Abstract
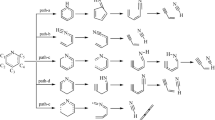
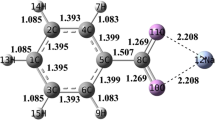
Pyridine is one of the main nitrogen-containing compounds in coal, and its pyrolytic mechanism to generate NOx precursors (mainly NH3 and HCN) remains unclear. In this work, the possible pathways for the pyrolysis of pyridine to form HCN and/or NH3 were investigated by the density functional theory method, and the effects of H2O on pyridine pyrolysis were also investigated. The results show that there are two possible reactions for the initial pyridine pyrolysis, i.e., internal hydrogen transfer and C-H bond homolysis, and that internal hydrogen transfer is more favorable. Nine possible reaction pathways following internal hydrogen transfer are obtained and analyzed. Among these pathways, pyridine prefers to produce HCN instead of NH3. The existence of H2O has significant effects on the decomposition of pyridine, as it participates in pyridine pyrolysis to form NH3 rather than HCN as the major product.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye C, Zheng Y, Xu Y, Li G, Dong C, Tang Y, Wang Q. Energy and exergy analysis of poly-generation system of hydrogen and electricity via coal partial gasification. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2020, 141: 106911
Xu M X, Wang H X, Ouyang H D, Zhao L, Lu Q. Direct catalytic decomposition of N2O over bismuth modified NiO catalysts. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 401: 123334
Satayeva A R, Howell C A, Korobeinyk A V, Jandosov J, Inglezakis V J, Mansurov Z A, Mikhalovsky S V. Investigation of rice husk derived activated carbon for removal of nitrate contamination from water. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 630: 1237–1245
Cheng S, Qiao Y, Huang J, Wang W, Wang Z, Yu Y, Xu M. Effects of Ca and Na acetates on nitrogen transformation during sewage sludge pyrolysis. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(3): 2715–2722
Kyriienko P I. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ethanol and other C1-4 oxygenates over Ag/Al2O3 catalysts: a review. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2020, 14(4): 471–491
Chu F, Su M, Yang G. Heat and mass transfer characteristics of ammonia regeneration in packed column. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 176: 115405
Fan W, Li Y, Guo Q, Chen C, Wang Y. Coal-nitrogen release and NOx evolution in the oxidant-staged combustion of coal. Energy, 2017, 125: 417–426
Zhang K, Li Y, Yuan T, Cai J, Glarborg P, Qi F. An experimental and kinetic modeling study of premixed nitromethane flames at low pressure. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(1): 407–414
Ye C, Wang Q, Zheng Y, Li G, Zhang Z, Luo Z. Techno-economic analysis of methanol and electricity poly-generation system based on coal partial gasification. Energy, 2019, 185: 624–632
Peng Z, Chen L H, Sun M H, Wu P, Cai C, Deng Z, Li Y, Zheng W H, Su B L. Template-free synthesis of hierarchically macromesoporous Mn-TiO2 catalysts for selective reduction of NO with NH3. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018, 12(1): 43–49
Xu M H, Yu D X, Yao H, Liu X W, Qiao Y. Coal combustion-generated aerosols: formation and properties. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(1): 1681–1697
Zhang H, Jiang X M, Liu J X, Liu J G. Theoretical study on the reactions originating from solid char (N): radical preference and possible surface N2 formation reactions. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(39): 18021–18026
Hämäläinen J P, Aho M J, Tummavuori J L. Formation of nitrogen oxides from fuel-N through HCN and NH3: a model-compound study. Fuel, 1994, 73(12): 1894–1898
Molina A, Eddings E G, Pershing D W, Sarofim A F. Char nitrogen conversion: implications to emissions from coal-fired utility boilers. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2000, 26(4): 507–531
Adamczyk W P, Werle S, Ryfa A. Application of the computational method for predicting NOx reduction within large scale coal-fired boiler. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014, 73(1): 343–350
Wang C A, Du Y, Jin X, Che D. Pyridine and pyrrole oxidation under oxy-fuel conditions. Energy Sources. Part A, Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2016, 38(7): 975–981
Bacskay G B, Martoprawiro M, Mackie J C. The thermal decomposition of pyrrole: an ab initio quantum chemical study of the potential energy surface associated with the hydrogen cyanide plus propyne channel. Chemical Physics Letters, 1999, 300(3–4): 321–330
Liu J, Zhang X L, Lu Q, Shaw A, Hu B, Jiang X Y, Dong C Q. Mechanism study on the effect of alkali metal ions on the formation of HCN as NOx precursor during coal pyrolysis. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2019, 92(3): 604–612
Liu J, Lu Q, Jiang X Y, Hu B, Zhang X L, Dong C Q, Yang Y P. Theoretical investigation of the formation mechanism of NH3 and HCN during pyrrole pyrolysis: the effect of H2O. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2018, 23(4): 711–721
Duan L, Zhao C, Zhou W, Qu C, Chen X. Investigation on coal pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(7): 3826–3830
Mackie J C, Colket M B, Nelson P F. Shock tube pyrolysis of pyridine. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1990, 94(10): 4099–4106
Ikeda E, Mackie J C. Thermal decomposition of two coal model compounds—pyridine and 2-picoline. Kinetics and product distributions. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 1995, 34(1): 47–63
Hong X, Zhang T C, Zhang L D, Qi F. Identification of intermediates in pyridine pyrolysis with molecular-beam mass spectrometry and tunable synchrotron VUV photoionization. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2009, 22(2): 204–209
Liang X R, Wang Q H, Luo Z Y, Zhang H, Li K K, Feng Y, Shaikh A R, Cen J M. Simulation of nitrogen transformation in pressurized oxy-fuel combustion of pulverized coal. RSC Advances, 2018, 8 (62): 35690–35699
Li X, Zhang S, Yang W, Liu Y, Yang H, Chen H. Evolution of NOx precursors during rapid pyrolysis of coals in CO2 atmosphere. Energy & Fuels, 2015, 29(11): 7474–7482
Ninomiya Y, Dong Z B, Suzuki Y, Koketsu J. Theoretical study on the thermal decomposition of pyridine. Fuel, 2000, 79(3–4): 449–457
Liu J, Zhang X L, Hu B, Lu Q, Liu D J, Dong C Q, Yang Y P. Formation mechanism of HCN and NH3 during indole pyrolysis: a theoretical DFT study. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2020, 93(2): 649–657
Liu J, Zhang X L, Lu Q, Shaw A, Hu B, Jiang X Y, Dong C Q. Mechanism study on the effect of alkali metal ions on the formation of HCN as NOx precursor during coal pyrolysis. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2019, 92(3): 604–612
Han X X, Chen B, Li Q Y, Tong J H, Jiang X M. Organic nitrogen conversion during the thermal decomposition of Huadian oil shale of China. Oil Shale, 2017, 34(2): 97
Hu E, Zeng X, Ma D, Wang F, Yi X, Li Y, Fu X. Effect of the moisture content in coal on the pyrolysis behavior in an indirectly heated fixed-bed reactor with internals. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31 (2): 1347–1354
Park D C, Day S J, Nelson P F. Nitrogen release during reaction of coal char with O2, CO2, and H2O. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30(2): 2169–2175
Yang H K. Experimental study on N migration of biomass pyrolysis and gasification process in tubular furnace. Dissertation for the Master’s Degree. Anhui: University of Science and Technology of China, 2016, 32–37
Tian F J, Yu J L, McKenzie L J, Hayashi J, Li C Z. Conversion of fuel-N into HCN and NH3 during the pyrolysis and gasification in steam: a comparative study of coal and biomass. Energy & Fuels, 2007, 21(2): 517–521
Frisch M, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, Scuseria G E, Robb M A, Cheeseman J R, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson G, et al. Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009
Becke A. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. the role of exact exchange. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1993, 98(7): 5648–5652
Zhang X L, Li J, Yang W H, Blasiak W. Formation mechanism of levoglucosan and formaldehyde during cellulose pyrolysis. Energy & Fuels, 2011, 25(8): 3739–3746
Zhang H, Jiang X M, Liu J X, Shen J. Theoretical study on the specific role of superfine char surface oxygen—NO consumption mechanism. Powder Technology, 2013, 249: 82–88
Shinohara Y, Tsubouchi N. Effect of the electronic state on low-rank coals with Ca2+ ion exchange. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2020, 1218: 128544
Zhan J H, Wu R C, Liu X X, Gao S Q, Xu G W. Preliminary understanding of initial reaction process for subbituminous coal pyrolysis with molecular dynamics simulation. Fuel, 2014, 134: 283–292
Bagdžiūnas G, Ramanavičius A. Towards direct enzyme wiring: a theoretical investigation of charge carrier transfer mechanisms between glucose oxidase and organic semiconductors. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2019, 21(6): 2968–2976
Liu S, Wu Y G, Zhou C S, Wu J M, Zhang Y L. Study on the CO formation mechanism during coal ambient temperature oxidation. Energies, 2020, 13(10): 2587
Ling L X, Zhang R G, Wang B J, Xie K C. Density functional theory study on the pyrolysis mechanism of thiophene in coal. Journal of Molecular Structure THEOCHEM, 2009, 905(1–3): 8–12
Beste A, Buchanan A III. Computational study of bond dissociation enthalpies for lignin model compounds. Substituent effects in phenethyl phenyl ethers. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2009, 74(7): 2837–2841
Mphahlele M J, Maluleka M M, Rhyman L, Ramasami P, Mampa R M. Spectroscopic, DFT, and XRD studies of hydrogen bonds in N-unsubstituted 2-aminobenzamides. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2017, 22(1): 83–96
Jiang X Y, Lu Q, Hu B, Liu J, Dong C Q, Yang Y P. A comprehensive study on pyrolysis mechanism of substituted β-O-4 type lignin dimers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(11): 2364–2377
Lin J Y, Zhang S, Zhang L, Min Z H, Tay H L, Li C Z. HCN and NH3 formation during coal/char gasification in the presence of NO. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(10): 3719–3723
Li C Z, Tan L L. Formation of NOx and SOx precursors during the pyrolysis of coal and biomass. Part III. Further discussion on the formation of HCN and NH3 during pyrolysis. Fuel, 2000, 79(15): 1899–1906
Chang L, Xie Z, Xie K C, Pratt K C, Hayashi J I, Chiba T, Li C Z. Formation of NOx precursors during the pyrolysis of coal and biomass. Part VI. Effects of gas atmosphere on the formation of NH3 and HCN. Fuel, 2003, 82(10): 1159–1166
Chang L P, Xie Z L, Xie K C. Study on the formation of NH3 and HCN during the gasification of brown coal in steam. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2006, 84(6): 446–452
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51922040 and 51821004), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2019TQ0091), Grants from Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation (Grant No. 161051), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2020DF01, 2020 MS020, 2018ZD08) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Materials
11705_2020_2024_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A theoretical investigation on the thermal decomposition of pyridine and the effect of H2O on the formation of NOx precursors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Fan, X., Zhao, W. et al. A theoretical investigation on the thermal decomposition of pyridine and the effect of H2O on the formation of NOx precursors. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 15, 1217–1228 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-2024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-2024-8