Abstract
Background
Bariatric surgery leads to several anatomo-physiological modifications that may affect pharmacokinetic parameters and consequently alter the therapeutic effect of drugs, such as antibiotics. The pharmacokinetics of oral amoxicillin after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery is unknown.
Objectives
The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of bariatric surgery on the pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin.
Methods
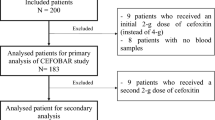
This study was performed as a randomized, open-label, single-dose clinical trial, with two periods of treatment, in which obese subjects (n = 8) received an amoxicillin 500 mg capsule orally before and 2 months after the RYGB surgery. The amoxicillin plasma concentration was determined by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
Results
After the surgery, the mean weight loss was 17.03 ± 5.51 kg, and mean body mass index (BMI) decreased from 46.21 ± 2.82 to 38.82 ± 3.32 kg/m2. The mean amoxicillin area under the plasma concentration versus time curve from time zero to the time of the last quantifiable concentration (AUC0–tlast) increased significantly (3.5-fold); the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) increased 2.8-fold after the bariatric surgery. No correlation was found between amoxicillin absorption, BMI, and weight loss percentage.
Conclusion
The alterations observed in the amoxicillin pharmacokinetics suggest that obese subjects included in this trial had a substantially increase in amoxicillin systemic exposure after RYGB surgery. However, despite this increase, its exposure was lower than the values reported for non-obese volunteers.
Trial Registration
Identifiers: NCT03588273





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards A, Ensom MH. Pharmacokinetic effects of bariatric surgery. Ann. Pharmacother. 2012;46(1):130–6. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1345/aph.1Q414
Ontario HQ. Bariatric surgery: an evidence-based analysis. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2005;5(1):1–148. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3382415/
Wang Y, Zhang C. Bariatric surgery to correct morbid obesity also ameliorates atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009;1(1):56–69. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2776741/
Brocks DR, Ben-Eltriki M, Gabr RQ, et al. The effects of gastric bypass surgery on drug absorption and pharmacokinetics. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012;8(12):1505–19. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.2012.722757.
Pei Q, Yang G-P, Li Z-J, et al. Simultaneous analysis of amoxicillin and sulbactam in human plasma by HPLC-DAD for assessment of bioequivalence. J Chromatogr B. 2011;879(21):2000–4. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1570023211003266
Liew KB, Loh GO, Tan YT, et al. Randomized two-way cross-over bioequivalence study of two amoxicillin formulations and inter-ethnicity pharmacokinetic variation in healthy Malay volunteers. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014;28(9):1246–53. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3153.
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of antimicrobial consumption in Europe 2012. Stockholm: 2014. Available from: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/antimicrobial-consumption-europe-esac-net-2012.pdf.
de Velde F, consortium on behalf of the C-N, de Winter BCM, et al. Non-linear absorption pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin: consequences for dosing regimens and clinical breakpoints. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016;71(10):2909–17. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkw226.
Dollery C. Therapeutic drugs. 2nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1998.
Mouton JW, Brown DFJ, Apfalter P, et al. The role of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics in setting clinical MIC breakpoints: the EUCAST approach. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012;18(3):E37–45. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03752.x.
Paintaud G, Alván G, Dahl ML, et al. Nonlinearity of amoxicillin absorption kinetics in human. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;43(3):283–8. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1425893
Barr WH, Zola EM, Candler EL, et al. Differential absorption of amoxicillin from the human small and large intestine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;56(3):279–85. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.1994.138.
Schramm SG. Use of meta-analysis to evaluate the interchangeability of medicines [in Portuguese; habilitation thesis]. São Paulo (BR): University of São Paulo, 2008.
Lacy CF, Armstrong LL, Goldman MP, et al. Drug information handbook: a comprehensive resource for all clinicians and healthcare professionals. 17th ed. Lexi-Comp: American Pharmacists Association. Ed; 2008-2009.
Arancibia A, Guttmann J, González G, et al. Absorption and disposition kinetics of amoxicillin in normal human subjects. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1980;17(2):199–202. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC283758/
Miller AD, Smith KM. Medication and nutrient administration considerations after bariatric surgery. Am. J. Heal. Pharm. 2006;63(19):1852–7. Available from: http://www.ajhp.org/content/63/19/1852.long?sso-checked=true
Oliveira CH, Abib E, Vannuchi YB, et al. Comparative bioavailability of 4 amoxicillin formulations in healthy human volunteers after single dose administration. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;39(4):167–72. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11332873
Guidance for industry bioanalytical method validatione, 2001. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidance/ucm070107.pdf.
Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária, 2003. Available from: http://www.anvisa.gov.br/hotsite/genericos/legis/resolucoes/2003/899_03re_e.pdf.
Hamilton R, Thai XC, Ameri D, et al. Oral bioavailability of linezolid before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: is dose modification necessary in obese subjects? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013;68(3):666–73. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dks431.
Longo C, Bartlett G, Macgibbon B, et al. The effect of obesity on antibiotic treatment failure: a historical cohort study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2013;22(9):970–6. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1002/pds.3461.
Chagnac A, Weinstein T, Herman M, et al. The effects of weight loss on renal function in patients with severe obesity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003;14(6):1480–6. Available from: http://jasn.asnjournals.org/content/14/6/1480.abstract
Skottheim IB, Stormark K, Christensen H, et al. Significantly altered systemic exposure to atorvastatin acid following gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009;86(3):311–8. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2009.82.
De Smet J, Colin P, De Paepe P, et al. Oral bioavailability of moxifloxacin after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012;67(1):226–9. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkr436.
Navarro-Díaz M, Serra A, Romero R, et al. Effect of drastic weight loss after bariatric surgery on renal parameters in extremely obese patients: long-term follow-up. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006;17(12 suppl 3):S213–7. Available from: http://jasn.asnjournals.org/content/17/12_suppl_3/S213.abstract
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development through the public announcement PQ10/2011—productivity in research—PQ-2011 (grant number 309228/2011-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of the Federal University of Ceará (number 255.607) and the Scientific Committee of the Hospital General Dr. César Cals.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, M.B.S., De Nucci, G., Lemos, F.N. et al. Impact of Bariatric Surgery on the Pharmacokinetics Parameters of Amoxicillin. OBES SURG 29, 917–927 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3591-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3591-3