Abstract
Background
Despite the success of the Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch procedure (BPD-DS) in weight loss and comorbidities resolution, reversal of BPD-DS is necessary in 0.2–0.6% of BPD-DS cases for vitamin, protein, and other micronutrient deficiencies. Different techniques are available to reverse the malabsorptive component of the BPD-DS.
Methods
A retrospective chart review for a 37-year-old female patient who presented with lower leg edema and signs of malnutrition 5 years after a BPD/DS. The patient was not compliant with the required daily vitamin and protein intake. Thus, after extensive discussion with the patient, a decision was made to reverse the malabsorptive component of the BPD-DS.
Results
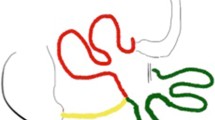
A laparoscopic reversal of the malabsorptive component of the BPD-DS was concluded by transecting the roux limb distally at the ileo-ileal anastomosis and reconnecting it to the proximal jejunum thus substantially lengthening the common channel for absorption. At 6 months follow-up, the patient normalized her vitamin deficiency and had a normal level of serum protein. Her weight, BMI, EWL%, and TBWL% were 72 kg, 27.5 kg/m2, 90%, and 45%, respectively.
Conclusions
Proper nutrition and vitamin supplementation is essential to avoid nutritional complications. Different techniques are available to reverse the malabsorptive component of the BPD-DS. However, no standard approach is adopted by the surgical community. We demonstrate our preferred technique in reversing the malabsorptive component of the BPD-DS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchwald H et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292(14):1724–37.
Marceau P et al. Long-term metabolic outcomes 5 to 20 years after biliopancreatic diversion. Obes Surg. 2015;25(9):1584–93.
Topart P, Becouarn G, Delarue J. Weight loss and nutritional outcomes 10 years after biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Obes Surg. 2017;27(7):1645–50.
Topart PA, Becouarn G. Revision and reversal after biliopancreatic diversion for excessive side effects or ineffective weight loss: a review of the current literature on indications and procedures. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015;11(4):965–72.
Hess DS, Hess DW, Oakley RS. The biliopancreatic diversion with the duodenal switch: results beyond 10 years. Obes Surg. 2005;15(3):408–16.
Almahmeed T, Pomp A, Gagner M. Laparoscopic reversal of biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2006;2(4):468–71.
Dapri G, Cadiere GB, Himpens J. Laparoscopic restoration of gastrointestinal continuity after duodenal switch. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008;4(3):451–4.
Halawani HM, Antanavicius G, Bonanni F. How to switch to the switch: implementation of biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch into practice. Obes Surg. 2017;27:2506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-017-2801-8.
Bolckmans R, Himpens J. Long-term (>10 yrs) outcome of the laparoscopic biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Ann Surg. 2016;264(6):1029–37.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Farah Khalifeh, M.S.c. for reviewing this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study has been approved by the institutional research ethics committee and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
(MP4 161258 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halawani, H.M., Antanavicius, G. Laparoscopic Reversal of the Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch: a Step by Step Video Case. OBES SURG 27, 3327–3329 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-017-2945-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-017-2945-6