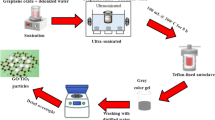
Abstract
Hydration and dispersion are the two most common problems encounter in shale formation. These problems eventually give rise to some serious wellbore instability issues, which are difficult to handle through conventional mud systems. The application of nanotechnology has now provided some inimitable solution to those integrity issues. In the current study, for the first time comparison between activated carbon and silica coated iron oxide nanoparticles in terms of filtration and shale stability is reported. Limited literature is available for both these entities; therefore focus was primarily on these particles. Both the particles were added in water-base mud system in two different concentrations of (0.25–0.50) wt% that are equivalent to 0.875–1.75 g respectively. Result reveals that the effect of high concentration of activated carbon was effective in terms of reducing the loss of filtrate volume from the mud system. Furthermore, thin and smooth filter cake was obtained for both samples of nanoparticles and high weight percent samples of activated carbon. Moreover, both the samples of activated carbon demonstrate better shale inhibition characteristics. After an immersion test, the recovered shale sample from activated carbon exhibits less erosion and cracks on its outer surface. On the contrary, a larger quantity of salt deposition on the shale surface was witnessed in the nanoparticle sample. In addition, shale samples behave more hydrophobic under the influence of activated carbon. This hydrophobicity increases as the concentration of activated carbon increases in the mud system. The results of filtration and immersion tests were also modeled using the image processing technique in order to validate all the findings of this study.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdo J, Haneef MD (2013) Clay nanoparticles modified drilling fluids for drilling of deep hydrocarbon wells. Appl Clay Sci 86:76–82
Aftab A, Ismail AR, Khokhar S, Ibupoto ZH (2016) Novel zinc oxide nanoparticles deposited acrylamide composite used for enhancing the performance of water-based drilling fluids at elevated temperature conditions. J Petro Sci Eng 146:1142–1157
Aftab A, Ismail AR, Ibupoto ZH, Akeiber H, Malghani MGK (2017) Nanoparticles based drilling muds a solution to drill elevated temperature wells: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:1301–1313
Aftab A, Ismail AR, Ibupoto ZH (2017) Enhancing the rheological properties and shale inhibition behavior of water-based mud using nanosilica, multi-walled carbon nanotube, and graphene nanoplatelet. Egypt J Petro 26(2):291–299
Aftab A, Ali M, Sahito MF, Mohanty US, Jha NK, Akhondzadeh H, Azhar MR, Ismail AR, Keshavarz A, Iglauer S (2020) Environmental friendliness and high performance of multifunctional tween 80/ZnO-nanoparticles-added water-based drilling fluid: an experimental approach. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(30):11224–11243
Agwu OE, Akpabio JU, Archibong GW (2019) Rice husk and saw dust as filter loss control agents for water-based muds. Heliyon 5(7):e02059
Aminu I, Gumel SM, Ahmad WA, Idris AA (2020) Adsorption isotherms and kinetic studies of congo-red removal from waste water using activated carbon prepared from jujube seed. Am J Anal Chem 11:47–59
Asab G, Zereffa EA, AbdoSeghne T (2020) Synthesis of silica-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles by microemulsion method: characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial activity. Int J Biomater 2020:1–11
AT Al-Hameedi, HH Alkinani, S Dunn-Norman, MA Al-Alwani, Alshammari, AF Albazzaz, HW Alkhamis, MM Rusul AM and WH Al-Bazzaz (2019) Proposing a new eco-friendly drilling fluid additive to enhance the filtration properties of water-based drilling fluid systems. In paper presented at the spe gas and oil technology showcase and conference, SPE, Editor Dubai, UAE
Barry MM, Jung Y, Lee J-K, PhuocMinking TX, Chyu K (2015) Fluid filtration and rheological properties of nanoparticle additive and intercalated clay hybrid bentonite drilling fluids. J Petro Sci Eng 127:338–346
Buchman JT, Rebeca TP, Rodriguez S, Feng ZV, Haynes CL (2019) Coating iron oxide nanoparticles with mesoporous silica reduces their interaction and impact on S oneidensis MR-1. Chemosphere 237:124511
Butt AS (2012) Shale characterization using X-ray diffraction in petroleum engineering program Dalhousie University Halifax
Dagher S et al (2018) Photocatalytic removal of methylene blue using titania and silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Mater Res Express 5:065518
Deng Y-H, Wang C-C, Hu J-H, Yang W-L, Fu S-K (2005) Investigation of formation of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles via sol–gel approach. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 262(13):87–93
Dutta D, Das BM (2021) Development of smart bentonite drilling fluid introducing iron oxide nanoparticles compatible to the reservoirs of Upper Assam. Upstream Oil Gas Technol 7:100058
Elkady M, Shokry H, Hamad H (2020) New activated carbon from mine coal for adsorption of dye in simulated water or multiple heavy metals in real wastewater. Materials (basel) 30(11):2498
Husin HE, Elaries KA, Choi HJ, Aman Z (2018) Influence of graphene nanoplatelet and silver nanoparticle on the rheological properties of water-based mud. Appl Sci 8:1386
Jung, YBM, Lee J, Phuoc Tran, Soong Y, Martello D, Chyu M (2011) Effect of nanoparticle-additives on the rheological properties of clay-based fluids at high temperature and high pressure. Am Assoc Drill Eng 1–4
Lalji SM, Ali SI, Ahmed R et al (2022a) Influence of graphene oxide on salt-polymer mud rheology and Pakistan shale swelling inhibition behavior. Arab J Geosci 15:612
Lalji SM, Ali SI, Sohail H et al (2022b) Combine effect of graphene oxide, pure-bore and sodium alginate on rheological and filtration properties and cutting carrying capacity of water-based drilling fluid. Chem Pap 76:6461–6473
Lalji SM, Ali SI, Ullah R et al (2023a) Experimental investigation of rheological behaviour and stability of mud system using novel image processing application in presence of activated carbon and silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 13(9):6405–6420
Lalji SM, Ali SI, Asad M (2023b) Experimental effect of biopolymers, synthetic and modified polymers on Western Pakistan shale (GHAZIJ) stability. Arab J Sci Eng 48(12):16639–16653
Lekomtsev A, Keykhosravi A, Moghaddam MB, Daneshfar R, Rezvanjou O (2022) On the prediction of filtration volume of drilling fluids containing different types of nanoparticles by ELM and PSO-LSSVM based model. Petroleum 8(3):424–435
Lien Y-H, Wu T-M (2008) Preparation and characterization of thermosensitive polymers grafted onto silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 326(2):517–521
Lomba R (2010) Fundamentos de filtração e controle das propriedades de filtração
Mahmoud O, Nasr-El-Din HA, Vryzas Z, and Kelessidis VC (2016) Nanoparticle-based drilling fluids for minimizing formation damage in HP/HT applications. In paper presented at the SPE International Conference and Exhibition on formation damage contro SPE: Lafayette, Louisiana, USA
Mahto V (2013) Effect of Activated Charcoal on the rheological and filtration properties of water-based drilling fluids. Int J Chem 3(4):27–32
Moslemizadeh A, Shadizadeh SR (2017) A natural dye in water-based drilling fluids: swelling inhibitive characteristic and side effects. Petroleum 3(3):355–366
Nawaz T, Zulfiqar S, Sarwar MI et al (2020) Synthesis of diglycolic acid functionalized core-shell silica coated Fe3O4 nanomaterials for magnetic extraction of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) ions. Sci Rep 10:10076
Ng ZJ, Teow YHAW, Mohammad, Ho KC, and, Yeap SP (2020) Synthesis of silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: effect of particle sizes and silica coating. Int J Nanoelectron Mater 13:565–576
Omri A, Benzina M (2019) Influence of the origin of carbon support on the structure and properties of TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by dip coating method. Arab J Chem 12(8):2926–2936
Pham H, Nguyen QP (2014) Effect of silica nanoparticles on clay swelling and aqueous stability of nanoparticle dispersions. J Nanopart Res 16:2137
Rana A, Saleh TA (2022) An investigation of polymer-modified activated carbon as a potential shale inhibitor for water-based drilling muds. J Petro Sci Eng 216:110763
Rezaei A, Nooripoor V, Shahbazi K (2020) Applicability of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for improving rheological and filtration properties of bentonite-water drilling fluids in the presence of sodium, calcium, and magnesium chlorides. J Petrol Explor Prod Technol 10:2453–2464 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-020-00920-6
Roustaei A, Bagherzadeh H (2015) Experimental investigation of SiO2 nanoparticles on enhanced oil recovery of carbonate reservoirs. J Petrol Explor Prod Technol 5:27–33
S Medhi, Gupta DK, Sangwai JS (2021) Impact of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the rheological and fluid-loss properties, and the hydraulic performance of non-damaging drilling fluid. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 88:103834
Saboori R, Sabbaghi S, Kalantariasl A et al (2018) Improvement in filtration properties of water-based drilling fluid by nanocarboxymethyl cellulose/polystyrene core–shell nanocomposite. J Petrol Explor Prod Technol 8:445–454
Salih AH, Elshehabi TA Bilgesu HI (2016) Impact of Nanomaterials on the rheological and fltration properties of water-based drilling fuids, In Paper presented at the SPE Eastern Regional Meeting Canton, Ohio, USA
Vargas J, Roldán LJ, Lopera SH, Cardenas JC, Zabala RD, Franco CA, and Cortés FB (2019) Effect of silica nanoparticles on thermal stability in bentonite free water-based drilling fluids to improve its rheological and filtration properties after aging process, in paper presented at the offshore technology conference, SPE, Editor Brazil, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Vryzas Z, Zaspalis V, Nalbandian L, Terzidou A, Kelessidis VC (2018) Rheological and HP/HT fluid loss behavior of nano-based drilling fluids utilizing Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater Today: Proc 5(1):27387–27396
Wajheeuddin M, Hossain ME (2018) Development of an environmentally-friendly water-based mud system using natural materials. Arab J Sci Eng 43(5):2501–2513
Wang WJ, Qiu ZS, Zhong HY, Huang WA, Dai WH (2016) Thermosensitive polymer nanospheres as a smart plugging agent for shale gas drilling operations. Petro Sci 14:116–125
Zeeshan Ali J-PA, Bandyopadhyay S (2023) Fine-tuning of particle size and morphology of silica coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 62(12):4831–4839
Zhu D, Guo Z, Pan J, Zhang F (2016) Synchronous upgrading iron and phosphorus removal from high phosphorus oolitic hematite ore by high temperature flash reduction. Metals 6:123
Funding
There is no funding related with this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lalji, S.M., Ali, S.I., Ali, S.M. et al. Investigation of silica coated iron oxide nanoparticles and activated carbon as a potential fluid loss additive and Pakistan shale inhibitor in water-based mud system coupled with advance image processing technique. Chem. Pap. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-024-03505-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-024-03505-3