Abstract
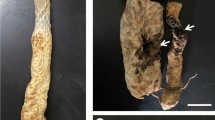
Five isolates collected from different pepper-cropping regions in Guangdong Province, China were determined. Based on their morphological characteristics and symptoms after being re-inoculated to pepper, these isolates were identified as Phytophythora capsici Leonian. The sporangia induced on carrot medium (CA) were morphologically similar and most of their shapes were ovate or elliptic, and obviously papillate. The mean size of the sporangium was 40.8–45.9 (l) μm × 23.2–30.9 (b) μm, with l/b ratio 1.4–1.8. There were evident differences in my celial growth rate, productivity of sporangia and pathogenicity to pepper among the isolates. A test of physiological characteristics showed that one isolate was determined as Race 1, and the other four isolates belonged to Race 3. It is concluded that Race 3 is most likely to be the predominent race in Guangdong Province, China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black L L (1999). Studies on Phytophthora Blight in Pepper. In: Talekar N S, ed. AVRDC Report 1998, Shanhua: Asian Vegetable Research and Development Center, 25–27
Lu J Y, Gong L Y, He H X (1984). Studies on biology and classification of Phytophthora. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, (1): 20–31 (in Chinese)
Lu Z K, Fan Z G, Huang G (1995). Studies on the occurrence and control of phytophthora blight in China. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, (2): 22–25 (in Chinese)
Oelke L M, Bosland P W (2003). Differentiation of race specific resistance to phytophthora root rot and foliar blight in Capsicum annuum. J Amer Soc Hort Sci, 128(2): 213–218
Peng H X, Liu B W, Li W (2005). Biological characteristic and identification method of pepper resistance to Phytophthora capsici in Sichuan. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 20(1): 140–144 (in Chinese)
Polach F J, Webster R K (1972). Identification of strains and inheritance of pathogenicity in Phytophthora capsici. Phytopathology, 62: 20–26
Wang D Y, An K, Wang N X (2001). Pathogenic identification of phytophthora blight in Guangzhou. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, (2): 37–39 (in Chinese)
Yang X H, Xiao C G, Yuan N X (2004). Studies on identification of Phytophthora capsici in Guizhou Province and on its biological characteristics. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University, 26(4): 413–416 (in Chinese)
Yi T Y, Zhang B X, Xie B Y, Gao B D, Ma X W (2003). Comparison of three inoculation methods for phytophthora blight resistance. China Vegetables, (2): 16–18 (in Chinese)
Zheng X B (1977). Phytophthora and Its Research Techniques. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 10–132 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2007, 28(1): 50–54 [译自: 华南农业大学学报]
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Long, W., Zheng, J. et al. Isolation and identification of Phytophthora capsici in Guangdong Province and measurement of their pathogenicity and physiological race differentiation. Front. Agric. China 1, 377–381 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-007-0063-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-007-0063-2