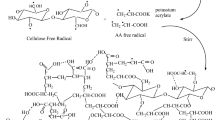
Abstract
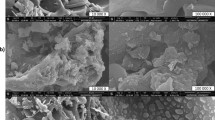
Burning of rice straw has been causing a number of environmental issues in Northern India which enforces researchers to find out different ways for valorization of this unavoidable biomass. Rice straw biopolymers, i.e. cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin can be used for production of various sustainable organic products. In the present study, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and lignin were extracted from rice straw by dilute acid pre-treatment method followed by alkaline hydrolysis. MCC and lignin were used as raw material for synthesis of hydrogels using polyvinyl alcohol as matrix template, glutaraldehyde/epichlorohydrin as cross-linkers. The characterization of synthesized hydrogels with FT-IR and SEM analysis revealed that hydrogels using glutaraldehyde have less porosity and tight bonding network whereas epichlorohydrin caused loose bonding between polymers and resulted in formation of large pores in hydrogels. Swelling ratio and reswelling capacity of hydrogels showed that lignin hydrogels performed best than all other hydrogels. The effects of hydrogels on total fresh and dry biomass, leaf area, seedling length of germinated seedlings of wheat and moong bean were observed under control and water stress conditions. All hydrogels performed well under stress conditions as compared to control. However, both lignin hydrogels performed best and gave significant highest growth under stress conditions. These biopolymer based hydrogels can be recommended for use as growth media ingredient in water deficient soils.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya S, Liyanage S, Parajuli P, Rumi SS, Shamshina JL, Abidi N (2021) Utilization of cellulose to its full potential: a review on cellulose dissolution, regeneration, and applications. Polym 13(24):4344. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244344
Ahmad S, Ali H, Khan RA, Ahmad RJZ, Fatima WZ, Abbas G, Irfan M, Ali H, Khan MA, Hasanuzzaman M (2015) Measuring leaf area of winter cereals by different techniques: a comparison. Pak J Life Soc Sci 13(2):117–125
Ahmed EM, Aggor FS, Awad EI-Aref AT AM (2013) An innovative method for preparation of nanometal hydroxide superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 91(2):693–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.08.056
Alam MN, Islam MS, Christopher LP (2019) Sustainable production of cellulose-based hydrogels with superb absorbing potential in physiological saline. ACS Omega 4:9419–9426. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00651
Banu JR, Kavitha PS, Tyagi VK (2021) Lignocellulosic biomass based biorefinery: a successful platform towards circular bioeconomy. Fuel 302:121086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121086
Bian H, Wei L, Lin C, Ma Q, Dai H, Zhu JY (2018) Lignin-containing cellulose nanofibril-reinforced polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(4):4821–4828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04172
Chin K, Ting SS, Lin OH, Owi WT (2017) Extraction of microcrystalline cellulose from rice straw and its effect on polyvinyl alcohol biocomposites film. AIP Conf Proc 1865:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4993348
Ciolacu D, Opera AM, Anghel N, Cazacu G, Cazacu M (2012) New cellulose-lignin hydrogels and their application in controlled release of polyphenols. Mater Sci Eng C 32:452–463
Dai L, Zhou N, Hui Li et al (2020) Recent advances in improving lignocellulosic biomass-based bio-oil production. JAAP 149:104845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104845
Dey A K, Guha P, Sharma M, Meshram M R (2019) Comparison of different methods of in-situ leaf area measurement of betel leaf (Piper betle L.). Int J Recent Technol Eng 7(6):1512–1516.
Distantina S, Rochmadi, Fahrurrozi M, Wiratni (2012) Preparation of hydrogel based on glutaraldehyde-crosslinked carrageenan. In: 3rd International conference on chemistry and chemical engineering, vol 38. IACSIT Press, Singapore, pp-1–5
Du H, Liu W, Zhang M, Si C, Zhang X, Li B (2019) Cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym 209:130–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.020
Fan G, Wang Y, Song G, Yan J, Li J (2017) Preparation of microcrystalline cellulose from rice straw under microwave irradiation. J Appl Polm Sci 134(2):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44901
Fu LH, Qi C, Ma MG, Wan P (2019) Multifunctional cellulose-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem B 7:1541–1562. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB02331J
Ge Y, Li Z (2018) Application of lignin and its derivatives in adsorption of heavy metal ions in water: a review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(5):7181–7192. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b01345
Guan Y, Zhang B, Pang, Sun BJFRC (2014) Nanoreinforced hemicellulose-based hydrogels prepared by freeze–thaw treatment. Cellulose 21:1709–1721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0211-9
Ji X, Zhang Z, Chen J, Yang G, Chen H, Lucia LA (2017) Synthesis and characterization of alkali lignin-based hydrogels from ionic liquids. Bio Res 12(3):5395–5406
Kaur R, Uppal SK (2015) Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of lignin from sugarcane bagasse. Colloid Polym Sci 293:2585–2592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3653-1
Kaur R, Uppal SK, Sharma P (2018) Phenolic acids from sugarcane bagasse lignin: qualitative and quantitative determination, isolation, derivatization, and biological activity evaluation. Chem Nat Compd 54:1211–1215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-018-2600-z
Kaur R, Sharma R, Chahal GK (2021) Synthesis of lignin-based hydrogels and their applications in agriculture: a review. Chem Pap 75:4465–4478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01712-w
Kirkok SK, Kibet JK, Okanga F, Kinyanjui T, Nyamori V (2019) Mechanistic formation of hazardous molecular heterocyclic amines from high temperature pyrolysis of model biomass materials: cellulose and tyrosine. BMC Chem Biol 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-019-0644-1
Kleinert M, Barth T (2008) Phenols from lignin. Chem Eng Technol 31(5):736–745. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.200800073
Kundu D, Banerjee T (2020) Development of microcrystalline cellulose based hydrogels for in vitro delivery of Cephalexin. Heliyon 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03027
Li X, Pan X (2010) Hydrogels based on hemicellulose and lignin from lignocellulose biorefinery: a mini-review. J Bio Mat Bioeng 4:289. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbmb.2010.1107
Liu Y, Nie Y, Lu X et al (2019) Cascade utilization of lignocellulosic biomass to high-value products. Green Chem 21(13):3499–3535. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC00473D
Mantha S, Pillai S, Khayambashi P, Upadhyay A, Tao ZYO, Pham HM, Tran SD (2019) Smart hydrogels in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Mater 12(20):1–33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203323
Meng Y, Lu J, Cheng Y, Li Q, Wang H (2019) Lignin-based hydrogels: a review of preparation, properties and application Int J Biol Macromol 135:1006–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.198
Montesano FF, Parentea A, Santamariab P, Sanninoc A, Serio F (2015) Biodegradable superabsorbent hydrogel increases water retention properties of growing media and plant growth. Agric Agric Sci Proc 4:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2015.03.052
Mota OL, Gimenezb LF (2022) Cellulose-based materials crosslinked with epichlorohydrin: A mini review. Rev Virtual Quim, pp 1–12. https://doi.org/10.21577/1984-6835.20220071
Musa BH, Hameed NJ (2021) Effect of crosslinking agent (glutaraldehyde) on the mechanical properties of (PVA/Starch) blend and (PVA/PEG) binary blend films. J Phys Conf Ser 1795:1–10
Paksung N, Pfersich J, Arauzo PJ, Jung D, Kruse A (2020) Structural effects of cellulose on hydrolysis and carbonization behavior during hydrothermal treatment. ACS Omega 5(21):12210–12223. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00737
Patchan MW, Chae JJ, Lee JD, Calderon-Colon X, Maranchi JP, McCally RL, Schein OD, Elisseeff JH, Trexler MM (2015) Evaluation of the biocompatibility of regenerated cellulose hydrogels with high strength and transparency for ocular applications. J Biomater Appl 30(7):1049–1059. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328215616273
Peng Z, Chen F (2011) Synthesis and properties of lignin-based polyurethane hydrogels. J Polym Mater 60:674–683. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2010.551353
Quintero JA, Rincon LE, Cardona C (2011) A production of bioethanol from agroindustrial residues as feedstocks. In: Biofuels. Manizales, Colombia, pp 251–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385099-7.00011-5
Rehman A, Ahmad A, Safdar M (2011) Effect of hydrogels on performance of aerobic rice sown under different techniques. J Plant Soil Environ 7:321–325. https://doi.org/10.17221/81/2011-PSE
Silverstein RM, Webster FX, Kiemle DJ (2005) Spectrometric identifications of organic compounds, 7th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 72–126
Sowjanya P, Komali BV, Babu CHA (2013) A review article on hydrogels. Int J Res Pharm Nano Sci 2(5):548–553
Subramanian KG, Vijayakumar V (2015) Hydrogels: classification, synthesis, characterization, and applications. Encyclo Biomed Poly Polym Biomat 11:3879–3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040182
Tanan W, Panichpakdee J, Saengsuwan S (2019) Novel biodegradable hydrogel based on natural polymers: Synthesis, characterization, swelling/reswelling and biodegradability. Eur Polym J 112:678–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.10.033
Tang H, Zhang L, Hu L et al (2014) Application of chitin hydrogels for seed germination, seedling growth of rapeseed. J Plant Growth Regul 33:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-013-9361-5
Thakur VK, Thakur MK, Raghav P et al (2014) Progress in green polymer composites from lignin for multicational applications: a review. J ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2(5):794–801
Wang W, Wu X, Chen A et al (2016) Mitigating effects of ex situ application of rice straw on CH4 and N2O emissions from paddy-upland coexisting system. J Sci Rep 6:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37402
Wang Y (2008) Cellulose fiber dissolution in sodium hydroxide solution at low temperature: dissolution kinetics and solubility improvement. PhD dissertation, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, pp 28–32.
Weraduwage SM, Chen J, Anozie FC, Morales A, Weise SE, Sharkey TD (2015) The relationship between leaf area growth and biomass accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 6:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00167
Wu L, Huang S, Zheng J, Qiu Z, Lin X, Qin Y (2019) Synthesis and characterization of biomass lignin-based PVA super-absorbent hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol 140:538–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.142
Yang W, Fortunati E, Bertoglio F, Owczarek JS, Bruni G, Kozanecki M, Kenny JM, Torre L, Visai L, Puglia D (2018) Polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan hydrogels with enhanced antioxidant and antibacterial properties induced by lignin nanoparticles. Carbohyd Polym 181:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.084
Zhang Z (2021) Waste pretreatment technologies for hydrogen production. In: Waste to renewable biohydrogen. Henan Agricultutral University, Zhengzhou, China, Vol 1, pp 109–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821659-0.00004-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JK contributed to investigation, methodology, data curation, visualization and writing original draft. RKM contributed to conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, proof-reading and editing. GKC contributed to data analysis and writing, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, J., Mankoo, R.K. & Chahal, G.K. Synthesis of rice straw biopolymers based hydrogels and their use as media for growth of monocot (wheat) and dicot (moong bean) plants. Chem. Pap. 77, 2539–2555 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02644-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02644-9