Abstract
Objective
A questionnaire for the compliance with moxibustion was designed based on the 4-item Morisky scale, and the reliability and validity of the questionnaire was investigated.
Methods
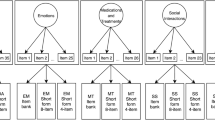
A modified Morisky scale was designed based on the 4-item Morisky scale for the compliance with moxibustion, and 146 patients having received moxibustion for over 2 weeks were investigated using this scale to evaluate their compliance with moxibustion; the internal equity and the construct validity of the scale were statistically analyzed.
Results
The analysis of reliability showed that in item of internal consistency, the Cronbach’s α was 0.72 and the split-half coefficient was 0.71, the correlation coefficients between the 4 component scores and the total score ranged 0.67-0.80, and the between-component correlation coefficients ranged 0.24-0.56; the exploratory factor analysis (EFA) totally extracted 1 common factor, and the explicable variation was 55.02%, and the loads of the 4 items were respectively 0.82, 0.81, 0.74 and 0.58.
Conclusion
The reliability and validity of the modified Morisky scale for the compliance with moxibustion are acceptable, while several items need further modification and improvement in the expression and content.
摘要
目的
基于Morisky 依从性量表4个条目设计艾灸依从性调查问卷, 探讨该问卷的信度和效度。
方法
根 据Morisky 依从性量表4个条目设计用于艾灸依从性评价的修改版Morisky 问卷, 并对146例接受艾灸治疗超过2 星期的患者使用该问卷进行调查, 评价艾灸治疗依从性; 统计分析该量表的内部一致性及其结构效度。
结果
信 度分析显示, 修改版Morisky 问卷的内部一致性Cronbach’s α 系数为0.72, 折半系数为0.71, 4个条目与量表总分之 间的相关系数为0.67~0.80, 4 个条目之间的相关系数为0.24~0.56, 探索性因子分析共提取1个公共因子, 可解 释的总变异量为55.02%, 4条目的载荷值分别为0.82、0.81、0.74和0.58。
结论
修改版Morisky 问卷调查艾灸依从 性的信度和效度尚可, 但部分条目在语言表述和内容上仍需进一步修订和完善。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li JW, Yu YA, Cai JF, Zhang ZC. Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2nd Edition. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2006: 424.
Zhang QY, Hu SP. Current research and analysis of the mechanism of moxibustion. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2008, 27(5): 47–50.
Yu SG, Tang Y, Yin HY, Wu QF, Luo L, Zhang CS, Wang JP, Zhao L, Lu J, Zuo J, Fan YP, Zhou XY. Biological basis of local acupoint responses to moxibustion stimulation. Shijie Zhongyiyao, 2013, 8(8): 867–870.
Tang ZL, Song XG, Zhang FQ, Wang NX, Xu B, Hou ZM, Chen QZ, Yuan J, Chen XT, Zhang DQ, Wang YX. Study on the action mechanism of moxibustion in anti–inflammation and immunoregulation in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2003, 28(4): 292–298.
Cai HH, Wang LL, Jiang JF, Wu S, Jiang W. Effects of warm moxibustion on CD40–CD40L axis in rabbits with atherosclerosis. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2014, 34(1): 55–60.
Zhang CY, Tang ZL. Progress of mechanism study on rheumatoid arthritis treated by moxibustion. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2009, 7(2): 65–70.
Mo F, Chi C, Guo M, Chu X, Li Y, Shen X. Characteristics of selected indoor air pollutants from moxibustion. J Hazard Mater, 2014, 270(4): 53–60.
Berni A, Ciani E, Cecioni I, Poggesi L, Abbate R, Boddi M. Adherence to antihypertensive therapy affects Ambulatory Arterial Stiffness Index. Eur J Intern Med, 2011, 22(1): 93–98.
Berry DL, Blonquist TM, Hong F, Halpenny B, Partridge AH. Self–reported adherence to oral cancer therapy: relationships with symptom distress, depression, and personal characteristics. Patient Prefer Adherence, 2015, 9(11): 1587–1592.
Saadat Z, Nikdoust F, Aerab–Sheibani H, Bahremand M, Shobeiri E, Saadat H, Moharramzad Y, Morisky DE. Adherence to antihypertensives in patients with comorbid condition. Nephrourol Mon, 2015, 7(4): e29863.
Paterson DL, Swindells S, Mohr J, Brester M, Vergis EN, Squier C, Wagener MM, Singh N. Adherence to protease inhibitor therapy and outcomes in patients with HIV infection. Ann Intern Med, 2000, 133(1): 21–30.
Granger BB, Swedberg K, Ekman I, Granger CB, Olofsson B, Mc Murray JJ, Yusuf S, Michelson EL, Pfeffer MA; CHARM investigators. Adherence to candesartan and placebo and outcomes in chronic heart failure in the CHARM programme: double–blind, randomised, controlled clinical trial. Lancet, 2005, 366(9502): 2005–2011.
Morisky DE, Green LW, Levine DM. Concurrent and predictive validity of a self–reported measure of medication adherence. Med Care, 1986, 24(1): 67–74.
Sherbourne CD, Hays RD, Ordway L, Di Matteo MR, Kravitz RL. Antecedents of adherence to medical recommendations: results from the Medical outcomes study. J Behav Med, 1992, 15(5): 447–468.
Li K, Liang HY, Li X, Chen JP, Zhao L, Lü Y, Yang Y, Zhou BS. Validity and reliability of the Morisky questionnaire in assessing antihypertensive therapy compliance of hypertension patients in community. Zhonghua Gaoxueya Zazhi, 2010, 18(11): 1067–1070.
Bao LJ, Hu ZH, Xiao JW, Shao YR, Yin HF. Validity and reliability of the Morisky questionnaire in assessing medication compliance in patients with major depressive disorder. Linchuang Jingshen Yixue Zazhi, 2014, 24(6): 380–382.
Morisky DE, Ang A, Krousel–Wood M, Ward HJ. Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich), 2008, 10(5): 348–354.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 国家重点基础研究发展 计划, No.2015CB554504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yang, H., Yu, C. et al. Evaluation of the reliability and validity of the modified Morisky scale for patient’s compliance with moxibustion. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 15, 199–203 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1000-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1000-4
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Moxa Cone Moxibustion
- Moxa Stick Moxibustion
- Compliance
- Surveys and Questionnaires
- Modified Morisky Scale
- Reproducibility of Results