Abstract
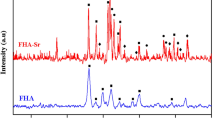
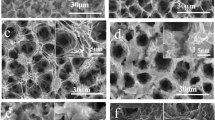
Bone-implant bonding can be achieved by stimulating the apatite formation with the alkaline chemical process applied to the surface of Ti and its alloys. Although the bioactivity can improve the osseointegration feature of the implant, the shortening of the implant life due to the risk of infection during implantation is a problem frequently encountered in biomedical applications and causes the removal of the implant. Therefore, in this study, NaOH pretreatment was performed on Ti plates to create a nano-networked surface that can stimulate apatite formation. It aimed to reduce the risk of infection by loading antibiotics on these surfaces. After alkali treatment, a nano-network structure with 80–150 nm pore sizes with alpha titanium and sodium hydrogen titanate phases was formed. It has been observed that this surface provides apatite formation when kept in simulated body fluid for 3 days. The appearance of an inhibition zone after drug loading proved its antibacterial property. At the same time, the cell viability of the drug-loaded alkaline treated surface was 85%. It was concluded that antibiotic-loaded nano-networked NaOH surfaces could be recommended for dental and orthopedic implants in terms of both cellular behavior and infection risk.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman FA-Z et al (2016) Exploitation of 3D-microporous architecture surface of titanium ımplant as local drug delivery system. Open J Dentistry Oral Med 4(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.13189/ojdom.2016.040101.
Ahuja G, Pathak K (2009) Porous carriers for controlled/modulated drug delivery. Indian J Pharm Sci 71(6):599–607. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.59540
Albayrak O, El-Atwani O, Altintas S (2008) Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate by electrophoretic deposition method: effects of titanium dioxide inner layer on adhesion strength and hydroxyapatite decomposition. Surf Coat Technol 202(11):2482–2487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2007.09.031
Ames JM et al (2009) Contemporary methacrylate resin-based root canal sealers exhibit different degrees of ex vivo cytotoxicity when cured in their self-cured mode. Journal of Endodontics 35(2):225–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2008.11.008
Ayon AA et al (2006) Drug loading of nanoporous TiO2 films. Biomed Mater 1(4):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/1/4/L01
Baino F, Yamaguchi S (2020) The use of simulated body fluid (SBF) for assessing materials bioactivity in the context of tissue engineering: review and challenges. Biomimetics 5(4):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics5040057
Ballo MA et al (2011) Dental ımplant surfaces—physicochemical properties, biological performance, and trends. In: Implant dentistry—a rapidly evolving practice. https://doi.org/10.5772/17512.
Chen ST et al (2021) Drug-release dynamics and antibacterial activities of chitosan/cefazolin coatings on Ti implants. Prog Org Coat 159(February):106385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106385
de Jesus J et al (2014) In vivo evaluation of titanium ımplants bioactivated by a modified Kokubo’s treatment. J Biosci Med 02(02):22–29. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbm.2014.22004
Fang C et al (2017) Infection after fracture osteosynthesis—Part I: Pathogenesis, diagnosis and classification. J Orthop Surg 25(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1177/2309499017692712
Geuli O et al (2017) Synthesis, coating, and drug-release of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles loaded with antibiotics. J Mater Chem B Royal Soc Chem 5(38):7819–7830. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb02105d
Hanawa T (2019) Titanium-tissue interface reaction and its control with surface treatment. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7(JUL). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00170.
Hangzhou Z et al (2013) Improved antibacterial activity and biocompatibility on vancomycin-loaded TiO2 nanotubes: in vivo and in vitro studies. Int J Nanomed, pp 4379–4389. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S53221.
Heimann RB (2016) Plasma-sprayed hydroxylapatite-based coatings: chemical, mechanical, microstructural, and biomedical properties. J Thermal Spray Technol 25(5):827–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-016-0421-9
Hsu HC et al (2017) Effect of different post-treatments on the bioactivity of alkali-treated Ti-5Si alloy. Bio-Med Mater Eng 28(5):503–514. https://doi.org/10.3233/BME-171693
Jauković V et al (2021) Influence of selective acid-etching on functionality of halloysite-chitosan nanocontainers for sustained drug release. Mater Sci Eng, C 123:112029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112029
Jonášová L et al (2004) Biomimetic apatite formation on chemically treated titanium. Biomaterials 25(7–8):1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.08.009
Kokubo T, Yamaguchi S (2010) Novel bioactive titanate layers formed on ti metal and its alloys by chemical treatments. Materials 3(1):48–63. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3010048
Liang F, Zhou L, Wang K (2003) Apatite formation on porous titanium by alkali and heat-treatment. Surf Coat Technol 165(2):133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(02)00735-1
Pattanayak DK et al (2011) Nanostructured positively charged bioactive TiO2 layer formed on Ti metal by NaOH, acid and heat treatments. J Mater Sci Mater Med 22(8):1803–1812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4372-x
Prasanna APS, Venkatasubbu GD (2018) Sustained release of amoxicillin from hydroxyapatite nanocomposite for bone infections. Progress Biomater 7(4):289–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-018-0103-4
Resende CX et al (2010) Cell adhesion on different titanium-coated surfaces. Revista Materia 15(2):420–425
Ribeiro M, Monteiro FJ, Ferraz MP (2012) Infection of orthopedic implants with emphasis on bacterial adhesion process and techniques used in studying bacterial-material interactions. Biomatter 2(4):176–194. https://doi.org/10.4161/biom.22905.
Souza JGS et al (2021) Targeting implant-associated infections: titanium surface loaded with antimicrobial. iScience 24(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.102008.
Su EP et al (2018) Effects of titanium nanotubes on the osseointegration, cell differentiation, mineralisation and antibacterial properties of orthopaedic implant surfaces. Bone Joint J 100B(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.100B1.BJJ-2017-0551.R1
Swanson T E, Cheng X, Friedrich C (2011) Development of chitosan-vancomycin antimicrobial coatings on titanium implants. J Biomed Mater Res A 97 A(2):167–176. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.33043.
Xiao J et al (2009) A composite coating of calcium alginate and gelatin particles on Ti6Al4V implant for the delivery of water soluble drug. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 89(2):543–550. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.31246
Xing H et al (2014) Osteogenic activity of titanium surfaces with nanonetwork structures. Int J Nanomed 9(1):1741–1755. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S58502
Yamaguchi S et al (2009) Morphological study of apatite formation on NaOH- and heat-treated titanium metal. Key Eng Mater 396–398:361–364. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.396-398.361
Yamaguchi S et al (2011) Preparation of bioactive Ti-15Zr-4Nb-4Ta alloy from HCl and heat treatments after an NaOH treatment. J Biomedi Mater Res A 97 A(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.33036.
Yao C, Webster TJ (2009) Prolonged antibiotic delivery from anodized nanotubular titanium using a co-precipitation drug loading method. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 91(2):587–595. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.31433
Yılmaz E, Gökçe A, Findik F, Gulsoy HÖ (2018a) Assessment of Ti–16Nb–xZr alloys produced via PIM for implant applications. J Therm Anal Calorim 134(1):7–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6808-0
Yılmaz E, Gökçe A, Findik F, Gulsoy HÖ (2018b) Metallurgical properties and biomimetic HA deposition performance of Ti-Nb PIM alloys. J Alloy Compd 746:301–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.274
Yılmaz E et al (2019) Novel hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide/collagen bioactive composite coating on Ti16Nb alloys by electrodeposition. Mater Sci Eng C 101(March):292–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.03.078
Zhang S et al (2018) Electrochemical deposition of calcium phosphate/Chitosan/Gentamicin on a titanium alloy for bone tissue healing. Int J Electrochem Sci 13:4046–4054. https://doi.org/10.20964/2018.05.39.
Zhukova Y et al (2017) The role of titanium surface nanostructuring on preosteoblast morphology, adhesion, and migration. Adv Healthcare Mater 6(15):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201601244
Acknowledgements
This study was supported Scientific Research Projects Commission of Sakarya University (Project number: 2019-5-19-134). We would like to thank biologist Mustafa Çelik for the antibacterial study. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EY: Investigation, Writing-original draft. ST: Investigation, Writing-original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yılmaz, E., Türk, S. Loading antibiotics on the surface of nano-networked sodium hydroxide treated titanium. Chem. Pap. 76, 2459–2467 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-02045-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-02045-4