Abstract
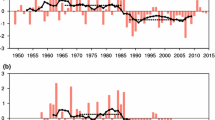
Using a historical database (1952–2007) of sea surface temperature (SST) from a subtropical high-controlled area (110°E–140°E, 15°N–35°N) of the west Pacific Ocean and the precipitation over Hunan Province of southeast China, we analyzed time series variations of precipitation in relation to the East Asian summer monsoon and a global warming setting. The results show that there has been a significant increase in SST of the subtropical high-controlled area in the recent 50 years. Although the increase in annual summer monsoon precipitation during the same period has been subtle over Hunan province, seasonal rainfall distribution has obviously changed, represented by a reduction in May, but a significant increase through June to August, especially in July. We suggest that the mechanism of seasonal redistribution of monsoon precipitation is primarily due to the increasing SST that delays the intrusion of the west Pacific Subtropical High, therefore leading to a postponing of migration of the East Asian summer monsoon rainfall belt inland and northward.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akio K, Masahiro H, Yukimasa A, Kamiguchi K (2005). Future projections of precipitation characteristics in East Asia simulated by the MRI CGCM2. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 22(4): 467–478
Chang C P (2004), East Asian monsoon. Singapore: World Scientific Press, 33–34
Chen L T (1977). Impact of sea surface temperature anomaly in eastern equatorial Pacific ocean on tropical atmospheric circulation and the rainfall in flood season in China. Scientia Atmospheric Sinica, 1(1): 1–12 (in Chinese)
Chen L T, Wu R G (1998). The joint effects of SST anomalies over different Pacific regions on summer rain-belt patterns in eastern China. Scientia Atmospheric Sinica, 22(5): 718–726
Duan D Y, Wang K J, Lu K D (1999). Evolution trends of floodwaterlogging damage and its contributing factors of Hunan province in the last 40 years. Meteorology, 25(6): 42–46 (in Chinese)
Huang R H, Xu Y H, Zhou L T (1999). The Interdecadal variation of summer precipitations in China and the drought trend in North China. Plateau Meteorology, 18: 465–476 (in Chinese)
Huang Y M, Zhang X P, Liu F, Huang Y B (2007). Precipitation change in Hunan and its relationship to that in India. Tropical Geography, 27(5): 416–419 (in Chinese)
IPCC (2007). Climate change 2007. In: Core Writing Team, Pachauri R K, Reisinger A, ed. IPCC fourth assessment report. Geneva, pp 104
Jin J D, Yan X D, Lei Y, Chen J, Yan H S (2006). Impact of the pacific SST field in earlier stages variation on the flood season precipitation over Guizhou. Journal of tropical meteorology, 22(2): 192–197 (in Chinese)
Li F, He L F (2002). Study of interdecadal/interannual variation of rainfall over mid-lower reaches of Changjiang River and its mechanism. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 13(6): 718–726 (in Chinese)
Li C Y, He J H, Zhu J H (2004). A review of decadal/interdecadal climate variation studies in China. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 21(3): 425–436
Lin J, He J H, Zhang Y Y (1999). Relationship of summer eap to the rainfall in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 22(3): 312–320 (in Chinese)
Liu H Y, Lin Z S, Zhang M Y (2004). Space-time characteristics of precipitation anomaly during the raining season in Hunan. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 20(4): 409–418 (in Chinese)
Liu M G (2000). Physical geography atlas of China. Beijing: China Map Press, 36 (in Chinese)
Liu X S, Arnold V, Letitia A (2008). Regional news portrayals of global warming and climate change. Environmental Science & Policy, 11(5): 379–393
Lu J M, Ren J Z, Ju J H (2004). The interdecadal variability of East Asia monsoon and its effect on the rainfall over China. Journal of tropical meteorology, 20(1): 73–80 (in Chinese)
Mao W S, Wang Q Q, Jing Y, Li R Q, Yang X (2007). SVD analysis of precipitation in the Changjiang-Huaihe River Valley and the sea surface temperature of the western Pacific Ocean in winter. Meteorology, 33(8): 83–89 (in Chinese)
Sun S Q, Liu G, Zhang Q Y (2007). The influence of the circulation anomalies in the southern hemisphere on the tropical cyclone frequency in summer over the western pacific and its mechanism. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 31(6): 1189–1200 (in Chinese)
Sun S Q, Ma S J (2003). Analysis and numerical experiment on the relationship between the 1998 summer monsoon activities and SSTA in tropical regions. Scientia Atmospheric Sinica, 27(1): 36–52 (in Chinese)
Tan G R, Sun Z B, Zhu Y F (2007). Diagnosis and numerical experiments on relationship between summer rainfall in Changjiang-Huaihe valley and northwest Pacific SSTA. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 30(4): 472–478 (in Chinese)
Wang H, Wang Q Q (2002). Relationship between summer precipitation anomalies in the Huaihe Basin and SSTA over the north pacific. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 25(1): 45–54 (in Chinese)
Xu HM(1997). Relationship between south China summer precipitation and global SST. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 20(3): 392–399 (in Chinese)
Yan H S, Lu J M, Ju J H, Wang H J (2002). The influencing of winter pacific SST upon May precipitation of China. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 22(4): 410–415 (in Chinese)
Zeng Q H, Wen K G (2006). China meteorological disaster canon. Hunan volume. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 4–5, 121, 134 (in Chinese)
Zhao Z G (1996). Impact of El Nino phenomenon on atmospheric circulations in the northern hemisphere and precipitation in China. Scientia Atmospheric Sinica, 20(4): 422–427 (in Chinese)
Zhou S Z (1979). Meteorology and climatology. Beijing: People Education Press, 144–148 (in Chinese)
Zhu J H, Wang S W (2001). 80a-oscillation of summer rainfall over the east part of China and East-Asian summer monsoon. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 18(5): 1043–1051 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Xu, H. & Wang, Z. Changes in summer monsoon precipitation over Hunan Province during 1952–2007: response to the west Pacific sea surface temperature and global warming. Front. Earth Sci. China 3, 411–418 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-009-0063-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-009-0063-z