Abstract
Objective
To investigate the efficacy and mechanisms of moxibustion-based treatment of chronic gastritis (CG), and to provide an objective basis for treating CG using moxibustion.
Methods
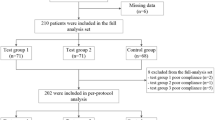
A total of 61 CG patients were divided into an herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion group and a mild-warm moxibustion group. In both treatment groups, bilateral Tianshu (ST 25), Zhongwan (CV 12) and Qihai (CV 6) were selected for moxibustion. Before and after treatment, all the enrolled patients’ gastrointestinal disease-related traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndrome scores and visual analog scale (VAS) scores were measured, and the changes in the serum levels of the brain-gut peptides ghrelin, somatostatin (SS) and motilin (MTL) were observed.
Results
There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in the clinical efficacy rate (P>0.05). After treatment, the gastrointestinal disease-related TCM syndrome scores and VAS scores were reduced to varying extents in both groups, the intra-group differences were statistically significant (all P<0.01). In both groups, the serum levels of ghrelin and MTL increased and the serum levels of SS decreased after treatment (all P<0.01). And there were no serious adverse events occurred.
Conclusion
Both herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion and mild-warm moxibustion are effective for CG; these two therapies exhibited similar therapeutic efficacy of epigastric discomfort or pain. And both the two therapies act to anti-inflammation, promote the recovery of gastric mucosa and improve the gastric motility, which is possibly their crucial action mechanism in treating CD.
摘要
目的
探讨艾灸治疗慢性胃炎的疗效与机制, 为艾灸治疗慢性胃炎提供客观依据。
方法
将61 例慢性胃炎患者分为隔药饼灸组和温和灸组。两组治疗均选双侧天枢、中脘、气海施灸。治疗前后所有入选病例均进行胃肠疾病中医证候评分、视觉模拟评分(visual analog score, VAS), 并检测血清促生长素、生长抑素(somatostatin, SS)和胃动素(motilin, MTL)含量的变化。
结果
隔药饼灸组与温和灸组治疗慢性胃炎总有效率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗后, 两组胃肠疾病中医证候评分、VAS 评分均明显降低, 与本组治疗前均有统计学差异(均P<0.01)。 两组治疗后血清促生长素、MTL 升高, SS 降低, 治疗前后比较均有显著性差异(均P<0.01)。并且在治疗期间无不良事件发生。
结论
隔药饼灸与温和灸均是治疗慢性胃炎的有效方法, 两者在改善腹部不适和胃痛方面疗效相当。 隔药饼灸与温和灸在抗炎、促进胃粘膜修复和改善胃动力方面起重要作用, 该作用可能是其有效治疗慢性胃炎的重要机制。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu FY, Wang L, Shi DH, Tan T, Jin LJ, Xu S. Epidemiologic study on TCM syndrome classification of chronic gastritis. Shijie Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2008, 3(2): 95–98.
Chinese Society of Gastroenterology. Chinese consensus on chronic gastritis. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2013, 18(1): 24–36.
Xu RJ. Internal Medicine. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2006: 163–164.
Yuan J. Research progress in the regulation of immune function by moxibustion. Anhui Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao, 2007, 26(2): 60–62.
Shang XK. Clinical examples of prolonged mild-warm moxibustion developed by Zhou Mei-sheng. Tianjin Zhongyiyao, 1998, 15(4): 150–151.
Xie H, Chang XR, Yan J, Yi Z, Liu M, Yi SX, Yue ZH, Lin YP, Song J. Clinical study on treatment of superficial gastritis in deficient and cold pattern of spleen and stomach by mild moxibustion. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2011, 26(12): 2856–2858.
Huang XX. Auxiliary treatment of 40 cases of chronic gastritis in deficient and cold pattern by ginger-partitioned moxibustion. Guangxi Yixue, 2012, 34(3): 305–306.
Gao XY, Lü JX, Liu WL, Guan ZX, Meng D, Niu XS, Zhou HQ. Experimental research of acupuncture and moxibustion on the function of grastric mucosal barrier. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Keji, 2001, 8(5): 277–278.
Zhao LY, Chu HM. Relationships between the pathologies of chronic gastritis and traditional Chinese medicine syndromes. Hebei Zhongyi, 2004, 26(11): 813–814.
Qian C, Wei K, Shi Z. Research progress of mechanism of moxibustion in treating chronic gastritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2012, 10(4): 260–264.
Wang FY, Tang XD, Yao NL. Discussion on adjusting activity of qi in gastrointestinal disease. SH J TCM, 2006, 40(3): 20–21.
Wei W, Yang Y. Present situation and the treatment of traditional Chinese medicine of diagnosis and treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis. J Tradit Chin Med, 2016, 57(1): 36–40.
State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1994: 9.
Jeffery PL, McGuckin MA, Linden SK. Endocrine impact of Helicobacter pylori: focus on ghrelin and ghrelin o-acyltransferase. World J Gastroenterol, 2011, 17(10): 1249–1260.
Xie SY. Study on Chinese medicine syndromes of chronic gastritis. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2009, 11(4): 53–54.
Wei BH, Chen ZS, Zhang WD. TCM scoring of gastrointestinal disease. World Chin J Digestol, 2004, 12(11): 2701–2703.
Fu MD. Clinical study on the mild moxibustion therapy for chronic superficial gastritis. Master Thesis of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011.
Qi L, Liu HR, Yi T, Wu LY, Liu XR, Zhao C, Shi Y, Ma XP, Wu HG. Warm moxibustion relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia in rats: relations to spinal dynorphin and orphanin-FQ system. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2013: 920675.
Han JS. The Neurochemical Basis of Acupuncture Analgesia: Volume 3 (1997-2006). Beijing: Peking University Medical Press, 2008: 4.
Wang ZT, Peng L, Ouyang FS, Lu D, Zhong YT. The acupoint selection method for the acupuncture treatment of pain syndromes and the mechanisms of action of acupuncture analgesia. Changsha Yixueyuan Xuebao, 2007, 12(25): 24–27.
Zhang Y. An exploration of the principles of acupuncture analgesia from the holographic law. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Xiandai Yuancheng Jiaoyu, 2009, 7(9): 1.
Wang LL. Characteristic of moxibustion and its warmdredging effect. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2011, 31(10): 865–868.
Yang HY, Hu ZC. Biophysical characteristics of moxibustion. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2009, 29(11): 897–899.
Han JS. Neuroscience. 3rd Edition. Beijing: Peking University Medical Press, 2009: 676–677.
Akamizu T, Iwakura H, Ariyasu H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin and functional dyspepsia. Int J Pept, 2010: 548457.
Wisser AS, Habbel P, Wiedenmann B, Klapp BF, Mönnikes H, Kobelt P. Interactions of gastrointestinal peptides: ghrelin and its anorexigenic antagonists. Int J Pept, 2010: 817457.
Chen P, Wang CS, Kong LB. Advances in motilin and functional dyspepsia. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao, 2008, 3(3): 187–189.
Ariga H, Nakade Y, Tsukamoto K, Imai K, Chen C, Mantyh C, Pappas TN, Takahashi T. Ghrelin accelerates gastric emptying via early manifestation of antro-pyloric coordination in conscious rats. Regul Pept, 2008, 146(1-3): 112–116.
Chen Y, Ren J, Wang XY. Related study of substance P and motilin expression in model rats with liver-qi stagnation syndrome of chronic gastritis. Shandong Zhongyi Zazhi, 2015, 34(9): 694–698.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, C., Wang, Ss., Wu, Hg. et al. Observation on the efficacy of moxibustion for chronic gastritis and a clinical study of moxibustion’s effects on serum brain-gut peptides. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 14, 101–109 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-016-0908-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-016-0908-4
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Gastritis
- Point, Tianshu (ST 25)
- Point, Zhongwan (CV 12)
- Point, Qihai (CV 6)
- Mechanism