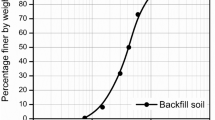
Abstract
In the present study, a comparison between the new shallow tunneling method (STM) and the traditional pile and rib method (PRM) was conducted to excavate and construct subway stations in the geological conditions of Tehran. First, by selecting Station Z6 located in the Tehran Subway Line 6 as a case study, the construction process was analyzed by PRM. The maximum ground settlement of 29.84 mm obtained from this method was related to the station axis, and it was within the allowable settlement limit of 30 mm. The acceptable agreement between the results of numerical modeling and instrumentation data indicated the confirmation and accuracy of the excavation and construction process of Station Z6 by PRM. In the next stage, based on the numerical model validated by instrumentation data, the value of the ground surface settlement was investigated during the station excavation and construction by STM. The results obtained from STM showed a significant reduction in the ground surface settlement compared to PRM. The maximum settlement obtained from STM was 6.09 mm as related to the front of the excavation face. Also, the sensitivity analysis results denoted that in addition to controlling the surface settlement by STM, it is possible to optimize some critical geometric parameters of the support system during the station excavation and construction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang C, Zhang D, Wang M. Analysis of ground subsidence induced by shallow-buried tunnel construction and its control techniques. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26: 3601–3608
Sadeghi M, Pourhashemi S M, Dehghan A N, Ahangari K. The effect of excavation progress on the behavior of Hakim Highway Tunnel using geotechnical instrumentation. In: TA-AITES World Tunnel Congress. San Francisco: Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, 2016, 22–28
Fang Q, Zhang D, Wong L N Y. Shallow tunnelling method (STM) for subway station construction in soft ground. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2012, 29: 10–30
Guan Y P, Zhao W, Li S G, Zhang G B. Key techniques and risk management for the application of the Pile-Beam-Arch (PBA) excavation method: A case study of the Zhongjie subway station. The Scientific World Journal, 2014, 2014: 275362
Kuesel T R, King E H, Bickel J O. Tunnel Engineering Handbook. Secaucus: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012
Zhang Y, Zhuang X, Lackner R. Stability analysis of shotcrete supported crown of NATM tunnels with discontinuity layout optimization. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2018, 42(11): 1199–1216
Alebouyeh A, Dehghan A N, Goshtasbi K. Identifying the geological hazards during mechanized tunneling in urban areas—The case of Tehran alluvium conditions. In: Proceedings of the WTC 2019 ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress (WTC 2019). Naples: CRC Press, 2019, 5264–5274
Avanaki M J, Dehghan A N. Seismic performance of steel fiber reinforced concrete segmented lining tunnels. In: Proceedings of the WTC 2019 ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress (WTC 2019). Naples: CRC Press, 2019, 5685–5691
Sun Z, Zhang Y, Yuan Y, Mang H A. Stability analysis of a fire-loaded shallow tunnel by means of a thermo-hydro-chemomechanical model and discontinuity layout optimization. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2019, 43(16): 2551–2564
Dehghan A N, Bagheri E, Khodaei M, Kalehsar R I. Evaluating the effect of EPBM operational parameters on surface settlement in soft ground. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 2021, 18(1): 47–61
Loganathan N, Poulos H G. Analytical prediction for tunneling-induced ground movements in clays. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1998, 124(9): 846–856
Gong W, Luo Z, Juang C H, Huang H, Zhang J, Wang L. Optimization of site exploration program for improved prediction of tunneling-induced ground settlement in clays. Computers and Geotechnics, 2014, 56: 69–79
Hasanipanah M, Noorian-Bidgoli M, Jahed Armaghani D, Khamesi H. Feasibility of PSO-ANN model for predicting surface settlement caused by tunneling. Engineering with Computers, 2016, 32(4): 705–715
Zhang Y. Multi-slicing strategy for the three-dimensional discontinuity layout optimization (3D DLO). International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2017, 41(4): 488–507
Wu D, Deng T, Zhao R, Wang Y. THM modeling of ground subsidence induced by excavation of subway tunnel. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 94: 1–11
Li E, Zhuang X, Zheng W, Cai Y. Effect of graph generation on slope stability analysis based on graph theory. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 6(4): 380–386
Dehghan A N, Goshtasbi K, Ahangari K, Jin Y, Bahmani A. 3D numerical modeling of the propagation of hydraulic fracture at its intersection with natural (pre-existing) fracture. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(2): 367–386
Zhou M, Wang F, Du Y J. Numerical modeling on localized ground subsidence induced by the tunneling in sand. In: GeoShanghai International Conference. Shanghai: Springer, 2018, 84–92
Zhang Y, Zhuang X. Cracking elements: A self-propagating strong discontinuity embedded approach for quasi-brittle fracture. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2018, 144: 84–100
Zhang Y, Zhuang X. Cracking elements method for dynamic brittle fracture. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2019, 102: 1–9
Farsimadan M, Dehghan A N, Khodaei M. Determining the domain of in situ stress around Marun Oil Field’s failed wells, SW IRAN. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2020, 10(4): 1317–1326
Khodaei M, Delijani E B, Hajipour M, Karroubi K, Dehghan A N. On dispersion of stress state and variability in fractured media: Effect of fracture scattering. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2020: 1–8
Naghipour O, Dehghan A N, Ahangari K. Evaluation of geometrical parameters affecting on the optimal slope design of Shadan Gold-Copper Open Pit Mine. Iranian Journal of Mining Engineering, 2020, 15(48): 28–44
Khodaei M, Delijani E B, Hajipour M, Karroubi K, Dehghan A N. Analyzing the correlation between stochastic fracture networks geometrical properties and stress variability: A rock and fracture parameters study. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production, 2021, 11(2): 685–702
Imani Kalehsar R, Khodaei M, Dehghan A N, Najafi N. Numerical modeling of effect of surcharge load on the stability of nailed soil slopes. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2021: 1–12
Valizadeh Kivi A, Sadaghiani M H, Ahmadi M M. Numerical modeling of ground settlement control of large span underground metro station in Tehran Metro using Central Beam Column (CBC) structure. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2012, 28: 1–9
Zhou S, Zhuang X, Zhu H, Rabczuk T. Phase field modelling of crack propagation, branching and coalescence in rocks. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2018, 96: 174–192
Liu X, Liu Y, Yang Z, He C. Numerical analysis on the mechanical performance of supporting structures and ground settlement characteristics in construction process of subway station built by Pile-Beam-Arch method. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2017, 21(5): 1690–1705
Dehghan A N. Influence of forepoling umbrella on the settlements induced by shallow urban tunneling. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2020, 38(5): 5005–5022
Dehghan A N, Shafiee S M, Rezaei F. 3-D stability analysis and design of the primary support of Karaj metro tunnel: Based on convergence data and back analysis algorithm. Engineering Geology, 2012, 141–142: 141–149
Tehran Urban and Suburban Railways Company (TUSRC). Report of Engineering Geology and Geotechnical. Abshenasan Station-Line 6, 2017 (in Persian)
Tehran Urban and Suburban Railways Company (TUSRC). Report of Design and Construction Method for the Abshenasan Station (Z6)-Line 6, 2018 (in Persian)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiri, S., Dehghan, A.N. Comparison of shallow tunneling method with pile and rib method for construction of subway station in soft ground. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 16, 704–717 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-021-0746-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-021-0746-4