Abstract
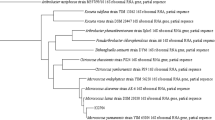
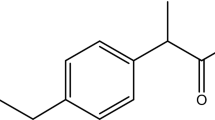
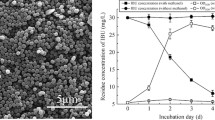
Ibuprofen (IBP), a commonly recommended nonsteroidal, antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug, is a widespread ecological contaminant with harmful consequences. This issue has necessitated the development of a comprehensive scientific strategy for the removal of drugs as well as their by-products from the environment. Biodegradation is a method for breaking down complex chemicals into simpler forms that is both eco-friendly and effective. The current research studies the biodegradation of IBP by isolating a promising bacterial strain isolated from a pharmaceutical industrial wastewater. Microbacterium paraoxydans (Genbank accession numbers: Forward OL614700 and Reverse OL614701) was identified as the bacterium strain by 16S rRNA sequencing. Enhancement of IBP biodegradation efficiency was attained by optimization of parameters using central composite design (CCD). Due to their critical impact on IBP degradation, five parameters were selected for optimization: pH, yeast extract, temperature, inoculum dose, incubation time, and agitation speed. The other two parameters, concentration and time, were kept unchanged. At ideal conditions of pH 7, inoculum dose OD600, agitation speed of 150 rpm, 30 °C temperature, and 0.3% yeast extract, the target drug concentration was reduced by 92.01%. The results suggest that Microbacterium paraoxydans could be an efficient microbe for degrading pharmaceutical wastewater and reducing harmful environmental effects.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Almeida B, Kjeldal H, Lolas I, Knudsen AD, Carvalho G, Nielsen KL, Barreto Crespo MT, Stensballe A, Nielsen JL (2013) Quantitative proteomic analysis of ibuprofen-degrading Patulibacter sp. Strain I11. Biodegradation 24:615–630
Chorost MS, Smith NC, Hutter JN, Ong AC, Stam JA, McGann PT, Kamau E (2018) Bacteraemia due to Microbacterium paraoxydans in a patient with chronic kidney disease refractory hypertension and sarcoidosis. JMM Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmmcr.0.005169
Couto FC, Lange LC, Amaral MCS (2018) A critical review on membrane separation processes applied to remove pharmaceutically active compounds from water and wastewater. J Water Process Eng 26:156–175
Dai L, Wu TQ, Xiong YS, Ni HB, Ding Y, Zhang WC, Yu J (2019) Ibuprofen-mediated potential inhibition of biofilm development and quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci 237:116947. https://doi.org/10.1101/576447
Delgado-Moreno L, Bazhari S, Nogales R, Romero E (2019) Innovative application of biobed bioremediation systems to remove emerging contaminants: adsorption, degradation and bioaccesibility. Sci Total Environ 651:990–997
Encarnação T, Aguiar A, Palito C, Pais AA, Campos MG, Sobral AJ, Burrows HD (2020a) Development and validation of a RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous analysis of paracetamol, ibuprofen, olanzapine, and simvastatin during microalgae bioremediation. MethodsX 7:101083
Encarnação T, Palito C, Pais AACC, Valente AJM, Burrows HD (2020b) Removal of pharmaceuticals from water by free and Imobilised microalgae. Molecules 25:1–13
Fortunato MS, Fuentes Abril NP, Martinefski M, Trípodi V, Papalia M, Rádice M, Korol SE (2016) Aerobic degradation of ibuprofen in batch and continuous reactors by an indigenous bacterial community. Environ Technol 37(20):2617–2626
Girijan S, Kumar M (2019) Immobilized biomass systems: an approach for trace organics removal from wastewater and environmental remediation. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 12:18–29
Iovino P, Canzano S, Capasso S, Erto A, Musmarra D (2015) A modeling analysis for the assessment of ibuprofen adsorption mechanism onto activated carbons. Chem Eng J 277:360–367
Jiang M, Yang W, Zhang Z, Yang Z, Wang Y (2015) Adsorption of three pharmaceuticals on two magnetic ion-exchange resins. Res J Environ Sci 31:226–234
Jiménez-Silva VA, Santoyo-Tepole F, Ruiz-Ordaz N, Galíndez-Mayer J (2019) Study of the ibuprofen impact on wastewater treatment mini-plants with bioaugmented sludge. Process Saf Environ 123:140–149
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Struct 16:111–120
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549
Langenhoff A, Inderfurth N, Veuskens T, Schraa G, Blokland M, Roeleveld KK, Rijnaarts H (2013) Microbial removal of the pharmaceutical compounds ibuprofen and diclofenac from wastewater. Biomed Res Int, 1–9
Marchlewicz A, Domaradzka D, Guzik U, Wojcieszyńska D (2016) Bacillus thuringiensis B1(2015b) is a Gram-positive bacteria able to degrade naproxen and ibuprofen. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:197
Marchlewicz A, Guzik U, Katarzyna Hupert-Kocurek K, Nowak A, Wilczyńska S, Wojcieszyńska D, D, (2017) Toxicity and biodegradation of ibuprofen by Bacillus thuringiensis B1(2015b). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:7572–7584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8372-3
Marco-Urrea E, Pérez-Trujillo M, Vicent T, Caminal G (2009) Ability of white-rot fungi to remove selected pharmaceuticals and identification of degradation products of ibuprofen by Trametes versicolor. Chemosphere 74:765–772
Maryam B, Buscio V, Odabasi SU, Buyukgungor H (2020) A study on behavior, interaction and rejection of Paracetamol, Diclofenac and Ibuprofen (PhACs) from wastewater by nanofiltration membranes. Environ Technol Innov 18:100641
Matamoros V, Uggetti E, García J, Bayona JM (2016) Assessment of the mechanisms involved in the removal of emerging contaminants by microalgae from wastewater: a laboratory scale study. J Hazard Mater 301:197–205
Navrozidou E, Melidis P, Ntougias S (2019) Biodegradation aspects of ibuprofen and identification of ibuprofen-degrading microbiota in an immobilized cell bioreactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:14238–14249
Samanta S, Datta D, Halder G (2020) Biodegradation efficacy of soil inherent novel sp. Bacillus tropicus (MK318648) onto low density polyethylene matrix. J Poly Res 27(10):1–16
Santaeufemia S, Torres E, Abalde J (2018) Biosorption of ibuprofen from aqueous solution using living and dead biomass of the microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Appl Phycol 30:471–482
Sarkar P, Dey A (2020) 4-Nitrophenol biodegradation by an isolated and characterized microbial consortium and statistical optimization of physicochemical parameters by Taguchi Methodology. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5):104347
Sarkar P, Show S, Tiwari H, Dey A (2022) Strategic utilization of groundnut shell (Arachis hypogaea) immobilized bacterial consortium for enhanced 4-nitrophenol remediation: statistical optimization, kinetic modeling, and reusability. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02458-5
Sharma K, Kaushik G, Thotakura N, Raza K, Sharma N, Nimesh S (2019) Fate of ibuprofen under optimized batch biodegradation experiments using Micrococcus yunnanensis isolated from pharmaceutical sludge. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(12):8315–8328
Show S, Karmakar B, Halder G (2020) Sorptive uptake of anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen by waste biomass–derived biochar: experimental and statistical analysis. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00922-8
Show S, Chakraborty P, Karmakar B, Halder G (2021) Sorptive and microbial riddance of micro-pollutant ibuprofen from contaminated water: a state of the art review. Sci Total Environ 786:147327
Sutherland DL, Ralph PJ (2019) Microalgal bioremediation of emerging contaminants-Opportunities and challenges. Water Res 164:114921
Zwiener C (2007) Occurrence and analysis of pharmaceuticals and their transformation products in drinking water treatment. Anal Bioanal Chem 387(4):1159–1162
Acknowledgements
Sincere thanks to Dr. Soumya Banerjee for his assistance in preparation of the manuscript. The authors would like to extend their gratitude to the Department of Chemical Engineering as well as Biotechnology at NIT-Durgapur, India. Prof. Apurba Dey provided laboratory facilities, while Mr. Harshit Tiwari and Mr. Pankaj Garkoti, both M.Tech students at the institute, provided important support in completing this experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Show, S., Sarkar, P., Barman, S. et al. Microbial remediation of ibuprofen contaminated water using novel isolate Microbacterium paraoxydans. Chem. Pap. 77, 517–531 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02499-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02499-0