Abstract
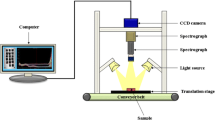
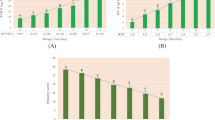
In this study, deep learning method coupled with near-infrared (NIR) hyperspectral imaging (HSI) technique was used for nondestructively determining total viable count (TVC) of peeled Pacific white shrimp. Firstly, stacked auto-encoders (SAE) was conducted as a big data analytical method to extract 20 deep hyperspectral features from NIR hyperspectral image (900–1700 nm) of peeled shrimp stored at 4 °C, and the extracted features were used to predict TVC by fully-connected neural network (FNN). The SAE–FNN method obtained high prediction accuracy for determining TVC, with R 2P = 0.927. Additionally, TVC spatial distribution of peeled shrimp during storage could be visualized via applying the established SAE–FNN model. The results demonstrate that SAE–FNN combined with HSI technique has a potential for non-destructive prediction of TVC in peeled shrimp, which supply a novel method for the hygienic quality and safety inspections of shrimp product.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Valdimarsson, H. Einarsson, B. Gudbjörnsdottir, H. Magnusson, Microbiological quality of Icelandic cooked-peeled shrimp (Pandalus borealis). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 45(2), 157–161 (1998)
X. Carrión-Granda, I. Fernández-Pan, I. Jaime, J. Rovira, J.I. Maté, Improvement of the microbiological quality of ready-to-eat peeled shrimps (Penaeus vannamei) by the use of chitosan coatings. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 232, 144–149 (2016)
L. Huang, J. Zhao, Q. Chen, Y. Zhang, Rapid detection of total viable count (TVC) in pork meat by hyperspectral imaging. Food Res. Int. 54, 821–828 (2013)
H. Duan, R. Zhu, X. Yao, E. Lewis, Sensitive variables extraction, non-destructive detection and visualization of total viable count (TVC) and pH in vacuum packaged lamb using hyperspectral imaging. Anal. Methods 9(21), 3172–3183 (2017)
F. Tao, Y. Peng, C.L. Gomes, K. Chao, J. Qin, A comparative study for improving prediction of total viable count in beef based on hyperspectral scattering characteristics. J. Food Eng. 162, 38–47 (2015)
D. Wu, D.W. Sun, Potential of time series-hyperspectral imaging (TS-HSI) for non-invasive determination of microbial spoilage of salmon flesh. Talanta 111, 39–46 (2013)
J.H. Cheng, D.W. Sun, Rapid and non-invasive detection of fish microbial spoilage by visible and near infrared hyperspectral imaging and multivariate analysis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 62, 1060–1068 (2015)
Z.E. Sikorski, A. Kolakowska, J.R. Burt, Postharvest biochemical and microbial changes, in Seafood: Resources, Nutritional Composition and Preservation, ed. by Z.E. Sikorski (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1990), pp. 55–76
Q. Dai, D.W. Sun, Z. Xiong, J.H. Cheng, X.A. Zeng, Recent advances in data mining techniques and their applications in hyperspectral image processing for the food industry. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 13, 891–905 (2014)
G. ElMasry, D.W. Sun, P. Allen, Non-destructive determination of water-holding capacity in fresh beef by using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Food Res. Int. 44(9), 2624–2633 (2011)
D. Wu, H. Shi, Y. He, X. Yu, Y. Bao, Potential of hyperspectral imaging and multivariate analysis for rapid and non-invasive detection of gelatin adulteration in prawn. J. Food Eng. 119(3), 680–686 (2013)
M. Kamruzzaman, G. ElMasry, D.W. Sun, P. Allen, Nondestructive assessment of instrumental and sensory tenderness of lamb meat using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Food Chem. 141(1), 389–396 (2013)
Y. Roggo, A. Edmond, P. Chalus, M. Ulmschneider, Infrared hyperspectral imaging for qualitative analysis of pharmaceutical solid forms. Anal. Chim. Acta 535, 79–87 (2005)
Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, G.E. Hinton, Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015)
W. Zhao, Z. Guo, J. Yue, X. Zhan, L. Luo, On combining multiscale deep learning features for the classification of hyperspectral remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 36(13), 3368–3379 (2015)
J. Yang, Y.Q. Zhao, J.C.W. Chan, Learning and transferring deep joint spectral–spatial features for hyperspectral classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 55, 4729–4742 (2017)
X. Yu, L. Tang, X. Wu, H. Lu, Nondestructive freshness discriminating of shrimp using visible/near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technique and deep learning algorithm. Food Anal. Meth. 11(3), 768–780 (2017)
H.I. Suk, S.W. Lee, D. Shen, Latent feature representation with stacked auto-encoder for AD/MCI diagnosis. Brain Struct. Funct. 220(2), 841–859 (2015)
E. Biganzoli, P. Boracchi, L. Mariani, E. Marubini, Feed forward neural networks for the analysis of censored survival data: a partial logistic regression approach. Stat. Med. 17(10), 1169–1186 (1998)
A. Rady, N. Ekramirad, A.A. Adedeji, M. Li, R. Alimardani, Hyperspectral imaging for detection of codling moth infestation in GoldRush apples. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 129, 37–44 (2017)
S. Wold, M. Sjostrom, L. Eriksson, PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 58, 109–130 (2001)
F. Pedregosa, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, V. Michel, B. Thirion, O. Grisel, M. Blondel, P. Prettenhofer, R. Weiss, V. Dubourg, J. Vanderplas, A. Passos, D. Cournapeau, M. Brucher, M. Perrot, É. Duchesnay, Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
J.A.K. Suykens, J. De Brabanter, L. Lukas, J. Vandewalle, Weighted least squares support vector machines: robustness and sparse approximation. Neurocomputing. 48, 85–105 (2002)
C. Tao, H. Pan, Y. Li, Z. Zou, Unsupervised spectral–spatial feature learning with stacked sparse autoencoder for hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 12(12), 2438–2442 (2015)
L. Huang, L. Wang, Accelerated Monte Carlo simulations with restricted Boltzmann machines. Phys. Rev. B (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.95.035105
C. Xing, L. Ma, X. Yang, Stacked denoise autoencoder based feature extraction and classification for hyperspectral images. J. Sens. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3632943
K. Gopalakrishnan, S.K. Khaitan, A. Choudhary, A. Agrawal, Deep convolutional neural networks with transfer learning for computer vision-based data-driven pavement distress detection. Constr. Build. Mater. 157, 322–330 (2017)
F. Chollet, Keras: theano-based deep learning library. https://github.com/fchollet. Accessed 4 Sept 2018
R.A.V. Rossel, R.N. McGlynn, A.B. McBratney, Determining the composition of mineral-organic mixes using UV-vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 137, 70–82 (2006)
H. Mu, H. Chen, X. Fang, J. Mao, H. Gao, Effect of cinnamaldehyde on melanosis and spoilage of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 92, 2177–2182 (2012)
A. Cadun, S. Cakli, D. Kisla, A study of marination of deepwater pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris, Lucas, 1846) and its shelf life. Food Chem. 90, 53–59 (2005)
D. Wu, H. Shi, S. Wang, Y. He, Y. Bao, K. Liu, Rapid prediction of moisture content of dehydrated prawns using online hyperspectral imaging system. Anal. Chim. Acta 726, 57–66 (2012)
I. Murray, P.C. Williams, Chemical principles of near-infrared technology, in Near-infrared Technology in the Agricultural and Food Industries, 2nd edn., ed. by P.C. Williams, K. Norris (American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul, 2001), pp. 23–26
S.C. Flores, D.L. Crawford, Postmortem quality changes in iced Pacific shrimp (Pandalus jordani). J. Food Sci. 38(4), 575–579 (1973)
D.F. Barbin, G. ElMasry, D.W. Sun, P. Allen, N. Morsy, Non-destructive assessment of microbial contamination in porcine meat using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 17, 180–191 (2013)
W. Huang, G. Song, H. Hong, K. Xie, Deep architecture for traffic flow prediction: deep belief networks with multitask learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 15(5), 2191–2201 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Ningbo Science and Technology Special Project of China, Grant Number (2017C110002); Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant Number (31201446); Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, under the following Grant Numbers (LY17C190008, LY16F030012 and LY15F030016); Ningbo Science Foundation of China, Grant Number (2017A610118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Yu, X., Wen, S. et al. Using deep learning and hyperspectral imaging to predict total viable count (TVC) in peeled Pacific white shrimp. Food Measure 13, 2082–2094 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00129-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00129-0