Abstract
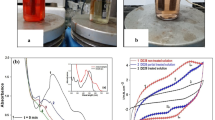
To avoid environmental pollution due to organic dye solutions, the electrophoresis and degradation of dye in organic solvents such as alcohol were investigated. Many dyes were tested in the Indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode driving cell, and about 15 dyes moved under voltage driving. Both the curves of ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) and infrared (IR) spectra of the electrophoresis samples showed that the metal complexes Red 04 and Acid Black 1 were degradable in alcohol solution by electrochemical reaction. The cyclic volt-ampere curves of the samples from the electrochemical working station proved that electrochemical reactions took place. Based on the analysis of UV-Vis and IR spectra, the electrochemical degradation products of azo and metal complex azo dyes at lower voltage driving (1-5 V) in organic solvents are oxidized azobenzene, not hydrazine, which was found in the electrochemical degradation of dye water solutions. When the ITOelectrode is modified by a polyimide (PI) film to a thickness less than 4 μm, the electrochemical degradation of the dye in alcohol solution will not appear in the cyclic volt-ampere curves. A dye electrophoresis in organic solution flexible prototype e-paper display was formed and the display picture is shown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y S, Yang W S. Journal of Liaoning Normal University (Natural Science), 1998, 21(2): 139–143 (in Chinese)
Comiskey B, Albert J D, Yoshizawa H. An electrophoretic ink for all printed reflective electronic displays. Nature, 1998 (394), 16: 253
Li L H, Wang M, Li Y Y. A Study on protected ITO electrode for epaper. Asia Display 2007, March, 1688–1692
Yu L, Jian P L. Acta Scientiarun Naturalium Universities Sunyatseni, 1997, l36(2): 131–132 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wang, M., Fang, Y. et al. Investigation of electrochemical degradation and application of e-paper dyes in organic solvents. Front. Chem. Eng. China 3, 182–185 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-009-0062-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-009-0062-3