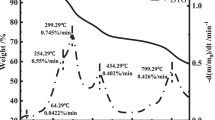
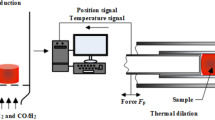
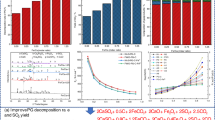
Abstract
Supercritical water gasification is a promising technology in dealing with the degradation of hazardous waste, such as oily sludge, accompanied by the production of fuel gases. To evaluate the mechanism of Fe2O3 catalyst and the migration pathways of heteroatoms and to investigate the systems during the process, reactive force field molecular dynamics simulations are adopted. In terms of the catalytic mechanisms of Fe2O3, the surface lattice oxygen is consumed by small carbon fragments to produce CO and CO2, improving the catalytic performance of the cluster due to more unsaturated coordination Fe sites exposed. Lattice oxygen combines with •H radicals to form water molecules, improving the catalytic performance. Furthermore, the pathway of asphaltene degradation was revealed at an atomic level, as well as products. Moreover, the adsorption of hydroxyl radical on the S atom caused breakage of the two C-S bonds in turn, forming •HSO intermediate, so that the organic S element was fixed into the inorganic liquid phase. The heteroatom O was removed under the effects of supercritical water. Heavy metal particles presented in the oily sludge, such as iron in association with Fe2O3 catalyst, helped accelerate the degradation of asphaltenes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao N, Li J, Quan C, Tan H. Product property and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals during pyrolysis of oily sludge with fly ash additive. Fuel, 2020, 266: 117090
Hamidi Y, Ataei S A, Sarrafi A. A highly efficient method with low energy and water consumption in biodegradation of total petroleum hydrocarbons of oily sludge. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 293: 112911
Liu J, Zhang Y, Peng K, Zhao X, Xiong Y, Huang X. A review of the interfacial stability mechanism of aging oily sludge: heavy components, inorganic particles, and their synergism. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 415: 125624
Zou H, Liu C, Evrendilek F, He Y, Liu J. Evaluation of reaction mechanisms and emissions of oily sludge and coal co-combustions in O2/CO2 and O2/N2 atmospheres. Renewable Energy, 2021, 171: 1327–1343
Gao N, Li J, Quan C, Wang X, Yang Y. Oily sludge catalytic pyrolysis combined with fine particle removal using a Ni-ceramic membrane. Fuel, 2020, 277: 118134
Li Z, Zhou Y, Meng X, Wang S. Harmless and efficient treatment of oily drilling cuttings. Journal of Petroleum Science Engineering, 2021, 202: 108542
Gao Y, Ding R, Wu S, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Yang M. Influence of ultrasonic waves on the removal of different oil components from oily sludge. Environmental Technology, 2015, 36(13–16): 1771–1775
Chen G, Li J, Li K, Lin F, Tian W, Che L, Yan B, Ma W, Song Y. Nitrogen, sulfur, chlorine containing pollutants releasing characteristics during pyrolysis and combustion of oily sludge. Fuel, 2020, 273: 117772
Kruse A, Dahmen N. Water—a magic solvent for biomass conversion. Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2015, 96: 36–45
Okolie J A, Nanda S, Dalai A K, Kozinski J A. Optimization and modeling of process parameters during hydrothermal gasification of biomass model compounds to generate hydrogen-rich gas products. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(36): 18275–18288
Ding W, Shi J, Wei W, Cao C, Jin H. A molecular dynamics simulation study on solubility behaviors of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in supercritical water/hydrogen environment. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(3): 2899–2904
Khan M K, Cahyadi H S, Kim S M, Kim J. Efficient oil recovery from highly stable toxic oily sludge using supercritical water. Fuel, 2019, 235: 460–472
Adar E, Ince M, Bilgili M S. Supercritical water gasification of sewage sludge by continuous flow tubular reactor: a pilot scale study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 391: 123499
Hantoko D, Antoni, Kanchanatip E, Yan M, Weng Z, Gao Z, Zhong Y. Assessment of sewage sludge gasification in supercritical water for H2-rich syngas production. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 131: 63–72
Lin J, Liao Q, Hu Y, Ma R, Cui C, Sun S, Liu X. Effects of process parameters on sulfur migration and H2S generation during supercritical water gasification of sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123678
Chen Y, Yi L, Li S, Yin J, Jin H. Catalytic gasification of sewage sludge in near and supercritical water with different catalysts. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124292
Qian L, Wang S, Xu D, Guo Y, Tang X, Wang L. Treatment of municipal sewage sludge in supercritical water: a review. Water Research, 2016, 89: 118–131
Cao C, Xie Y, Mao L, Wei W, Shi J, Jin H. Hydrogen production from supercritical water gasification of soda black liquor with various metal oxides. Renewable Energy, 2020, 157: 24–32
Han Y, Wang Y, Ma T, Li W, Zhang J, Zhang M. Mechanistic understanding of Cu-based bimetallic catalysts. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2020, 14(5): 689–748
Gao Y, Zhu W, Liu J, Lin P, Zhang J, Huang T, Liu K. Mesoporous sulfur-doped CoFe2O4 as a new Fenton catalyst for the highly efficient pollutants removal. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 295: 120273
van Duin A C T, Dasgupta S, Lorant F, Goddard W A. ReaxFF: a reactive force field for hydrocarbons. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2001, 105(41): 9396–9409
Han Y, Jiang D, Zhang J, Li W, Gan Z, Gu J. Development, application and challenges of ReaxFF reactive force field in molecular simulations. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2016, 10(1): 16–38
Zhang J, Weng X, Han Y, Li W, Cheng J, Gan Z, Gu J. The effect of supercritical water on coal pyrolysis and hydrogen production: a combined ReaxFF and DFT study. Fuel, 2013, 108: 682–690
Han Y, Ma T, Chen F, Li W, Zhang J. Supercritical water gasification of naphthalene over iron oxide catalyst: a ReaxFF molecular dynamics study. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(57): 30486–30498
Zhang J, Gu J, Han Y, Li W, Gan Z, Gu J. Supercritical water oxidation vs supercritical water gasification: which process is better for explosive wastewater treatment? Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(4): 1251–1260
Han Y, Chen F, Ma T, Gong H, Al-Shwafy K W A, Li W, Zhang J, Zhang M. Size effect of a Ni nanocatalyst on supercritical water gasification of lignin by reactive molecular dynamics simulations. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(51): 23014–23024
Jiang D, Wang Y, Zhang M, Zhang J, Li W, Han Y. H2 and CO production through coking wastewater in supercritical water condition: ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(15): 9667–9678
Han Y, Ma T, Chen F, Li W, Zhang J. Synergistic mechanism of Ni catalyst and supercritical water during refractory organic wastewater treatment. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(4): 1535–1547
Bai Y, Sui H, Liu X, He L, Li X, Thormann E. Effects of the N, O, and S heteroatoms on the adsorption and desorption of asphaltenes on silica surface: a molecular dynamics simulation. Fuel, 2019, 240: 252–261
Schuler B, Meyer G, Pena D, Mullins O C, Gross L. Unraveling the molecular structures of asphaltenes by atomic force microscopy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(31): 9870–9876
Stephens P J, Devlin F J, Chabalowski C F, Frisch M J. Ab initio calculation of vibrational absorption and circular dichroism spectra using density functional force fields. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1994, 98(45): 11623–11627
Krishnan R, Binkley J S, Seeger R, Pople J A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XX. A basis set for correlated wave functions. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1980, 72(1): 650–654
Shin Y K, Kwak H, Vasenkov A V, Sengupta D, van Duin A C T. Development of a ReaxFF reactive force field for Fe/Cr/O/S and application to oxidation of butane over a pyrite-covered Cr2O3 catalyst. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(12): 7226–7236
Hu Y, Qi L, Rao K T V, Zhao B, Li H, Zeng Y, Xu C. Supercritical water gasification of biocrude oil from low-temperature liquefaction of algal lipid extraction residue. Fuel, 2020, 276: 118017
Sorensen M R, Voter A F. Temperature-accelerated dynamics for simulations of infrequent events. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2000, 112(21): 9599–9606
Wang X, Xue X, Zhang C. Early events of the carburization of Fe nanoparticles in ethylene pyrolysis: reactive force field molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(20): 10835–10845
Bentria E T, Akande S O, Becquart C S, Mousseau N, Bouhali O, El-Mellouhi F. Capturing the iron carburization mechanisms from the surface to bulk. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(52): 28569–28579
Liu X, Wen X, Hoffmann R. Surface activation of transition metal nanoparticles for heterogeneous catalysis: what we can learn from molecular dynamics. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(4): 3365–3375
Chen H, He Z, Zhang B, Feng H, Kandasamy S, Wang B. Effects of the aqueous phase recycling on bio-oil yield in hydrothermal liquefaction of spirulina platensis, α-cellulose, and lignin. Energy, 2019, 179: 1103–1113
Meng N, Jiang D, Liu Y, Gao Z, Cao Y, Zhang J, Gu J, Han Y. Sulfur transformation in coal during supercritical water gasification. Fuel, 2016, 186: 394–404
Dasireddy V D B C, Likozar B. Direct methanol production from mixed methane/H2O/N2O feedstocks over Cu−Fe/Al2O3 catalysts. Fuel, 2021, 301: 121084
Kou J, Yi L, Li G, Cheng K, Wang R, Zhang D, Jin H, Guo L. Structural effect of ZrO2 on supported Ni-based catalysts for supercritical water gasification of oil-containing wastewater. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(24): 12874–12885
Mastuli M S, Kamarulzaman N, Kasim M F, Mahat A M, Matsumura Y, Taufiq-Yap Y H. Catalytic supercritical water gasification of oil palm frond biomass using nanosized MgO doped Zn catalysts. Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2019, 154: 104610
Samiee-Zafarghandi R, Hadi A, Karimi-Sabet J. Graphene-supported metal nanoparticles as novel catalysts for syngas production using supercritical water gasification of microalgae. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2019, 121: 13–21
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21978210 and U20A20151), Tianjin Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant No. 19JCYBJC20000) and the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFA0702403). The Gaussian 09 software was supported by the National Supercomputing Center in Shenzhen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Chen, F., Xu, J. et al. Chemical reactions of oily sludge catalyzed by iron oxide under supercritical water gasification condition. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 16, 886–896 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-021-2125-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-021-2125-z