Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of mild-warm moxa stick moxibustion on fatigue, immune state and quality of life (QOL) in sub-health population.
Methods
A total of 120 cases were randomly allocated into a moxibustion group ((n=60) and a Chinese patent medicine (CPM) group (n=60). People in the moxibustion group were intervened with mild-warm moxa stick moxibustion, once a day; while people in the control group took oral Bu Zhong Yi Qi Wan (Spleen/stomach-supplementing and Qi-boosting Pill), 3 doses a day. Two months made up a course of treatment. The fatigue, immune state and QOL were then observed after one treatment course, followed by a 12-month follow-up.
Results
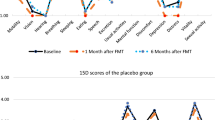
A total of 115 cases completed the clinical trial. After intervention, the fatigue scores, immune parameters and QOL scores were significantly increased in both groups, showing statistical significances (P<0.05). There were between-group significant differences in fatigue score, levels of immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG, natural killer (NK) cell activity and QOL score (P<0.05). After the 12-month follow-up, there were still significant between-group differences in fatigue score, physical health, psychological, social relationships and overall perception of QOL and overall perception of health (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Mild-warm moxibustion can markedly improve the fatigue, immune state and QOL in sub-health population.
摘要
目的
探讨艾条温和灸对疲劳性亚健康人群疲劳、免疫状态及生存质量的影响。
方法
将120 例患者按照就诊顺序随机分为艾灸组和中药组, 每组60 例。艾灸组采用艾条温和灸干预, 1 次/d, 中药组给予补中益气丸口服, 3 次/d, 连续治疗2 个月为1 个疗程。两组均在治疗1 疗程后观察患者疲劳、免疫状态及生存质量, 并随访12 个月。
结果
共115 例患者完成了临床试验, 两组患者治疗后疲劳评分、免疫学指标及生存质量评分与治疗前比较均显著改善, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。艾灸组患者治疗后疲劳评分, 免疫球蛋白M(immunoglobulin M, IgM)、IgG 含量及自然杀伤 (natural killer, NK)细胞活性, 生存质量评分与中药组差异比均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。12 个月随访结束时艾灸组患者疲劳评分及生理、心理、社会关系、生存质量主观感觉、健康状况主观感觉评分与中药组均有统计学差异(P<0.05)。
结论
温和灸可明显改善疲劳性亚健康人群的疲劳症状、免疫状态与生活质量。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin P, Yu JH, Lu SZ. An analysis of sub-health and related factors among college teachers in Nanjing city. Zhiye Yu Jiankang, 2015, 31(1): 95–97.
Cella M, White PD, Sharpe M, Chalder T. Cognitions, behaviors and comorbid psychiatric diagnoses in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Psychol Med, 2013, 43(2): 375–380.
Liang ZH, Yin DZ. Preventive treatment of traditional Chinese medicine as anti-stress and antiaging strategy. Rejuvenation Res, 2010, 13(2-3): 248–252.
Wang TF, Xue XL, Zhang YJ, Han P, Li Z, Wang WP, Xing JM, Wang QB, Tang Y, Li L, Wang JJ, Li GR, Ji SL, Wu LX, Zhao Y, Wu XY, Zhao RS. Effects of Xiaopi Yishen herbal extract granules in treatment of fatigue-predominant sub-health due to liver-qi stagnation and spleen-qi deficiency: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled and double-blind clinical trial. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao, 2011, 9(5): 515–524.
Xue XL, Wang TF, Han P, Wang JJ, Li GR, Zhang YJ. Study on the fatigue characters of fatigue-predominant sub-health people with different traditional Chinese medicine syndromes. Tianjin Zhongyiyao, 2011, 28(4): 284–287.
Qiao J, Li RH, Wu CY, Chen X. Clinical observation of Jian Pi Shu Gan decoction treatment on fatigability sub-health with seismic prevention and disaster mitigation workers. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi, 2014, 20(9): 211–215.
Chen J, Yu ZM, Zhao XS, Luo R. Current development and analysis of the research on sub-health in China. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Yu Linchuang Kangfu, 2007, 11(47): 9566–9568.
Yin HF. Epidemiological survey on sub-health status of certain community residents in Chongwen District of Beijing. Zhongguo Xiaoyi, 2012, 26(10): 773–774.
Zhong WQ, Li SC, Gu TT. Observations on the therapeutic effect of warm needling moxibustion on chronic fatigue syndrome. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2014, 33(3): 206–208.
Huang F, Chen X, Zhou Z, Huang P, Guo LH. Clinical study on electroacupuncture plus interferential current therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2014, 12(3): 156–159.
Jiang P, Jin Z, Li ZX. Therapeutic observation of ginger-partitioned moxibustion plus Ba Zhen decoction for chronic fatigue syndrome. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2015, 34(4): 329–330.
Liu YY. Medicine-separated moxibustion combined with healthy guidance for improving human sub-healthy state. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2007, 27(8): 575–577.
Wang JD, Zhang CH, Hu SP. Intervention of yangdeficiency sub-health with moxibustion therapy for regulating Governor Vessel and warming yang. Xin Zhongyi, 2015, 47(2): 187–189.
Chen M, Li LY, Tian YF, Yuan Y, Wang J, Wu AH. Effect of moxibustion on blood cell series of young people and middle-aged man under sub-health state. Shanxi Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao, 2014, 15(1): 39–42.
Wang QQ, Zheng W, Yu CC, Wang C. Research progress on non-drug therapy of traditional Chinese medicine for insomnia patients in sub-health state. Yunnan Zhongyi Zhongyao Zazhi, 2015, 36(9): 74–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Rl., Hu, L., Li, Zh. et al. Effect of mild-warm moxibustion on fatigue, immune state and quality of life in sub-health population. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 14, 82–86 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-016-0905-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-016-0905-7