Abstract
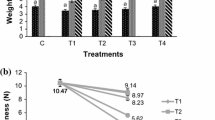
Silk fibroin coating was used in this study as an edible coating for Solanum ferox (S. ferox), tropical fruit from Borneo. The effect of different concentration coatings and dip time on fruit quality attributes during storage was evaluated via response surface methodology. The optimal parameters were 2% silk fibroin concentration and 2 min of dip time. The optimized data for silk fibroin-coated fruit, carboxymethylcellulose-coated fruit and uncoated fruit as a control were compared. The weight loss and firmness at day 11 for fruit coated with silk fibroin were 14.9% and 3.07 N, respectively, compared to 13.49% and 3.53 N for fruit coated with carboxymethylcellulose. Uncoated fruit revealed a weight loss was 28.11% and firmness was 4.3 N. On day 11, the fruit coated with silk fibroin had chemical properties of 3.6 and 4 for total soluble solids (TSS) and pH, respectively. The carboxymethylcellulose-coated fruit had a TSS of 4.2 and a pH of 3.3. The uncoated fruit had a TSS of 4.3 and a pH of 5.2. In comparison to uncoated fruits, the ripening process of fruits coated with silk fibroin was slowed. Silk fibroin is suggested to be an effective edible coating for preserving fruit quality and extending its shelf life.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Z.A. Rahman, M.W.A.M. Zaidan, A.N. Othman, M.A. Ahmad, S. Simoh, M.A.H. Ismail, Optimizing extraction of phenolics and flavonoids from Solanum ferox fruit. Nat. Sci. 11(4), 99–105 (2019)
S. Umar, R.M. Razili, W.M. Hua, N.N. Hamsein, M. Gumbek, Terung Asam Sarawak Technology Package, (Department of Agriculture, Sarawak, 2013), pp. 1–38
T.H. Yong, K.T. Wen Wen, Determination of Sarawak’s brinjal maturity using colour image processing technique. Borneo J. Sci. Technol. 1(2), 32–38 (2019)
S.Z. Raduan, K.N. Abdul Khalid, M.F. Ak Jihek, S. Ganasan, U.S. Salim, M.W.H. Abdul Aziz, Anticariogenic properties of Solanum ferox L. ethanol extract. Ann. Dent. 26, 22–29 (2019)
M.T. Chiu, H.J. Tham, J.S. Lee, Optimization of osmotic dehydration of Terung Asam (Solanum lasiocarpum Dunal). J. Food Sci. Technol. 54(10), 3327–3337 (2017)
H.P. Sharma, V. Chaudhary, M. Kumar, Importance of edible coating on fruits and vegetables: A review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 8(3), 4104–4110 (2019)
K.Á.R. de Oliveira, K.F.D. Fernandes, E.L. de Souza, Current advances on the development and application of probiotic-loaded edible films and coatings for the bioprotection of fresh and minimally processed fruit and vegetables. Foods. 10(9), 1–17 (2021)
E. Díaz-Montes, R. Castro-muñoz, Edible films and coatings as food-quality preservers: An overview. Foods. 10(2), 1–26 (2021)
B.J. Arroyo, A.C. Bezerra, L.L. Oliveira, S.J. Arroyo, E.A. de Melo, A.M.P. Santos, Antimicrobial active edible coating of alginate and chitosan add ZnO nanoparticles applied in guavas (Psidium guajava L.). Food Chem. 309, 1–9 (2020)
M. Farooq, E. Azadfar, A. Rusu, M. Trif, M.K. Poushi, Y. Wang, Improving the shelf life of peeled fresh almond kernels by edible coating with mastic gum. Coatings 11(6), 1–14 (2021)
S.Z. Tesfay, L.S. Magwaza, N. Mbili, and A. Mditshwa, Carboxyl methylcellulose (CMC) containing moringa plant extracts as new postharvest organic edible coating for Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) fruit. Sci. Hortic. 226, 201–207 (2017)
A. Nawab, F. Alam, A. Hasnain, Mango kernel starch as a novel edible coating for enhancing shelf-life of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 103, 581–586 (2017)
S. Md Nor, P. Ding, Trends and advances in edible biopolymer coating for tropical fruit: A review. Food Res. Int. 134, 1–17 (2020)
M.S.M. Basri, N.N. Abdul Karim Shah, A. Sulaiman, I.S. Mohamed Amin Tawakkal, M.Z. Mohd Nor, S.H. Ariffin, N.H. Abdul Ghani, F.S. Mohd Salleh, Progress in the valorization of fruit and vegetable wastes: Active packaging, biocomposites, by-products, and innovative technologies used for bioactive compound extraction. Polymers. 13(20), 1–37 (2021)
B. Marelli, M.A. Brenckle, D.L. Kaplan, F.G. Omenetto, Silk Fibroin as edible coating for perishable food preservation. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–11 (2016)
J.L. Valenzuela, S. Manzano, F. Palma, F. Carvajal, D. Garrido, M. Jamilena, Oxidative stress associated with chilling injury in immature fruit: Postharvest technological and biotechnological solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18(7), 1–26 (2017)
D.N. Rockwood, R.C. Preda, T. Yücel, X. Wang, M.L. Lovett, D.L. Kaplan, Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 6(10), 1–43 (2011)
J.H. Park, S. Choi, H.C. Moon, H. Seo, J.Y. Kim, S. Hong, B.S. Lee, E. Kang, J. Lee, D.H. Ryu, I.S. Choi, Antimicrobial spray nanocoating of supramolecular Fe(III)-tannic acid metal-organic coordination complex: Applications to shoe insoles and fruits. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 3–9 (2017)
A.T.K. Soon, P. Ding, A review on wild indigenous eggplant, terung asam sarawak (Solanum lasiocarpum Dunal.). Sains Malaysiana. 50(3), 595–603 (2021)
R.R. Mallepally, M.A. Marin, M.A. McHugh, CO2-assisted synthesis of silk fibroin hydrogels and aerogels. Acta Biomater. 10(10), 4419–4424 (2014)
N. Azarakhsh, A. Osman, H.M. Ghazali, C.P. Tan, N. Mohd Adzahan, Optimization of alginate and gellan-based edible coating formulations for fresh-cut pineapples. Int. Food Res. J. 19(1), 279–285 (2012)
H. Zhang, L. Li, F. Dai, H. Zhang, B. Ni, W. Zhou, X. Yang, Y. Wu, Preparation and characterization of silk fibroin as a biomaterial with potential for drug delivery. J. Transl. Med. 10(1), 1–9 (2012)
D.S. Çirkin, M. Yüksek, Fibroin nanofibers production by electrospinning method. Turkish J. Chem. 45(4), 1279–1298 (2021)
T.M. Bawazeer, M.S. Alsoufi, Surface characterization and properties of raw and degummed (Bombyx mori) silk fibroin fiber toward high performance applications of ‘Kisswa Al- Kabba. Int. J. Curr. Res. 9(3), 48335–48343 (2017)
Y. Qi, H. Wang, K. Wei, Y. Yang, R. Zheng, I.S. Kim, K. Zhang, A review of structure construction of silk fibroin biomaterials from single structures to multi-level structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18(3), 1–21 (2017)
G.H. Darshan, D. Kong, J. Gautrot, S. Vootla, Physico-chemical characterization of Antheraea mylitta silk mats for wound healing applications. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–11 (2017)
M. K. Sah, K. Pramanik, Regenerated silk fibroin from B. mori silk cocoon for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 1(5), 404–408 (2010)
M.H. Hamzah, S. Bowra, P. Cox, Effects of ethanol concentration on organosolv lignin precipitation and aggregation from Miscanthus x giganteus. Processes. 8(7), 1–16 (2020)
M.H. Hamzah, S. Bowra, M.J.H. Simmons, P.W. Cox, The impact of process parameters on the purity and chemical properties of lignin extracted from Miscanthus x giganteus using a modified organosolv method. 24th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, 1754–1759 (2016)
X.M. Zhang, P. Wyeth, Using FTIR spectroscopy to detect sericin on historic silk. Sci. China Chem. 53(3), 626–631 (2010)
S.W. Ha, A.E. Tonelli, S.M. Hudson, Structural studies of Bombyx mori silk fibroin during regeneration from solutions and wet fiber spinning. Biomacromol 6(3), 1722–1731 (2005)
E. Onelli, A. Ghiani, R. Gentili, S. Serra, S. Musacchi, S. Citterio, Specific changes of exocarp and mesocarp occurring during softening differently affect firmness in melting (MF) and non melting flesh (NMF) fruits. PLoS ONE 10(12), 1–20 (2015)
B. Maringgal, N. Hashim, I.S. Mohamed Amin Tawakkal, M.T. Muda Mohamed, Recent advance in edible coating and its effect on fresh/fresh-cut fruits quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 96, 253–267 (2020)
M. H. Jafarizadeh, A. Osman, C. P. Tan, R. Abdul Rahman, Development of an edible coating based on chitosan-glycerol to delay ‘Berangan’ banana (Musa sapientum cv. Berangan) ripening process. Int. Food Res. J. 18(3), 989–997 (2011)
M.A. Moya-León, E. Mattus-Araya, R. Herrera, Molecular events occurring during softening of strawberry fruit. Front. Plant Sci. 10, 1–11 (2019)
E. Ruggeri, S. Farè, L. De Nardo, B. Marelli, Edible Biopolymers for Food Preservation, in By A. ed. by S.F.P. Technology (Weinheim, Athanassiou (WILEY-VCH GmbH, 2021), pp. 57–105
M. Vidya, S. Rajagopal, Silk fibroin: A promising tool for wound healing and skin regeneration. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 1–10 (2021)
A. Chabbi, M.A. Yallese, I. Meddour, M. Nouioua, T. Mabrouki, F. Girardin, Predictive modeling and multi-response optimization of technological parameters in turning of Polyoxymethylene polymer (POM C) using RSM and desirability function. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 95, 99–115 (2017)
M.S. Muhamad, M.H. Osman, M.Y.R. Nizam Mohamad, N. Mohamed Sunar, R. Ali, N. Hamidon, N.H. Abdul Hamid, H. Harun, Response surface methodology optimization of concrete strength using hydroxyapatite nanopowder as admixture. Prog. Eng. Appl. Technol. 1(1), 134–141 (2020)
T.H. Ong, M.H. Hamzah, H. Che Man, Optimization of palm oil extraction from decanter cake using soxhlet extraction and effects of microwaves pre-treatment on extraction yield and physicochemical properties of palm oil. Food Res. 5, 25–32 (2021)
I. Nashier Gahlawat, Emerging new insights into significance and applications of plant pigments. J. Integr. Sci. Technol., 7(2), 29–34 (2019)
N. Charoenchongsuk, D. Matsumoto, A. Itai, H. Murayama, Ripening characteristics and pigment changes in russeted pear fruit in response to ethylene and 1-MCP. Horticulturae 4(3), 1–14 (2018)
W. Batista-Silva, V.L. Nascimento, D.B. Medeiros, A. Nunes-Nesi, D.M. Ribeiro, A. Zsögön, W.L. Araújo, Modifications in organic acid profiles during fruit development and ripening: Correlation or causation?. Front. Plant Sci. 871, 1–20 (2018)
S.S.M. Al-Qarni, M.D. Bazzi, Date fruit ripening with degradation of chlorophylls, carotenes, and other pigments. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 20(52), 5827–5839 (2020)
N. Alkan, A.M. Fortes, Insights into molecular and metabolic events associated with fruit response to post-harvest fungal pathogens. Front. Plant Sci. 6, 1–14 (2015)
J.B. Adams, H.M. Brown, Discoloration in raw and processed fruits and vegetables. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 47(3), 319–333 (2007)
G.H. de Almeida Teixeira, L.O. Santos, L.C. Cunha Júnior, J.F. Durigan, Effect of carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2) levels on quality of ‘Palmer’ mangoes under controlled atmosphere storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 55(1), 145–156 (2018)
M. Giannelli, V. Lacivita, T. Posati, A. Aluigi, A. Conte, R. Zamboni, M.A. Del Nobile, Silk fibroin and pomegranate by-products to develop sustainable active pad for food packaging applications. Foods. 10, 1–12 (2021)
E. Ruggeri, D. Kim, Y. Cao, S. Farè, L. De Nardo, B. Marelli, A multilayered edible coating to extend produce shelf life. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8(38), 14312–14321 (2020)
X. Zhang, Z. Chen, H. Bao, J. Liang, S. Xu, G. Cheng, Y. Zhu, Fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin/curcumin sustained-release film. Materials. 12, 1–15 (2019)
Z.H. Hassan, S. Lesmayati, R. Qomariah, A. Hasbianto, Effects of wax coating applications and storage temperatures on the quality of tangerine citrus (Citrus reticulata) var. Siam Banjar. Int. Food Res. J. 21(2), 641–648 (2014)
D. Van Hung, S. Tong, F. Tanaka, E. Yasunaga, D. Hamanaka, N. Hiruma, T. Uchino, Controlling the weight loss of fresh produce during postharvest storage under a nano-size mist environment. J. Food Eng. 106 (4), 325–330 (2011)
S. Kokoszka, A. Lenart, Edible coatings -formation, characteristics and use : A review. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 57(4), 399–404 (2007)
N.B. Gol, M.L. Chaudhari, T. V. R. Rao, Effect of edible coatings on quality and shelf life of carambola (Averrhoa carambola L.) fruit during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52(1), 78–91 (2015)
S.K. Amit, M.M. Uddin, R. Rahman, S.M.R. Islam, M.S. Khan, A review on mechanisms and commercial aspects of food preservation and processing. Agric. Food Secur. 6(1), 1–22 (2017)
C. Paniagua, S. Posé, V.J. Morris, A.R. Kirby, M.A. Quesada, J.A. Mercado, Fruit softening and pectin disassembly: An overview of nanostructural pectin modifications assessed by atomic force microscopy. Ann. Bot. 114(6), 1375–1383 (2014)
H.C. Wu, V.P. Bulgakov, T.L. Jinn, Pectin methylesterases: Cell wall remodeling proteins are required for plant response to heat stress. Front. Plant Sci. 871, 1–21 (2018)
K. Rama Krishna, D.V. Sudhakar Rao, Effect of chitosan coating on the physiochemical characteristics of guava (Psidium guajava L.) fruits during storage at room temperature. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 7(5), 554–558 (2014)
P.K. Raghav, N. Agarwal, M. Saini, Edible coating of fruits and vegetables : A review. Int. J. Sci. Mod. Educ. 1(1), 188–204 (2016)
M. Farokhi, F. Mottaghitalab, R.L. Reis, S. Ramakrishna, S.C. Kundu, Functionalized silk fibroin nanofibers as drug carriers: Advantages and challenges. J. Control. Release. 321, 324–347 (2020)
W. Sun, D.A. Gregory, M.A. Tomeh, X. Zhao, Silk fibroin as a functional biomaterial for tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(3), 1–28 (2021)
N.B. Gol, T.V. Ramana Rao, Banana fruit ripening as influenced by edible coatings. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 11(2), 119–135 (2011)
B. Maringgal, N. Hashim, I.S.M.A. Tawakkal, M.T.M. Mohamed, M.H. Hamzah, M.M. Ali, Effect of kelulut honey nanoparticles coating on the changes of respiration rate, ascorbic acid, and total phenolic content of papaya (Carica papaya l.) during cold storage. Foods. 10(2), 1–16 (2021)
T.M.P. Ngo, A. Reungsang, T.H. Nguyen, T.M. Quyen Dang, T.V. Thanh Do, N. Chaiwong, P. Rachtanapun, Effect of pectin/nanochitosan-based coatings and storage temperature on shelf-life extension of ‘Elephant’ mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit. Polymers. 13, 1–22 (2021)
M. Azene, T.S. Workneh, K. Woldetsadik, Effect of packaging materials and storage environment on postharvest quality of papaya fruit. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51(6), 1041–1055 (2014)
K. Vivek, K.V. Subbarao, Effect of edible chitosan coating on combined ultrasound and NaOCl treated kiwi fruits during refrigerated storage. Int. Food Res. J. 25(1), 101–108 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the support and technical facilities from the Department of Agriculture Malaysia, Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Department of Process and Food Engineering, Smart Farming Technology Research Centre, Faculty of Engineering Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Funding
This research was funded by the Geran Putra—Inisiatif Putra Muda (GP-IPM) through Universiti Putra Malaysia Grant (Grant No: GP-IPM/2018/9669700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Muhammad Hazwan Hamzah; Anies Zulaikha Md Rahim and Bernard Maringgal; Formal analysis, Anies Zulaikha Md Rahim; Investigation, Anies Zulaikha Md Rahim; Methodology, Anies Zulaikha Md Rahim and Bernard Maringgal; Supervision, Muhammad Hazwan Hamzah; Bernard Maringgal and Mohd Salahuddin Mohd Basri; Validation, Muhammad Hazwan Hamzah; Bernard Maringgal; Mohd Salahuddin Mohd Basri and Salis Ibrahim; Writing—original draft, Anies Zulaikha Md Rahim and Muhammad Hazwan Hamzah; Writing—review and editing, Bernard Maringgal; Mohd Salahuddin Mohd Basri and Salis Ibrahim. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Muhammad Hazwan Hamzah declares that he has no conflict of interest. Anies Zulaikha Md Rahim declares that she has no conflict of interest. Bernard Maringgal declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mohd Salahuddin Mohd Basri declares that he has no conflict of interest. Salis Ibrahim declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamzah, M.H., Rahim, A.Z.M., Maringgal, B. et al. Optimization of silk fibroin coating during storage using response surface methodology and its effect on the physicochemical properties of Solanum ferox (S. ferox). Food Measure 16, 3385–3401 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01448-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01448-5