands of Toll-like receptor 4. Zhongguo Yaolixue Yu Dulixue Zazhi, 2016, 30(4): 389–396.
Sun W, Xiong Y, Fu YY Research progress in Toll-like receptor. Shiyan Yu Jianyan Yixue, 2008, 26(4): 413–416.
Ding RR, Chen W, Guo CY, Liao WT, Yang X, Liao FE, Lin JM, Mei HF, Zeng Y. Danggui Shaoyao San attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation via the TLRs/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 105: 187–194.
Xu JJ, Lu CJ, Liu ZQ, Zhang P, Guo HL, Wang TT Schizandrin B protects LPS-induced sepsis via TLR4/ NF-κB/MyD88 signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res, 2018, 10(4): 1155–1163.
Raymond SL, Hawkins RB, Murphy TJ, Rincon JC, Stortz JA, López MC, Ungaro R, Ellett F, Baker HV, Wynn JL, Moldawer LL, Irimia D, Larson SD. Impact of Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation on human neonatal neutrophil spontaneous migration, transcriptomics, and cytokine production. J Mol Med (Berl), 2018, 96(7): 673–684.
Ii M, Matsunaga N, Hazeki K, Nakamura K, Takashima K, Seya T, Hazeki O, Kitazaki T, Iizawa Y. A novel cyclohexene derivative, ethyl (6R)-6-[N-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl) sulfamoyl]_cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate (TAK-242), selectively inhibits Toll-like receptor 4-mediated cytokine production through suppression of intracellular signaling. Mol Pharmacol, 2006, 69(4): 1288–1295.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Project of Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (安徽省自然科学基 金项目, No. 1608085QH219); National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 国家重点基础研究发展 计划项目, No. 2015CB554504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Cy., Hu, L., Wu, Zj. et al. Effects of moxibustion on serum IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in rats with experimental rheumatoid arthritis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 305–311 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1129-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1129-4
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Moxa Stick Moxibustion
- Suspended Moxibustion
- Arthritis, Rheumatoid
- Point, Shenshu (BL 23)
- Point, Zusanli (ST 36)
- Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
- Rats