Abstract
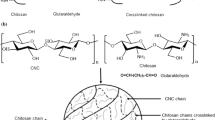
Chitosan (CS) rods were reinforced at high temperatures to form network structure by self-crosslinking of amino groups. Properties of treated CS rods were studied by FTIR spectroscopy, intrinsic viscosity measurement, mechanical properties testing and water absorption measurement. The FTIR spectra indicated that the CS configuration was transformed from β-CS for untreated CS rods to α-CS for thermally treated CS rods. Meanwhile, the crosslinking also occurred between amino groups of CS. Due to the increase in the crosslinking degree, the intrinsic viscosity increased with the rising of temperature. It was found that the network structure enhanced the bending strength of CS rods, which reached 154.8 MPa when CS rods were treated at 140°C for 2 h. Thermal treatment also reduced the water absorption of CS rods. Due to the improved mechanical properties, thermally treated CS rods could be used as a novel device for internal fixation of bone fracture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Martino A, Sittinger M, Risbud M V. A versatile biopolymer for orthopaedic tissue-engineering. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(30): 5983–5990
Kim S B, Kim Y J, Yoon T R, et al. The characteristics of a hydroxyapatite-chitosan-PMMA bone cement. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(26): 5715–5723
Zhu Y, Wang X H, Cui F Z, et al. In vitro cytocompatibility and osteoinduction of phosphorylated chitosan with osteoblasts. Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers, 2003, 18(5): 375–390
Leroux L, Hatim Z, Freche M, et al. Effects of various adjuvants (lactic acid, glycerol, and chitosan) on the injectability of a calcium phosphate cement. Bone, 1999, 25(2): 31–34
Hu Q L, Qian X Z, Li B Q, et al. Studies on chitosan rods prepared by in situ precipitation method. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(3): 528–531 (in Chinese)
Lim L Y, Khor E, Ling C E. Effects of dry heat and saturated steam on the physical properties of chitosan. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1999, 48(2): 111–116
Yu J H, Du Y M, Zheng H. Studies on the preparation, characterization and properties of nylon 1010-chitosan blend films. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2001, 17(5): 116–120 (in Chinese)
Li B Q, Hu Q L, Qian X Z, et al. Bioabsorbable chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite rod prepared by in-situ precipitation for internal fixation of bone fracture. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2002, (6): 828–833 (in Chinese)
Hu Q L, Li B Q, Wang M, et al. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite rods in in-situ hybridization: a potential material as internal fixation of bone fracture. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(5): 779–785
Jiang T D. Chitin. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003, 33–40 (in Chinese)
Hu Q L, Lei Y, Zhang Z M, et al. Surface biomimetic waterproof modification of chitosan rod. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(6): 1162–1165 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Zk., Hu, Ql., Fei, Rc. et al. Chitosan rod reinforced by self-crosslinking through thermal treatment. Front. Mater. Sci. China 2, 205–208 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-008-0034-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-008-0034-4