Abstract
Purpose
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) has been suggested to be effective for treating obesity and its related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). A small molecule named CY-09 is the selective inhibitor of the NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. We aim to investigate whether a surgery imitating ESG combined with CY-09 is more effective for treatment of obesity and NAFLD in a mouse model.
Material and Methods
Forty mice were randomly divided into a control group (n = 5) and an NAFLD group (n = 35) fed by high-fat diet (HFD). The NAFLD mice were randomly assigned to the following groups at the timepoint of 19 weeks: (1) sham surgery; (2) surgery; (3) the combination of surgery with CY-09 injection. NAFLD activity score (NAS) was used for histological evaluation of steatosis. We also detected fasting glucose and insulin to measure the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR).
Results
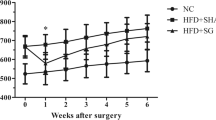
HFD resulted in significant obesity and metabolic disorders, indicating successful modelling of obesity and NAFLD. The combination therapy resulted in significantly lower body weight than surgery alone at the end of the 8-week follow-up (40.4 ± 4.8 vs. 45.0 ± 2.2 g, P = 0.025). Furthermore, more dramatic improvements in HOMA-IR (5.8 ± 1.1 vs. 12.2 ± 2.1 mmol mIU L−2, P = 0.036) and NAS (4.5 ± 1.3 vs. 8.0 ± 1.8, P = 0.006) were also observed in the combination group.
Conclusions
Surgery imitating ESG combined with CY-09 reduces body weight, improves insulin resistance and alleviates hepatic steatosis. The combination therapy may be a promising method for treating obesity and NAFLD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data supporting the results will be available and stored at the research office of our department.
References
Fan JG, Kim SU, Wong VW. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J Hepatol. 2017;67(4):862–73.
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15(1):11–20.
Cazzo E, Pareja JC, Chaim EA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and bariatric surgery: a comprehensive review. Sao Paulo Med J = Rev Paul Med. 2017;135(3):277–95.
Fakhry TK, Mhaskar R, Schwitalla T, et al. Bariatric surgery improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a contemporary systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(3):502–11.
Algooneh A, Almazeedi S, Al-Sabah S, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease resolution following sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Endosc. 2016;30(5):1983–7.
Kalinowski P, Paluszkiewicz R, Ziarkiewicz-Wroblewska B, et al. Liver function in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease randomized to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus sleeve gastrectomy: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg. 2017;266(5):738–45.
Sharaiha RZ, Kumta NA, Saumoy M, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty significantly reduces body mass index and metabolic complications in obese patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(4):504–10.
Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD. The inflammasome: a remote control for metabolic syndrome. Cell Res. 2012;22(7):1095–8.
Wree A, Eguchi A, McGeough MD, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in hepatocyte pyroptosis, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md). 2014;59(3):898–910.
Kubes P, Mehal WZ. Sterile inflammation in the liver. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(5):1158–72.
Jiang H, He H, Chen Y, et al. Identification of a selective and direct NLRP3 inhibitor to treat inflammatory disorders. J Exp Med. 2017;214(11):3219–38.
Oberbach A, Schlichting N, Heinrich M, et al. Gastric mucosal devitalization reduces adiposity and improves lipid and glucose metabolism in obese rats. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87(1):288–99. e6
Du J, Hu C, Bai J, et al. Intestinal glucose absorption was reduced by vertical sleeve gastrectomy via decreased gastric leptin secretion. Obes Surg. 2018;28(12):3851–61.
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94(9):2467–74.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md). 2005;41(6):1313–21.
Samuel VT, Shulman GI. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, insulin resistance, and ceramides. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(19):1866–9.
Nickel F, Tapking C, Benner L, et al. Bariatric surgery as an efficient treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a prospective study with 1-year follow-up : BariScan Study. Obes Surg. 2018;28(5):1342–50.
Yeo SC, Ong WM, Cheng KSA, et al. Weight loss after bariatric surgery predicts an improvement in the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) fibrosis score. Obes Surg. 2019;29(4):1295–300.
Espinet Coll E, Vila Lolo C, Diaz Galan P, et al. Bariatric and metabolic endoscopy in the handling of fatty liver disease. A new emerging approach? Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2019;111(4):283–93.
Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011;17(2):179–88.
Szabo G, Csak T. Inflammasomes in liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2012;57(3):642–54.
Haneklaus M, O’Neill LA. NLRP3 at the interface of metabolism and inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2015;265(1):53–62.
Ding S, Xu S, Ma Y, et al. Modulatory mechanisms of the NLRP3 inflammasomes in diabetes. Biomolecules. 2019;9(12)
Henao-Mejia J, Elinav E, Jin C, et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature. 2012;482(7384):179–85.
Authors’ Contribution Statement
Side Liu and Yue Li designed the study. Yue Li drafted the manuscript. Kangyue Sun and Jing Wang conducted the experiment and recorded the data. Kangyue Sun and Zhixian Lan analysed the experimental data. Ling Li and Aimin Li revised the manuscript. Yadong Wang reviewed and evaluated the hepatic histology.
Funding
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81600460), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2016A030310382) and the Guangdong Gastrointestinal Disease Research Center (No. 2017B020209003). All authors disclosed no financial relationships relevant to this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval Statement
The authors declare that an ethical approval was obtained for our study. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted and ethical approval was obtained from the Southern Medical University for the Ethical Use and Care of Experimental Animals. All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent does not apply.
Additional information
Prior Communications
We, the authors, state that the article is original, it has not been submitted for publication in another journal, and it has not yet been published either wholly or in part.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, K., Wang, J., Lan, Z. et al. Sleeve Gastroplasty Combined with the NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor CY-09 Reduces Body Weight, Improves Insulin Resistance and Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis in Mouse Model. OBES SURG 30, 3435–3443 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04571-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04571-8