Abstract
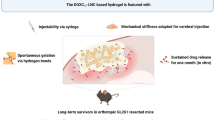
Many scientific efforts have been made to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and target glioblastoma cells, but the outcomes have been limited. More attention should be given to local inhibition of recurrence after glioblastoma resection to meet real medical needs. A biodegradable wafer containing the chemotherapeutics carmustine (1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea, BCNU) was the only local drug delivery system approved for clinical glioblastoma treatment, but with a prolonged survival time of only two months and frequent side effects. In this study, to improve the sustained release and prolonged therapeutic effect of drugs for inhibiting tumor recurrence after tumor resection, both free BCNU and BCNU- poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (the ratio of lactic acid groups to glycolic acid groups is 75/25) nanoparticles were simultaneously loaded into natural extracellular matrix hydrogel from pigskin to prepare BCNU gels. The hydrogel was injected into the resection cavity of a glioblastoma tumor immediately after tumor removal in a fully characterized resection rat model. Free drugs were released instantly to kill the residual tumor cells, while drugs in nanoparticles were continuously released to achieve a continuous and effective inhibition of the residual tumor cells for 30 days. These combined actions effectively restricted tumor growth in rats. Thus, this strategy of local drug implantation and delivery may provide a reliable method to inhibit the recurrence of glioblastoma after tumor resection in vivo.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R L, Miller K D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics 2019. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2019, 69(1): 7–34
Bastiancich C, Bianco J, Vanvarenberg K, Ucakar B, Joudiou N, Gallez B, Bastiat G, Lagarce F, Préat V, Danhier F. Injectable nanomedicine hydrogel for local chemotherapy of glioblastoma after surgical resection. Journal of Controlled Release, 2017, 264: 45–54
Stupp R, Brada M, van den Bent M J, Tonn J C, Pentheroudakis G. High-grade glioma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Annals of Oncology: Official Journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology, 2014, 25 (Suppl 3): 93–101
Wei X L, Chen X S, Ying M, Lu W Y. Brain tumor-targeted drug delivery strategies. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B, 2014, 4(3): 193–201
Chai Z L, Hu X F, Lu W Y. Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Science China Materials, 2017, 60(6): 504–510
Saucier-Sawyer J K, Seo Y E, Gaudin A, Quijano E, Song E, Sawyer A J, Deng Y, Huttner A, Saltzman W M. Distribution of polymer nanoparticles by convection-enhanced delivery to brain tumors. Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 232: 103–112
Strohbehn G, Coman D, Han L, Ragheb R R, Fahmy T M, Huttner A J, Hyder F, Piepmeier J M, Saltzman W M, Zhou J. Imaging the delivery of brain-penetrating PLGA nanoparticles in the brain using magnetic resonance. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 2015, 121(3): 441–449
Zhang C, Mastorakos P, Sobral M, Berry S, Song E, Nance E, Eberhart C G, Hanes J, Suk J S. Strategies to enhance the distribution of nanotherapeutics in the brain. Journal of Controlled Release, 2017, 267: 232–239
Shapira-Furman T, Serra R, Gorelick N, Doglioli M, Tagliaferri V, Cecia A, Peters M, Kumar A, Rottenberg Y, Langer R, Brem H, Tyler B, Domb A J. Biodegradable wafers releasing Temozolomide and Carmustine for the treatment of brain cancer. Journal of Controlled Release, 2019, 295: 93–101
Westphal M, Hilt D C, Bortey E, Delavault P, Olivares R, Warnke P C, Whittle I R, Jaaskelainen J, Ram Z. A phase 3 trial of local chemotherapy with biodegradable carmustine (BCNU) wafers (Gliadel wafers) in patients with primary malignant glioma. Neuro-Oncology, 2003, 5(2): 79–88
Attenello F J, Mukherjee D, Datoo G, McGirt M J, Bohan E, Weingart J D, Olivi A, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Brem H. Use of Gliadel (BCNU) wafer in the surgical treatment of malignant glioma: a 10-year institutional experience. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 2008, 15(10): 2887–2893
Subach B R, Witham T F, Kondziolka D, Lunsford D, Bozik M, Schiff D. Morbidity and survival after 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea wafer implantation for recurrent glioblastoma: a retrospective case-matched cohort series. Neurosurgery, 1999, 45(1): 17–22
Holmes T C, de Lacalle S, Su X, Liu G S, Rich A, Zhang S G. Extensive neurite outgrowth and active synapse formation on self-assembling peptide scaffolds. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(12): 6728–6733
Chen Q, Wang C, Zhang X D, Chen G, Hu Q, Li H, Wang J, Wen D, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Yang G, Jiang C, Wang J, Dotti G, Gu Z. In situ sprayed bioresponsive immunotherapeutic gel for post-surgical cancer treatment. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(1): 89–97
Park J, Doyle P S. Multifunctional hierarchically-assembled hydrogel particles with pollen grains via pickering suspension polymerization. Langmuir, 2018, 34(48): 14643–14651
De Leon-Rodriguez L M, Hemar Y, Mo G, Mitra A K, Cornish J, Brimble M A. Multifunctional thermoresponsive designer peptide hydrogels. Acta Biomaterialia, 2017, 47: 40–49
Bastiancich C, Danhier P, Preat V, Danhier F. Anticancer drug-loaded hydrogels as drug delivery systems for the local treatment of glioblastoma. Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 243: 29–42
Ghuman H, Massensini A R, Donnelly J, Kim S M, Medberry C J, Badylak S F, Modo M. ECM hydrogel for the treatment of stroke: characterization of the host cell infiltrate. Biomaterials, 2016, 91: 166–181
Medberry C J, Crapo P M, Siu B F, Carruthers C A, Wolf M T, Nagarkar S P, Agrawal V, Jones K E, Kelly J, Johnson S A, Velankar S S, Watkins S C, Modo M, Badylak S F. Hydrogels derived from central nervous system extracellular matrix. Biomaterials, 2013, 34(4): 1033–1040
Chan B P, Leong K W. Scaffolding in tissue engineering: general approaches and tissue-specific considerations. European Spine Journal, 2008, 17(S4 Suppl 4): 467–479
Zhu J M, Marchant R E. Design properties of hydrogel tissue-engineering scaffolds. Expert Review of Medical Devices, 2011, 8(5): 607–626
Sayiner O, Arisoy S, Comoglu T, Ozbay F G, Esendagli G. Development and in vitro evaluation of temozolomide-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in a thermoreversible hydrogel system for local administration in glioblastoma multiforme. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2020, 57: 1–10
Singh M, Chakrapani A, O’Hagan D. Nanoparticles and micro-particles as vaccine-delivery systems. Expert Review of Vaccines, 2007, 6(5): 797–808
McClements D J. Encapsulation, protection, and delivery of bioactive proteins and peptides using nanoparticle and microparticle systems: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 253: 1–22
Sheng J Y, Han L M, Qin J, Ru G, Li R X, Wu L H, Cui D Q, Yang P, He Y W, Wang J X. N-Trimethyl chitosan chloride-coated PLGA nanoparticles overcoming multiple barriers to oral insulin absorption. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(28): 15430–15441
Yang M B, Tamargo R J, Brem H. Controlled delivery of 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea from ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. Cancer Research, 1989, 49(18): 5103–5107
Badylak S F. The extracellar matrix as a scaffold for tissue reconstruction. Cell & Developmental Biology, 2002, 13(5): 377–383
Sheets K T, Bago J R, Paulk I L, Hingtgen S D. Image-guided resection of glioblastoma and intracranial implantation of therapeutic stem cell-seeded scaffolds. Jove-Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2018, 137(137): e57452
Lee P W, Pokorski J K. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) devices: production and applications for sustained protein delivery. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2018, 10(8): e1516
Parrish K E, Sarkaria J N, Elmquist W F. Improving drug delivery to primary and metastatic brain tumors: strategies to overcome the blood-brain barrier. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2015, 97(4): 336–346
Hamard L, Ratel D, Selek L, Berger F, van der Sanden B, Wion D. The brain tissue response to surgical injury and its possible contribution to glioma recurrence. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 2016, 128(1): 1–8
Ding L, Wang Q, Shen M, Sun Y, Zhang X, Huang C, Chen J, Li R, Duan Y. Thermoresponsive nanocomposite gel for local drug delivery to suppress the growth of glioma by inducing autophagy. Autophagy, 2017, 13(7): 1176–1190
Sherman J H, Redpath G T, Redick J A, Purow B W, Laws E R, Jane J A Jr, Shaffrey M E, Hussaini I M. A novel fixative for immunofluorescence staining of CD133-positive glioblastoma stem cells. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2011, 198(1): 99–102
Taal W, Bromberg J E C, van den Bent M J. Chemotherapy in glioma. CNS Oncology, 2015, 4(3): 179–192
Jung J, Gilbert M R, Park E M. Isolation and propagation of glioma stem cells from acutely resected tumors. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), 2016, 1516: 361–369
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 82074277 and 8177391), the Basic Research Cooperation Project of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei from the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (Grant Nos. 20JCZXJC00070 and J200018), and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program of Tianjin (Grant No. TJSQNTJ-2017-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Qiu, Q., Wang, D. et al. Long acting carmustine loaded natural extracellular matrix hydrogel for inhibition of glioblastoma recurrence after tumor resection. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 16, 536–545 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-021-2067-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-021-2067-5