Abstract
Herein, a sensitive electrochemical sensor based on a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was developed to measure the lansoprazole (LNS). The most suitable monomer was chosen by a computational method. A cyclic voltammetry technique was used to synthesize the sensor by electro-polymerization of pyrrole on a pencil graphite electrode in the presence of a template molecule. The differential pulse voltammetry technique was performed for all measurements. The characterization of the modified sensor was investigated by scanning electron microscopy. To optimize the critical factors, the Plackett–Burman design and central composite design methods were done. Linear range of 10–1000 µM and correlation coefficients (R2) of 0.9846 were obtained by plotting the calibration curve under optimal conditions. The limit of detection and the limit of quantitation were determined as 0.031 μM (S/N = 3) and 0.075 μM (S/N = 10), respectively. Finally, the proposed sensor was successfully applied to LNS determination in capsule and serum samples.
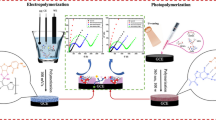
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afkhami A, Ghaedi H, Madrakian T, Ahmadi M, Mahmood-Kashani H (2013) Fabrication of a new electrochemical sensor based on a new nano-molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective and sensitive determination of tramadol in human urine samples. Biosens Bioelectron 44:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.11.030
Ahmad AA, Hameed BH, Ahmad AL (2009) Removal of disperse dye from aqueous solution using waste-derived activated carbon: optimization study. J Hazard Mater 170:612–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.021
Ahmadi F, Karamian E (2014) Computational aided–molecular imprinted polymer design for solid phase extraction of metaproterenol from plasma and determination by voltammetry using modified carbon nanotube electrode. Iran J Pharm Res 13:417–429. https://doi.org/10.22037/ijpr.2014.1488
Basavaiah K, Ramakrishna V, Anil Kumar UR, Kumar U (2006a) Spectrophotometric and performance liquid-chromatographic determination of lansoprazole in pharmaceuticals. Indian J Chem Technol 13:549–554
Basavaiah K, Ramakrishna V, Anil Kumar UR (2006b) Sensitive spectrophotometric determination of lansoprazole in pharmaceuticals using ceric ammonium sulphate based on redox and complex formation reactions. EQJ 31:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46702006000300009
Basavaiah K, Ramakrishna V, Anil Kumar UR, Somashekar BC (2007) Spectrophotometric determination of lansoprazole in pharmaceuticals using bromate-bromide mixture based on redox and complexation reactions. EQJ 32:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46702007000100008
Belal F, El-Enany N, Rizk M (2004) Anodic polarographic determination of lansoprazole and omeprazole in pure form and in pharmaceutical dosage forms. J Food Drug Anal 12:102–109. https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.2656
Chen D, Deng J, Liang J, Xie J, Huang K, Hu C (2013) Core–shell magnetic nanoparticles with surface imprinted polymer coating as a new adsorbent for solid phase extraction of metronidazole. Anal Methods 5:722–728. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ay25897h
Dogrukol-Ak D, Tuncel M, Aboul-Enien HY (2001) The determination of lansoprazole in pharmaceutical preparation by capillary electrophoresis. Chromatographia 54:527–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02491212
El-Enany N, Belal F, Rizk M (2008) The alternating current polarographic behavior and determination of lansoprazole and omeprazole in dosage forms and biological fluids. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:889–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2008.02.002
El-Sherif ZA, Mohamed AO, El-Bardeicy MG, El-Tarras MF (2005) Stability-indicating methods for the determination of lansoprazole. Spectrosc Lett 38:77–93. https://doi.org/10.1081/SL-200045505
Hall CA, Kelly JD, Whitlock HV, Ritchie L (1981) Prolonged anthelmintic effect of closantel and disophenol against a thiabendazole selected resistant strain of Haemonchus contortus in sheep. Res Vet Sci 31:104–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-5288(18)32531-1
Hong M, XuL RG, Chen J, Qi M (2012) Solubility of lansoprazole in different solvents. Fluid Phase Equilib 331:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2012.06.011
Hong Liu L, You W, Zhan XM, Gao ZN (2014) Electrochemical behavior of lansoprazole at a multiwalled carbon nanotubes–ionic liquid modified glassy carbon electrode and its electrochemical determination. J Serb Chem Soc 79:39–52. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC121216059L
Kan X, Zhou H, Li C, Zhu A, Xing Z, Zhao Z (2012) Imprinted electrochemical sensor for dopamine recognition and determination based on a carbon nanotube/polypyrrole film. Electrochim Acta 63:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.12.086
Karol MD, Granneman GR, Alexander K (1995) Determination of lansoprazole and five metabolites in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 668:182–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(95)00068-T
Kissinger PT, Heineman WR (1996) Laboratory techniques in electroanalytical chemistry. Marcel Dekker, New York
Kumar D, Prasad BB (2012) Multiwalled carbon nanotubes embedded molecularly imprinted polymer-modified screen printed carbon electrode for the quantitative analysis of Creactive protein. Sens Actuators B Chem 171:1141–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.06.053
Lai KC, Lam SK, Chu KM, Wong BCY, Hui WM, Hu WHC, Lau GKK, Wong WM, Yuen MF, Chan AOO, Lai CL, Wong J (2002) Lansoprazole for the prevention of recurrences of ulcer complications from long-term low-dose aspirin use. N Engl J Med 346:2033–2038. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa012877
Nassar MY, El-Shahat MF, Khalil SM, El-Moety EA (2017) Optimization and validation of spectrophotometric and potentiometric methods for determination of lansoprazole and omeprazole in pure and capsules. Indian J Pharm Sci 79:420–430. https://doi.org/10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000245
Nezhadali A, Mojarab M (2016) Computational design and multivariate optimization of an electrochemical metoprolol sensor based on molecular imprinting in combination with carbon nanotubes. Anal Chim Acta 924:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.04.017
Nezhadali A, Sadeghzadeh S (2017) Experimental design-artificial neural network-genetic algorithm optimization and computer-assisted design of celecoxib molecularly imprinted polymer/carbon nanotube sensor. J Electroanal Chem 795:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.04.032
Nezhadali A, Shadmehri R (2013) Computer–aided sensor design and analysis of thiocarbohydrazide in biological matrices using electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode. Sensor Actuat B Chem 177:871–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.11.103
Nezhadali A, Mehri L, Shadmehri R (2012) Determination of benzimidazole in biological model samples usingelectropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modifiedpencil graphite sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 171:1125–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.06.043
Pandya KK, Mody VD, Satia MC, Modi IA, Modi RI, Chakravarthy BK, Gandhi TP (1997) High–performance thin–layer chromatographic method for the detection and determination of lansoprazole in human plasma and its use in pharmacokinetic studies. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 693:199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(96)00516-6
Radi A (2002a) Adsorptive stripping square–wave voltammetric study of the degradation of lansoprazole in aqueous solutions. Microchem J 73:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-265X(02)00125-X
Radi A (2002b) Determination of lansoprazole in human serum by square wave adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Anal Lett 35:2449–2458. https://doi.org/10.1081/AL-120016536
Radi A (2003) Anodic voltammetric assay of lansoprazole and omeprazole on a carbon paste electrode. J Pharm Biomed Anal 31:1007–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0731-7085(02)00707-0
Rahman N, Khan S (2018) Experimental design approach in the optimization of potentiometric method for lansoprazole determination using lansoprazole–tungstate based ion–selective electrode. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:9351–9361. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b01281
Rahman N, Bano Z, Najmul S, Azmi H, Kashif M (2006) A kinetic spectrophotometric method for the determination of lansoprazole in pharmaceutical formulations. J Serb Chem Soc 71:1107–1120. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC0610107R
Roushani M, Nezhadali A, Jalilian Z, Azadbakht A (2017) Development of novel electrochemical sensor on the base of molecular imprinted polymer decorated on SiC nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for selective determination of loratadine. Mater Sci Eng C 71:1106–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.11.079
Sarafraz-Yazdi A, Razavi N (2015) Application of molecularly-imprinted polymers in solid-phase microextraction techniques. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 73:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.05.004
Silvestre CIC, Santos JLM, Lima JLFC, Feres MA, Zagatto EAG (2010) Single interface flow analysis with accuracy assessment. Microchem J 94:60–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2009.09.002
Simsek Z, Alagozlu H, Tuncer C, Dursun A (2007) Lymphocytic colitis associated with lansoprazole treatment. CTR 68:360–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2007.10.001
Song M, Gao X, Hang TJ, Wen AD (2008) Simultaneous determination of lansoprazole and its metabolites 5′-hydroxy lansoprazole and lansoprazole sulphone in human plasma by LC-MS/MS: application to a pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48:1181–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2008.08.034
Song M, Gao X, Hang TJ, Wen AD (2009) Pharmacokinetic properties of lansoprazole (30-mg Enteric-coated capsules) and its metabolites: a single dose, open-lable study in healthy chinese male subjects. CTR 70:228–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2009.05.002
Tivesten A, Folestad S, Schonbacher V, Swenson K (1997) Nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis for the analysis of labile pharmaceutical compounds. Chromatographia 49:7–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02468970
Tolia V, Fitzgerald J, Hassall HE, Huang B, Pilmer B, Kane R (2002) Safety of lansoprazole in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 35:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005176-200211004-00002
Us E, Perendeci NA (2012) Improvement of methane production from greenhouse residues: optimization of thermal and H2SO4 pretreatment process by experimental design. Chem Eng J 181:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.11.038
Wang H, Sun Y, Meng X, Yang B, Wang J, Yang Y, Gu J (2015) Determination of lansoprazole enantiomers in dog plasma by column-switching liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a preclinical pharmacokinetic study. J Sep Sci 38:2960–2967. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201500462
Whitcombe MJ, Chianella I, Larcombe L, Piletsky SA, Noble J, Porter R, Horgan A (2011) The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem Soc Rev 40:1547–1571. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00049c
Yardımc C, Özaltın N (2001) Electrochemical studies and differential pulse polarographic analysis of lansoprazole in pharmaceuticals. Analyst 126:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1039/B008800P
Yeniceli D, Dogrukol-Ak D, Tuncel M (2004) Determination of lansoprazole in pharmaceutical capsules by flow injection analysis using UV-detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 36:145–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2004.04.015
Zenita Devi O, Basavaiah K, Ramesh Pavagada J, Vinay Kanakapura B (2012) Development of a simple UV-spectrophotometric method for the determination of lansoprazole and study of its degradation profile. Quim Nova 35:386–391. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422012000200027
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Payame Noor University (PNU) Research Council for financial support of this work.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalili, Z., Nezhadali, A. Nanomolar detection of lansoprazole: computational–assisted to monomer–templet complex study based on molecularly imprinted polymer and electrochemical determination. Chem. Pap. 76, 1185–1198 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01933-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01933-z