Abstract
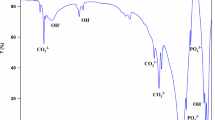
In this study, polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement (BC) was modified with ultra-fine glass fibers (UFGF) and nano-hydroxapatite (nano-HAP) synthesized by hydrothermal method. The results show that when the contents of both UFGF and nano-HAP powders are about 5%, the ultimate tensile strength (UTS), ultimate impact toughness (UIT), tensile strain (TS), and elastic modulus (EM) have been promoted a lot. The interface bond was improved by silicane treatment. Pre-grinding mixture of PMMA, UFGF, and nano-HAP can largely improve the mechanical property of PMMA. The PMMA modified with UFGF and HAP has better bioactivity than that modified with pure UFGF when they share the same content. Nano-HAP powder and modified PMMA were characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buddy D R, Allan S H, Frederick J S. Biomaterials science: an introduction to materials inn medicine. California, USA: Academic Press, 1996, 879–921
Cao D Y, Song X F, Chen Y P, et al. Research and development of biomaterial-bone cement. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2003, 20(5): 303–309 (in Chinese)
Zhou Y, Li C D, Mason J J. Shape optimization of randomly oriented short fibers for bone cement reinforcements. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2005, 393(1–2): 374–381
Jiang H G, Valdez J A, Theodore Zhu Y, et al. The strength and toughness of cement reinforced with bone-shaped steel wires. Composites Science and Technology, 2000, 60(9): 1,753–1,761
Topoleski L D T, Ducheyne P, Cuckler J M. Flow intrusion characteristics and fracture properties of titanium-fibre-reinforced bone cement. Biomaterials, 1998, 19(17): 1,569–1,577
Rhee S-H, Choi J-Y. Preparation of a bioactive poly(methyl mathacrylate)/silica nanocomposite. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2002, 85(5): 1,318–1,320
Serbetci K, Korkusuz F, Hasirci N. Thermal and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite impregnated acrylic bone cements. Polymer Testing, 2004, 23(2): 145–155
Tabtiang A, Lumlong S, Venables R A. The influence of preparation method upon the structure and relaxation characteristic of poly(methyl methacrylate)/clay composites. European Polymer Journal, 2000, 36(12): 2,559–2,568
Goto K, Tamura J, Shinzato S, et al. Bioactive bone cements containing nano-sized titania particles for use as bone substitutes. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(33): 6,496–6,505
Pilliar R M, Blackwell R, Macnab I, et al. Carbon fiber reinforced bone cement in orthopedic surgery. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1976, 10(6): 893–906
Kokubo T. Bioactive glass ceramics: properties and applications. Biomaterials 1991, 12(2): 155–163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Cheng, F. & Wei, W. Study on the mechanical and biological property of PMMA bone cement modified with ultra-fine glass fibers and nano-hydroxyapatite. Front. Mater. Sci. China 1, 247–251 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-007-0044-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-007-0044-7