Abstract
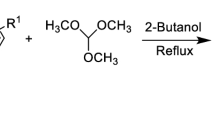
A range of substituted arylidene chromane-2,4-dione derivatives 1–30 were synthesized by the condensation reaction between 6-chloro-4-hydroxycoumarin and different benzaldehydes in ethanol. All synthesized derivatives are structurally new and fully characterized by various spectroscopic approaches. Compounds were tested for α-amylase inhibitory and radical (DPPH and ABTS) scavenging activities in vitro. When compared to the standard acarbose (IC50 = 12.9 ± 0.1 µM), all derivatives showed significant inhibitory activity against the α-amylase enzyme, with IC50 values ranging from 7.7 ± 0.1 to 60.7 ± 0.1 µM. Compounds were also found to be good radical scavengers of DPPH (IC50 = 21.6 ± 0.2 to 92.1 ± 0.1 µM) and ABTS (IC50 = 22.4 ± 0.1 to 92.7 ± 0.1 µM), compared to standard ascorbic acid (DPPH, IC50 = 14.4 ± 0.1; ABTS, IC50 = 14.9 ± 0.1 µM). Kinetic studies performed on most active molecules revealed competitive-type inhibition mechanisms. The structure–activity relationship (SAR) has been studied to determine the effect of different substitutions of compounds on inhibitory potential. Docking studies of these synthesized coumarin derivatives revealed significant binding interactions with the α-amylase enzyme's catalytic site.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal P, Gupta R (2016) Alpha-amylase inhibition can treat diabetes mellitus. Res Rev J Med Health Sci 5:1–8
Akande AA, Salar U, Khan KM, Syed S, Aboaba SA, Chigurupati S, Wadood A, Riaz M, Taha M, Bhatia S, Kanwal, (2021) Substituted benzimidazole analogues as potential α-amylase inhibitors and radical scavengers. ACS Omega 6:22726–22739. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03056
Al-Dabbas MM, Kitahara K, Suganuma T, Hashimoto F, Tadera K (2006) Antioxidant and α-amylase inhibitory compounds from aerial parts of varthemia iphionoides boiss. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:2178–2184. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60132
Al-Haiza M, Mostafa M, El-Kady M (2003) Synthesis and biological evaluation of some new coumarin derivatives. Molecules 8:275–286. https://doi.org/10.3390/80200275
Ali I, Rafique R, Khan KM, Chigurupati S, Ji X, Wadood A, Rehman AU, Salar U, Iqbal MS, Taha M, Perveen S (2020) Potent α-amylase inhibitors and radical (DPPH and ABTS) scavengers based on benzofuran-2-yl (phenyl) methanone derivatives: syntheses, in vitro, kinetics, and in silico studies. Bioorg Chem 104:104238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104238
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
Babatunde O, Hameed S, Salar U, Chigurupati S, Wadood A, Rehman AU, Perveen S (2021) Dihydroquinazolin-4 (1H)-one derivatives as novel and potential leads for diabetic management. Mol Div 26:849–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10196-5
Barnett AH (1991) Pathogenesis of diabetic microangiopathy: an overview. Am J Med 90:S67–S73. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(91)90421-S
Behrend L, Henderson G, Zwacka R (2003) Reactive oxygen species in oncogenic transformation. Biochem Soc Trans 31:1441–1444. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0311441
Bergamini CM, Gambetti S, Dondi A, Cervellati C (2004) Oxygen, reactive oxygen species, and tissue damage. Curr Pharm Des 10:1611–1626. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612043384664
Bhosale U, Hallale B (2011) Gamma radiation-induced mutations in black gram (vigna mungo (L) hepper). Asian J Plant Sci Res 1:96–100
Borges F, Roleira F, Milhazes N, Santana L, Uriarte E (2005) Simple coumarins and analogues in medicinal chemistry: occurrence, synthesis, and activity. Curr Med Chem 12:887–916. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867053507315
Čapkauskaitė E, Zakšauskas A, Ruibys V, Linkuvienė V, Paketurytė V, Gedgaudas M, Matulis D (2018) Benzimidazole design, synthesis, and docking to build selective carbonic anhydrase V.A. inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 26:675–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.12.035
Chakrabarti R, Rajagopalan R (2002) Diabetes and insulin resistance associated disorders: disease and the therapy. Curr Sci 83:1533–1538
Chohan ZH, Shaikh AU, Rauf A, Supuran CT (2006) Antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic properties of novel N-substituted sulfonamides from 4-hydroxycoumarin. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 21:741–748. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360600810340
Choi YJ, Chung YS (2016) Type 2 diabetes mellitus and bone fragility: special focus on bone imaging. Osteoporos Sarcopenia 2:20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afos.2016.02.001
Deckert T, Poulsen J, Larsen M (1978) Prognosis of diabetics with diabetes onset before the age of thirty-one. Diabetologia 14:371–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01228130
Dehghan H, Salehi P, Amiri MS (2018) Bioassay-guided purification of α-amylase, α-glucosidase inhibitors and DPPH radical scavengers from roots of Rheum turkestanicum. Ind Crops Prod 117:303–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.02.086
Duckworth WC (2001) Hyperglycemia and cardiovascular disease. Curr Atheroscler Rep 3:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-001-007
Duhan M, Kumar P, Sindhu J, Singh R, Devi M, Kumar A, Kumar R, Lal S (2021) Exploring biological efficacy of novel benzothiazole linked 2, 5-disubstituted-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole hybrids as efficient α-amylase inhibitors: synthesis, characterization, inhibition, molecular docking, molecular dynamics and monte carlo based QSAR studies. Comput Biol Med 138:104876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104876
Eckstein ML, Williams D, O’Neil L, Hayes J, Stephens J, Bracken R (2019) Physical exercise and non-insulin glucose-lowering therapies in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a clinical review. Diabet Med 36:349–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.13865
Egan D, O’kennedy R, Moran E, Cox D, Prosser E, Thornes RD (1990) The pharmacology, metabolism, analysis, and applications of coumarin and coumarin-related compounds. Drug Metab Rev 22:503–529. https://doi.org/10.3109/03602539008991449
Finaud J, Lac G, Filaire E (2006) Oxidative stress. Sports Med 36:327–358. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200636040-00004
Garg P, Reddy SR (2022) Biomass-derived sugar ionic liquid as a sustainable organocatalyst: an efficient synthesis of functionalized dihydropyrano coumarins. Asian J. Org. Chem 11:e202200322. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajoc.202200322
Goyal R, Jialal I. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (2021) In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (F.L.)
Gupta R, Paul S, Gupta AK, Kachroo P, Bani S (1997) Synthesis and biological activities of some 2-substituted phenyl-3-(3-alkyl aryl-5, 6-dihydro-s-triazolo-[3, 4-b][1,3,4] thiadiazol-6-yl) indoles. Chem Inform 29. Accession: 003291704
Harvey RG, Cortez C, Ananthanarayan T, Schmolka S (1988) A new coumarin synthesis and its utilization for the synthesis of polycyclic coumarin compounds with anticarcinogenic properties. J Org Chem 53:3936–3943. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00252a011
Hunt JV, Bottoms MA, Mitchinson MJ (1993) Oxidative alterations in the experimental glycation model of diabetes mellitus are due to protein-glucose adduct oxidation. some fundamental differences in proposed mechanisms of glucose oxidation and oxidant production. Biochem J 291:529–535. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2910529
Kaleem M, Asif M, Ahmed Q, Bano B (2006) Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of annona squamosa extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Singapore Med J 47:670–675 (PMID: 16865205)
Kanwal KKM, Chigurupati S, Ali F, Younus M, Aldubayan M, Perveen S (2021) Indole-3-acetamides: as potential antihyperglycemic and antioxidant agents; synthesis, in vitro α-amylase inhibitory activity, structure-activity relationship, and in silico studies. ACS Omega 6:2264–2275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05581
Kataoka S, Satoh J, Fujiya H, Toyota T, Suzuki R, Itoh K, Kumagai K (1983) Immunologic aspects of the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse: abnormalities of cellular immunity. Diabetes 32:247–253. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.32.3.247
Kawsar SM, Kabir AKM, Bhuiyan MM, Ferdous J, Rahman MS (2013) Synthesis, characterization and microbial screening of some new methyl 4, 6-o-(4-methoxy benzylidene)-α-D-glucopyranoside derivatives. J Bangladesh Acad Sci 37:145–158. https://doi.org/10.3329/jbas.v37i2.17554
Kirkiacharian BS, De Clercq E, Kurkjian R, Pannecouque C (2008) New synthesis and anti-HIV and antiviral properties of 3-aryl sulfonyl derivatives of 4-hydroxy coumarin and 4-hydroxy quinolone. Pharm Chem J 42:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-008-0103-0
Kostova I, Raleva S, Genova P, Argirova R (2006) Structure-activity relationships of synthetic coumarins as HIV-1 inhibitors. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/BCA/2006/68274
Lai LL, Wan Yusoff WNI, Vethakkan SR, Nik Mustapha NR, Mahadeva S, Chan WK (2019) Screening for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using transient elastography. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 34:1396–1403. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.14577
Lebovitz H (1997) Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 26:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-8529(05)70266-8
Like AA, Rossini AA, Guberski DL, Appel MC, Williams RM (1979) Spontaneous diabetes mellitus: reversal and prevention in the BB/W rat with antiserum to rat lymphocytes. Science 206:1421–1423. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.388619
Malek R, Hannat S, Nechadi A, Mekideche FZ, Kaabeche M (2019) Diabetes, and ramadan: a multicenter study in algerian population. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 150:322–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.02.008
Manohar CS, Manikandan A, Sridhar P, Sivakumar A, Kumar BS, Reddy SR (2018) Drug repurposing of novel quinoline acetohydrazide derivatives as potent COX-2 inhibitors and anti-cancer agents. J Mol Str 1154:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.10.075
Massey CN, Feig EH, Duque-Serrano L, Wexler D, Moskowitz JT, Huffman JC (2019) Well-being interventions for individuals with diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 147:118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.11.014
Medina FG, Marrero JG, Macías-Alonso M, González MC, Córdova-Guerrero I, García AGT, Osegueda-Robles S (2015) Coumarin heterocyclic derivatives: chemical synthesis and biological activity. Nat Prod Rep 32:1472–1507. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NP00162A
Moffett RB (1964) Central nervous system depressants. VII. 1 pyridyl coumarins. J Med Chem 7:446–449. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00334a010
Mukhtar F, Stieglitz K, Ali S, Ejaz A, Choudhary MI, Fakhri MI, Khan KM (2016) Coumarin and biscoumarin inhibit in vitro obesity model. Adv Biol Chem 6:152–168. https://doi.org/10.4236/abc.2016.65014
Muralidhar B, Victoria GG, Kumar KS, Reddy SR (2022) Copper-mediated relay strategy using chlorination/oxidation: an effective synthesis of functionalized coumarin derivatives. Asian J Org Chem 11:e202200044. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajoc.202200044
Nakamura I, Yamamoto Y (2004) Transition-metal-catalyzed reactions in heterocyclic synthesis. Chem Rev 104:2127–2198. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr020095i
Paik SG, Blue ML, Fleischer N, Shin SI (1982) Diabetes susceptibility of BALB/cBOM mice treated with streptozotocin: inhibition by lethal irradiation and restoration by splenic lymphocytes. Diabetes 31:808–815. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.31.9.808
Piconi L, Quagliaro L, Ceriello A (2003) Oxidative stress in diabetes. Clin Chem Lab Med 41:1144–1149. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2003.177
Rajashekar Reddy CB, Dinesh S, Anusha N, Itami T, Rajasekhara Reddy S, Sudhakaran R (2016) Antiviral activity of 3-(1-chloropiperidin-4-yl)-6-fluoro benzisoxazole 2 against White spot syndrome virus in freshwater crab, Paratelphusa hydrodomous. Aquac Res 8:2677–2681. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12704
Ramírez-Escudero M, Gimeno-Pérez M, González B, Linde D, Merdzo Z, Fernández-Lobato M, Sanz-Aparicio J (2016) Structural analysis of β-fructofuranosidase from Xantho-phyllomyces dendrorhous reveals unique features and the crucial role of N-glycosylation in oligomerization and activity. J Biol Chem 291:6843–6857. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m115.708495
Reddy CR, Reddy SR, Suthindhiran K, Sivakumar A (2016) HDAC and NF-κB mediated cytotoxicity induced by novel N-Chloro β-lactams and benzisoxazole derivatives. Chem Biol Interac 246:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.01.010
Refouvelet B, Guyon C, Jacquot Y, Girard C, Fein H, Bévalot F, Robert JF, Heyd B, Mantion G, Richert L, Xicluna A (2004) Synthesis of 4-hydroxycoumarin and 2, 4-quinolinediol derivatives and evaluation of their effects on the viability of HepG2 cells and human hepatocytes culture. Eur J Med Chem 39:931–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2004.07.006
Sai K, Thapa R, Devkota HP, Joshi KR (2019) Phytochemical screening, free radical scavenging and α-amylase inhibitory activities of selected medicinal plants from Western Nepal. Medicines. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6020070
Salar U, Taha M, Khan KM, Ismail NH, Imran S, Perveen S, Wadood A (2016) Syntheses of new 3-thiazolyl coumarin derivatives, in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, and molecular modeling studies. Eur J Med Chem 122:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.06.037
Salar U, Khan KM, Chigurupati S, Taha M, Wadood A, Vijayabalan S, Perveen S (2017a) New hybrid hydrazinyl thiazole substituted chromones: as potential α-amylase inhibitors and radical (DPPH & ABTS) scavengers. Sci Rep 7:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17261-w
Salar U, Khan KM, Iqbal J, Ejaz SA, Hameed A, Al-Rashida M, Tahir MN (2017b) Coumarin sulfonates: new alkaline phosphatase inhibitors; in vitro and in silico studies. Eur J Med Chem 131:29–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.03.003
Salar U, Khan KM, Chigurupati S, Syed S, Vijayabalan S, Wadood A, Perveen S (2019) New hybrid scaffolds based on hydrazinyl thiazole substituted coumarin; as novel leads of dual potential; in vitro α-amylase inhibitory and antioxidant (DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging) activities. Med Chem 15:87–101. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573406414666180903162243
Saleem F, Khan KM, Chigurupati S, Solangi M, Nemala AR, Mushtaq M, Perveen S (2021) Synthesis of azachalcones, their α-amylase, α-glucosidase inhibitory activities, kinetics, and molecular docking studies. Bioorg Chem 106:104489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104489
Salimon J, Salih N, Hameed A, Ibraheem H, Yousif E (2010) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of some new 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole and 1, 3, 4-thiadiazole derivatives. J Appl Sci Res 6:866–870. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.29127.55203
Sandler S, Andersson AK, Barbu A, Hellerström C, Holstad M, Karlsson E, Sternesjö J (2000) Novel experimental strategies to prevent the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ups J Med Sci 105:17–34. https://doi.org/10.1517/03009734000000053
Shah A, Channon K (2004) Free radicals and redox signalling in cardiovascular disease. Heart 90:486–487. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2003.029389
Sharma RK, Singh M, Ghimeray K, Juneja P, Dev G, Pulavarthi S, Reddy SR, Akundi RS (2021) Imidazopyridazine acetylcholinesterase inhibitors display potent anti-proliferative effects in the human neuroblastoma cell-line, IMR-32. Molecules 26:5319. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175319
Shewade Y, Tirth S, Bhonde R (2001) Pancreatic islet-cell viability, functionality, and oxidative status remain unaffected at pharmacological concentrations of commonly used antibiotics in vitro. J Biosci 26:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02703744
Sridhar P, Alagumuthu M, Arumugam S, Reddy SR (2016) Synthesis of quinoline acetohydrazide-hydrazone derivatives evaluated as DNA gyrase inhibitors and potent antimicrobial agents. RSC Adv 6:64460–64468. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA09891F
Stern P, Dezelic M, Kosak R (1957) Analgetic and antipyretic action of vitamin K and dicoumarol with special consideration of 4-hydroxycoumarin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 232:356–359 (PMID: 13526895)
Subramanian R, Asmawi MZ, Sadikun A (2008) In vitro alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase enzyme inhibitory effects of Andrographis paniculata extract and andrographolide. Acta Biochim Pol 55:391–398 (PMID: 18511986)
Taha M, Irshad M, Imran S, Rahim F, Selvaraj M, Almandil NB, Ismail NH (2019) Thiazole-based carbohydrazide derivatives as an α-amylase inhibitor and their molecular docking study. Heteroat Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7502347
Uchikoga N, Matsuzaki Y, Ohue M, Hirokawa T, Akiyama Y (2013) Re-docking scheme for generating near-native protein complexes by assembling residue interaction fingerprints. PLoS ONE 8:e69365. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069365
Victoria GG, Reddy SR (2021) Recent advances in the synthesis of organic chloramines and their insights into health care. New J Chem 45:8386–8408. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ01086G
Wang ZS, Hara K, Dan-oh Y, Kasada C, Shinpo A, Suga S, Sugihara H (2005) Photophysical and (photo) electrochemical properties of a coumarin dye. J Phys Chem B 109:3907–3914. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp044851v
Yousuf S, Khan KM, Salar U, Chigurupati S, Muhammad MT, Wadood A, Perveen S (2018) 2ʹ-Aryl and 4ʹ-arylidene substituted pyrazolones: as potential α-amylase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 159:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.09.052
Zacharski LR, Henderson WG, Rickles FR, Forman WB, Cornell C Jr, Forcier AJ, O’Donnell JF (1984) Effect of warfarin anticoagulation on survival in carcinoma of the lung, colon, head, and neck, and prostate: final report of V.A. Cooperative Study # 75. Cancer 53:2046–2052. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19840515)53:10%3c2046::aid-cncr2820531007%3e3.0.co;2-f
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Sindh Higher Education Commission (SHEC), Pakistan, vide letter No. NO.DD/SHEC/1-14/2014, Project code SHEC/SRSP/Med-3/15/2021 -21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Haq, I.u., Ali, I., Khan, K.M. et al. New arylidene-linked chromane-2,4-dione analogs as potential leads for diabetic management; syntheses, α-amylase inhibitory, and radical scavenging activities. Chem. Pap. 77, 2581–2604 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02648-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02648-5