Abstract
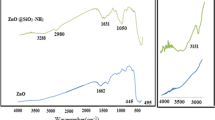
Liver cancer is known as a high morbidity and low survival disease all around the world. This cancer is the most traumatic disease because it affects the major organs of the body. Valproate is a branched-chain fatty acid, which has been widely used as an antiepileptic in liver cancer therapy. However, this drug can induce fulminant liver failure in patients treated with it. Herein, we prepared the desired ZnO and Ag-doped ZnO nanostructures via a simple and efficient method and characterized them with XRD and FESEM. Then, we investigated cytotoxicity potential of ZnO and Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles on a well-known human liver cell (HepG2) via trypan-blue dye exclusion assay with 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The performed experiments show that the prepared ZnO nanoparticles have a significant concentration (20 g/ml) and time-dependent cytotoxicity on the examined cell lines after 24 h and proved damage of the cancer cells in this time interval. Moreover, Ag-doped ZnO also exhibits better cytotoxicity potential compared to bare ZnO. Therefore, ZnO and 0.5% Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles may have less cytotoxic effects on the liver and can be applied as suitable candidates parallel with the existing valproate drug.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkhalek A, Al-Askar AA (2020) Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles mediated by Mentha Spicata extract induce plant systemic resistance against Tobacco mosaic virus. Appl Sci 10(15):5054
Anirudh BVM, Ezhilarasan D (2020) Reactive oxygen species–mediated mitochondrial dysfunction triggers sodium valproate-induced cytotoxicity in human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. J Gastrointest Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-020-00505-w
Cui CW, Yang C, Bao J, Huang XJ, Zeng XF, Chen JF (2020) Monodispersed ZnO nanoparticle-Poly(methylmethacrylate) composites with visible transparency for ultraviolet shielding applications. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3(9):9026–9034
Fan J, Freer R (1995) The roles played by Ag and Al dopants in controlling the electrical properties of ZnO varistors. J Appl Phys 77(9):4795–4800
Frisch MJ et al (2004) Gaussian 03, revision C. 02; Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT
Javadi F, Tayebee R (2016) Preparation and characterization of ZnO/nanoclinoptilolite as a new nanocomposite and studying its catalytic performance in the synthesis of 2-aminothiophenes via Gewald reaction. Mic Mes Mater 231:100–109
Ji QL, Lin R, Shi XL, Mao YH, Zhai XG (2010) Cytotoxicity and mechanisms of sodium and sodium valproate on HepG2 cells. J Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol 24(3):214–218
Kakhki RM, Tayebee R, Ahsani F (2017) New and highly efficient Ag doped ZnO visible nano photocatalyst for removing of methylene blue. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28(8):5941–5952
Komulainen T, Lodge T, Hinttala R, Bolszak M, Pietilä M, Koivunen P, Hakkola J, Poulton J, Morten KJ, Uusimaa J (2015) Sodium valproate induces mitochondrial respiration dysfunction in HepG2 in vitro cell model. Toxicology 331:47–56
Liu J, Wang P, Qu W, Li H, Shi L, Zhang D (2019) Nanodiamond-decorated ZnO catalysts with enhanced photocorrosion-resistance for photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene. Appl Catal B Environ 257:117880
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63
Narenji-Sani F, Tayebee R, Chahkandi M (2020) New task-specific and reusable ZIF-like grafted H6P2W18O62 catalyst for the effective esterification of free fatty acids. ACS Omega 5(17):9999–10010
Parvizi E, Tayebee R, Koushki E (2019) Mg-doped ZnO and Zn-doped MgO semiconductor nanoparticles; synthesis and catalytic, optical and electro-optical characterization. Semiconductors 53(13):1769–1783
Rithanya P, Ezhilarasan D (2020) Sodium valproate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, provokes reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Gastrointest Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-020-00370-7
Robertson TA, Sanchez WY, Roberts MS (2010) Are commercially available nanoparticles safe when applied to the skin? J Biomed Nanotechnol 6(5):452–468
Siddiqui MA, Singh G, Kashyap MP, Khanna VK, Yadav S, Chandra D, Pant AB (2008) Influence of cytotoxic doses of 4-hydroxynonenal on selected neurotransmitter receptors in PC-12 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 22:1681
Stewart BW, Wild CP (eds) (2015) World cancer report 2014. The international agency for research on cancer. World Health Organization, Geneva
Tayebee R, Nasr AH (2020) Studying adsorption and detoxification of sulfur mustard chemical warfare onto ZnO nanostructures. J Mol Liq 319:114357
Tsuchiya N, Sawada Y, Endo I, Saito K, Uemura Y, Nakatsura T (2015) Biomarkers for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 21(37):10573
Xie X, Zhang L, Zhang W, Tayebee R, Hoseininasr A, Vatanpour HH, Behjati Z, Li S, Nasrabadi M, Liu L (2020) Fabrication of temperature and pH sensitive decorated magnetic nanoparticles as effective biosensors for targeted delivery of acyclovir anti-cancer drug. J Mol Liq 309:113024
Zhihong Y, Ye Y, Pejhan A, Nasr AH, Nourbakhsh N, Tayebee R (2020) A theoretical study on the pure and doped ZnO nanoclusters as effective nanobiosensors for 5-fluorouracil anticancer drug adsorption. Appl Organomet Chem 34(4):e5534
Acknowledgements
Deepest thanks to Dr Xiaolan Yang and his research team (Chao Huang, Xin Zhang, Yanchu Li, Xiaolan Yang) because of performing some preliminary experiments and their valuable suggestions.
Funding
The project supported by Planned Self-Financing Foundation of Baoding Science and Technology 2019 (1941ZF087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, F., Zhang, R., Ma, F. et al. Synthesis, characterization and application of ZnO and Ag-doped ZnO nanostructures against human liver cells (HepG2). A suitable candidate for valproate. Chem. Pap. 75, 2191–2196 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01456-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01456-z