Abstract
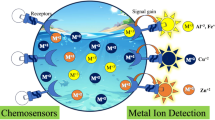
Chemosensor arrays have a great potential for on-site applications in real-world scenarios. However, to fabricate on chemosensor array a number of chemosensors are required to obtain various optical patterns for multi-analyte detection. Herein, we propose a minimized chemosensor array composed of only two types of carboxylate-functionalized polythiophene derivatives for the detection of eight types of metal ions. Upon recognition of the metal ions, the polythiophenes exhibited changes in their fluorescence intensity and various spectral shifts. Although both chemosensors have the same polymer backbone and recognition moiety, only the difference in the number of methylene groups contributed to the difference in the fluorescence response patterns. Consequently, the metal ions in aqueous media were successfully discriminated qualitatively and quantitatively by the chemosensor microarray on the glass chip. This study offers an approach for achieving a minimized chemosensor array just by changing the alkyl chain lengths without the necessity for many receptors and reporters.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzenbacher P Jr, Lubal P, Buček P, Palacios M A, Kozelkova M E. A practical approach to optical cross-reactive sensor arrays. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(10): 3954–3979
Li Z, Askim J R, Suslick K S. The optoelectronic nose: colorimetric and fluorometric sensor arrays. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(1): 231–292
Diehl K L, Anslyn E V. Array sensing using optical methods for detection of chemical and biological hazards. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(22): 8596–8611
Sasaki Y, Kubota R, Minami T. Molecular self-assembled chemosensors and their arrays. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2021, 429: 213607
Smith D G, Topolnicki I L, Zwicker V E, Jolliffe K A, New E J. Fluorescent sensing arrays for cations and anions. Analyst, 2017, 142(19): 3549–3563
Lavigne J J, Anslyn E V. Sensing a paradigm shift in the field of molecular recognition: from selective to differential receptors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2001, 40(17): 3118–3130
Geng Y, Peveler W J, Rotello V M. Array-based “chemical nose” sensing in diagnostics and drug discovery. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(16): 5190–5200
Shimizu K D, Stephenson C J. Molecularly imprinted polymer sensor arrays. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2010, 14(6): 743–750
Ikeda M, Ochi R, Hamachi I. Supramolecular hydrogel-based protein and chemosensor array. Lab on a Chip, 2010, 10(24): 3325–3334
Lemieux É J, Leclerc M. Conjugated Polyelectrolytes: Fundamentals and Applications. New Jersey: Wiley-VCH Weinheim, 2013, 231–261
McQuade D T, Pullen A E, Swager T M. Conjugated polymer-based chemical sensors. Chemical Reviews, 2000, 100(7): 2537–2574
Bunz U H F. Poly(p-phenyleneethynylene)s by alkyne metathesis. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2001, 34(12): 998–1010
Miranda O R, You C C, Phillips R, Kim I B, Ghosh P S, Bunz U H F, Rotello V M. Array-based sensing of proteins using conjugated polymers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(32): 9856–9857
Rhee H W, Lee S W, Lee J S, Chang Y T, Hong J I. Focused fluorescent probe library for metal cations and biological anions. ACS Combinatorial Science, 2013, 15(9): 483–490
Ihde M H, Pridmore C F, Bonizzoni M. Pattern-based recognition systems: overcoming the problem of mixtures. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(24): 16213–16220
Han J, Wang B, Bender M, Seehafer K, Bunz U H F. Water-soluble poly(p-aryleneethynylene)s: a sensor array discriminates aromatic carboxylic acids. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(31): 20415–20421
Sasaki Y, Kojima S, Hamedpour V, Kubota R, Takizawa S, Yoshikawa I, Houjou H, Kubo Y, Minami T. Accurate chiral pattern recognition for amines from just a single chemosensor. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(15): 3790–3796
Cao Z, Cao Y, Kubota R, Sasaki Y, Asano K, Lyu X, Zhang Z, Zhou Q, Zhao X, Xu X, Wu S, Minami T, Liu Y. Fluorescence anion chemosensor array based on pyrenylboronic acid. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2020, 8: 414
Cao Y, Zhang L, Huang X, Xin Y, Ding L. Discrimination of metalloproteins by a mini sensor array based on bispyrene fluorophore/surfactant aggregate ensembles. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(51): 35650–35659
Anzenbacher P Jr, Liu Y, Palacios M A, Minami T, Wang Z, Nishiyabu R. Leveraging material properties in fluorescence anion sensor arrays: a general approach. Chemistry—A European Journal, 2013, 19(26): 8497–8506
Sasaki Y, Leclerc É, Hamedpour V, Kubota R, Takizawa S, Sakai Y, Minami T. Simplest chemosensor array for phosphorylated saccharides. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(24): 15570–15576
Zaubitzer F, Buryak A, Severin K. Cp*Rh-based indicator-displacement assays for the identification of amino sugars and aminoglycosides. Chemistry—A European Journal, 2006, 12(14): 3928–3934
Palacios M A, Wang Z, Montes V A, Zyryanov G V, Anzenbacher P Jr Rational design of a minimal size sensor array for metal ion detection. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(31): 10307–10314
Liang X, Bonizzoni M. Boronic acid-modified poly(amidoamine) dendrimers as sugar-sensing materials in water. Journal of Materials Chemistry. B, Materials for Biology and Medicine, 2016, 4(18): 3094–3103
Liu C, Wang P, Liu X, Yi X, Zhou Z, Liu D. Supramolecular fluorescent sensor array for simultaneous qualitative and quantitative analysis of quaternary ammonium herbicides. New Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 42(21): 17317–17322
Yao Z, Feng X, Hong W, Li C, Shi G. A simple approach for the discrimination of nucleotides based on a water-soluble polythiophene derivative. Chemical Communications, 2009, 31(31): 4696–4698
Maynor M S, Deason T K, Nelson T L, Lavigne J J. Multidimensional response analysis towards the detection and identification of soft divalent metal ions. Supramolecular Chemistry, 2009, 21(3–4): 310–315
Li C, Shi G. Polythiophene-based optical sensors for small molecules. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(11): 4503–4510
Doré K, Dubus S, Ho H A, Lévesque I, Brunette M, Corbeil G, Boissinot M, Boivin G, Bergeron M G, Boudreau D, Leclerc M. Fluorescent polymeric transducer for the rapid, simple, and specific detection of nucleic acids at the zeptomole Level. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(13): 4240–4244
McCullough R D, Ewbank P C, Loewe R S. Self-assembly and disassembly of regioregular, water soluble polythiophenes: chemoselective ionchromatic sensing in water. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1997, 119(3): 633–634
Li C, Numata M, Takeuchi M, Shinkai S. A sensitive colorimetric and fluorescent probe based on a polythiophene derivative for the detection of ATP. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(39): 6371–6374
Ho H A, Leclerc M. New colorimetric and fluorometric chemosensor based on a cationic polythiophene derivative for iodidespecific detection. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(15): 4412–4413
Sasaki Y, Ito S, Zhang Z, Lyu X, Takizawa S, Kubota R, Minami T. Supramolecular sensor for astringent procyanidin C1: fluorescent artificial tongue for wine components. Chemistry—A European Journal, 2020, 26(69): 16236–16240
Domínguez S E, Meriläinen M, Ääritalo T, Damlin P, Kvarnström C. Effect of alkoxy-spacer length and solvent on diluted solutions of cationic isothiouronium polythiophenes. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(13): 7648–7657
Minami T, Kubo Y. Fluorescence sensing of phytate in water using an isothiouronium-attached polythiophene. Chemistry—A Asian Journal, 2010, 5(3): 605–611
An Y, Xiao K, Yao Z, Li C. Conjugated polyelectrolyte based colorimetric array for the discrimination of primary amino acids. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(18): 5400–5403
Liu L, Zhao L, Cheng D, Yao X, Lu Y. Highly selective fluorescence sensing and imaging of ATP using a boronic acid groups-bearing polythiophene derivate. Polymers, 2019, 11(7): 1139
Pal S, Chatterjee N, Bharadwaj P K. Selectively sensing first-row transition metal ions through fluorescence enhancement. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(51): 26585–26620
Wang Z, Palacios M A, Anzenbacher P Jr Fluorescence sensor array for metal ion detection based on various coordination chemistries: general performance and potential application. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(19): 7451–7459
Xu W, Ren C, Teoh C L, Peng J, Gadre S H, Rhee H W, Lee C L K, Chang Y T. An artificial tongue fluorescent sensor array for identification and quantitation of various heavy metal ions. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(17): 8763–8769
Smith D G, Sajid N, Rehn S, Chandramohan R, Carney I J, Khan M A, New E J. A library-screening approach for developing a fluorescence sensing array for the detection of metal ions. Analyst, 2016, 141(15): 4608–4613
Hwang I H, Hong K I, Jeong K S, Jang W D. Carbazole-based molecular tweezers as platforms for the discrimination of heavy metal ions. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(2): 1097–1102
Sasaki Y, Minamiki T, Tokito S, Minami T. A molecular self-assembled colourimetric chemosensor array for simultaneous detection of metal ions in water. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(49): 6561–6564
Inoue M B, Velazquez E F, Inoue M. One-step chemical synthesis of doped polythiophene by use of copper(II) perchlorate as an oxidant. Synthetic Metals, 1988, 24(3): 223–229
Minami T, Kubo Y. Selective anion-induced helical aggregation of chiral amphiphilic polythiophenes with isothiouronium-appended pendants. Supramolecular Chemistry, 2011, 23(1–2): 13–18
Derakhshesh M, Gray M R, Dechaine G P. Dispersion of asphaltene nanoaggregates and the role of rayleigh scattering in the absorption of visible electromagnetic radiation by these nanoaggregates. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(2): 680–693
Rasmussen S C, Evenson S J, McCausland C B. Fluorescent thiophene-based materials and their outlook for emissive applications. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(22): 4528–4543
Wang X, Zhao J, Guo C, Pei M, Zhang G. Simple hydrazide-based fluorescent sensors for highly sensitive and selective optical signaling of Cu2+ and Hg2+ in aqueous solution. Sensors and Actuators. B, Chemical, 2014, 193: 157–165
Keizer J. Nonlinear fluorescence quenching and the origin of positive curvature in stern-volmer plots. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1983, 105(6): 1494–1498
You J, Kim J, Park T, Kim B, Kim E. Highly fluorescent conjugated polyelectrolyte nanostructures: synthesis, self-assembly, and Al3+ ion sensing. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(7): 1417–1424
Chen Y, Pu K Y, Fan Q L, Qi X Y, Huang Y Q, Lu X M, Huang W. Water-soluble anionic conjugated polymers for metal ion sensing: effect of interchain aggregation. Journal of Polymer Science. Part A, Polymer Chemistry, 2009, 47(19): 5057–5067
Bala T, Prasad B L V, Sastry M, Kahaly M U, Waghmare U V. Interaction of different metal ions with carboxylic acid group: a quantitative study. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2007, 111(28): 6183–6190
Miller J N, Miller J C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry. 7th ed. Essex: Pearson Higher Education, 2018
Wolfbeis O S. Materials for fluorescence-based optical chemical sensors. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2005, 15(27–28): 2657–2669
Anzenbacher P Jr, Liu Y L, Kozelkova M E. Hydrophilic polymer matrices in optical array sensing. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2010, 14(6): 693–704
Guo T R, Zhang G P, Zhang Y H. Physiological changes in barley plants under combined toxicity of aluminum, copper and cadmium. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2007, 57(2): 182–188
Acknowledgements
Tsuyoshi Minami thanks JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP20K21204) and JST CREST (Grant No. JPMJCR2011). Yui Sasaki thanks JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP18J21190). We also thank Dr. Shin-ya Takizawa of the University of Tokyo for the measurements of emission quantum yield and lifetime.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supporting Information
11705_2021_2037_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A minimized fluorescent chemosensor array utilizing carboxylate-attached polythiophenes on a chip for metal ions detection
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, Y., Lyu, X., Zhang, Z. et al. A minimized fluorescent chemosensor array utilizing carboxylate-attached polythiophenes on a chip for metal ions detection. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 16, 72–80 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-021-2037-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-021-2037-y