Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the therapeutic effects of Tuina and hyperbaric oxygen on prolapse of lumbar intervertebral disc.
Methods
The included 160 cases of prolapse of lumbar intervertebral disc were allocated into a treatment group and a control group. The 100 cases in the treatment group were treated with tuina manipulation and hyperbaric oxygen. The 60 cases in the control group were treated with tuina manipulation. The total effect and scores of symptoms and signs were compared before and after treatment.
Results
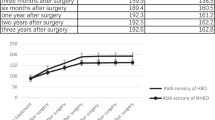
The total effective rate in the treatment group was 100.0%, and 83.0% in the control group.
Conclusion
Tuina and hyperbaric oxygen had excellent effects on the prolapse of lumbar intervertebral disc, by improving the clinical symptoms and signs of ache and movement restriction of lower back and leg, and recovering the ability of work and daily life.
摘要
目的
评价推拿手法配合高压氧治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效。
方法
符合纳入标准的腰椎间盘突出症患者160例, 分为治疗组和对照组。 治疗组100例, 采用推拿手法配合高压氧治疗。 对照组60例, 单纯采用推拿手法治疗。 比较治疗前后总体疗效及症状、 体征积分。
结果
治疗组总有效率为100.0%, 对照组总有效率83.0%。
结论
推拿手法配合高压氧治疗腰椎间盘突出症有良好的疗效, 可以明显改善腰腿酸痛活动受限等临床症状和体征, 恢复患者的日常工作、 生活能力。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of diagnosis and therapeutic effects for TCM diseases and syndromes. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1994: 186.
Sunami K, Takeda Y, Hashimoto M, Hirakawa M. Reduces infarct volume in rats by increasing oxygen supply to the ischemic periphery. Crit Care Med, 2000, 28(8): 2831–2836.
Le XH, Fu LP, Wang RH. Clinical observations on the treatment of paroxysmal deafness with electroacupuncture plus hyperbaric oxygen. Shang Hai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi, 2003, 22(4): 22–23.
Mink RB, Dutka AJ. Hyperbaric oxygen after global cerebral ischemia in rabbits reduces brain vascular permeability and blood flow. Stroke, 1995, 26(12): 2307–2312.
Liu L, Liu JC, Xin PZ, Lin SL. Study on the mechanism of alleviating intercerebral edema in gerbils after cerebral ischemia by hyperbaric oxygen. Di San Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao, 2001, 23(1): 42–44.
Wang SZ, Wang QS, Yang QH, Mei J, Zhang P. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on PC, PS, and AT-III in patients with ischemic stroke. Nan Jing Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2005, 11(11):833.
Shao GQ, Gao CJ, Ge H, Zhang J. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen (HPO) on coagulation factor in rats with cerebral ischemia. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Yi Xue, 2001, 6(3): 248.
Dai Y, Gao CJ, Wang GZ. Study on expression of VEGF mRNA in cerebral ischemia and hyperbaric treatment. Bei Jing Yi Xue, 2006, 28(10): 602–604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Wang, J. Therapeutic evaluation of Tuina and hyperbaric oxygen for prolapse of lumbar intervertebral disc. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 9, 58–61 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-011-0472-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-011-0472-x