Abstract
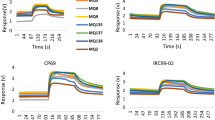
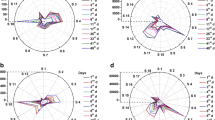
Mango (M. indica cv. Datainong) fruit quality rapid determination method based on electronic nose (E-nose) was investigated in this research. E-nose responses to mangoes stored at room temperature were examined for 9 days. Meanwhile, physicochemical and microbiological indexes including firmness, weight loss, surface colour, yellowing rate, pH, total soluble solids, polyphenol oxidase activity and total viable counts were measured to provide quality references for E-nose analysis. Principal component analysis (PCA) and stochastic resonance (SR) were utilized for E-nose data analysis. Results indicated that mango fruit quality decreased sharply during storage. PCA just allowed qualitative quality discrimination, while SNR spectrum using eigen values successfully characterized mango quality. Mango quality predictive model was developed by linear fitting SR eigen values. Validation experiment results demonstrated that the forecasting accuracy of the developed model reached 90%.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Cheema, M. Sommerhalter, Characterization of polyphenol oxidase activity in Ataulfo mango. Food. Chem. 171, 382–387 (2015)
D.S. Sogi, M. Siddiq, K.D. Dolan, Total phenolics, carotenoids and antioxidant properties of Tommy Atkin mango cubes as affected by drying techniques. LWT Food Sci. Tech. 62(1), 564–568 (2015)
D. Prusky, N.T. Keen, Involvement of preformed antifungal compounds and the resistance of subtropical fruits to fungal decay. Plant Dis. 77, 114–119 (1993)
P.E. Zerbini, M. Vanoli, A. Rizzolo, M. Grassi, R.M. de Azevedo Pimentel, L. Spinelli, A. Torricelli, Optical properties, ethylene production and softening in mango fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 101, 58–65 (2015)
X.L. Zheng, L.B. Ye, T.J. Jiang, G.X. Jing, J.R. Li, Limiting the deterioration of mango fruit during storage at room temperature by oxalate treatment. Food Chem. 130, 279–285 (2012)
K. Liu, X.L. Wang, M. Young, Effect of bentonite/potassium sorbate coatings on the quality of mangos in storage at ambient temperature. J. Food Eng. 137, 16–22 (2014)
P. Anusuya, R. Nagaraj, G.J. Janavi, K.S. Subramanian, G. Paliyath, J. Subramanian, Pre-harvest sprays of hexanal formulation for extending retention and shelf-life of mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruits. Sci. Hortic. 211, 231–240 (2016)
R. Desrochers, P. Keane, S. Ellis, K. Dowell, Expanding the sensitivity of conventional analytical techniques in quality control using sensory technology. Food Qual. Prefer. 13, 397–407 (2002)
Y.W. Tang, Z.Y. Gao, S. Wang, X. Gao, J.W. Gao, Y. Ma, X.Y. Liu, J.R. Li, Upconversion particles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers as fluorescence probe for detection of clenbuterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 71, 44–50 (2015)
N.C.T. Mariani, R.C. da Costa, K.M.G. de Lima, V. Nardini, L.C.C. Júnior, G.H. de Almeida Teixeira, Predicting soluble solid content in intact jaboticaba [Myrciaria jaboticaba (Vell.) O. Berg] fruit using near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Chem. 159, 458–462 (2014)
A. Campagnoli, V. Dell’Orto, Potential application of electronic olfaction systems in feedstuffs analysis and animal nutrition. Sensors 13, 14611–14632 (2013)
M. Peris, L. Escuder-Gilabert, On-line monitoring of food fermentation processes using electronic noses and electronic tongues: a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 804, 29–36 (2013)
K. Persaud, G.H. Dodd, Analysis of discrimination mechanisms in the mammalian olfactory system using a model nose. Nature 299, 352–355 (1982)
J. Gardner, P. Bartlett, Electronic Noses, Principles and Applications. (Oxford University Press, New York, 1999)
J.S. Vestergaard, M. Martens, P. Turkki, Analysis of sensory quality changes during storage of a modified atmosphere packaged meat product (pizza topping) by an electronic nose system. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 40(6), 1083–1094 (2007)
X.J. Tian, J. Wang, S.Q. Cui, Analysis of pork adulteration in minced mutton using electronic nose of metal oxide sensors. J. Food Eng. 119(4), 744–749 (2013)
R. Paolesse, A. Alimelli, E. Martinelli, C.D. Natale, A. D’Amico, M.G. D’Egidio, G. Aureli, A. Ricelli, C. Fanelli, Detection of fungal contamination of cereal grain samples by an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B 119(2), 425–430 (2006)
J. Perkowski, M. Buśko, J. Chmielewski, T. Góral, B. Tyrakowska, Content of trichodiene and analysis of fungal volatiles (electronic nose) in wheat and triticale grain naturally infected and inoculated with Fusarium culmorum. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 126, 127–134 (2008)
A.K.G. Kadegowda, L.S. Piperova, R.A. Erdman, Principal component and multivariate analysis of milk long-chain fatty acid composition during diet induced milk fat depression. J. Dairy Sci. 91, 749–759 (2008)
P. Verma, R.D.S. Yadava, Polymer selection for SAW sensor array based electronic noses by fuzzy c-means clustering of partition coefficients: model studies on detection of freshness and spoilage of milk and fish. Sens. Actuators B 209, 751–769 (2015)
L.R. Xu, X.Z. Yu, L. Liu, R. Zhang, A novel method for qualitative analysis of edible oil oxidation using an electronic nose. Food. Chem. 202, 229–235 (2016)
Y. Asikin, G. Maeda, H. Tamaki, M. Mizu, H. Oku, K. Wada, Cultivation line and fruit ripening discriminations of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) peel oils using aroma compositional, electronic nose, and antioxidant analyses. Food Res. Int. 67, 102–110 (2015)
L.Q. Pan, W. Zhang, N. Zhu, S.B. Mao, K. Tu, Early detection and classification of pathogenic fungal disease in post-harvest strawberry fruit by electronic nose and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 62, 162–168 (2014)
H.X. Wang, Z.Q. Hu, F.Y. Long, C.F. Guo, Y.H. Yuan, T.L. Yue, Early detection of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii—spawned spoilage in apple juice by electronic nose combined with chemometrics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 217, 68–78 (2016)
NY/T 2637, Refractometric method for determination of total soluble solids in fruits and vegetables (2014)
Y.S. Wang, S.P. Tian, Y. Xu, G.Z. Qin, H.J. Yao, Changes in the activities of pro- and anti-oxidant enzymes in peach fruit inoculated with Cryptococcus laurentii or Penicillium expansum at 0 or 20 °C. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 34, 21–28 (2004)
GB 4789.2., National food safety standard: food microbiological examination: aerobic plate count (2010)
R. Benzi, A. Sutera, A. Vulpiani, The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J. Phys. A 14(11), L453–L456 (1981)
J.J. Collins, C.C. Chow, T.T. Imhoff, Aperiodic stochastic resonance in excitable systems. Phys. Rev. E 52(4), 3321–3324 (1995)
C. Heneghan, C.C. Chow, J.J. Collins, T.T. Imhoff, S.B. Lowen, M.C. Teich, Information measures quantifying aperiodic stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. E 54(3), 2228–2231 (1996)
G.B. Seymour, J.E. Taylor, G.A. Tucker, Biochemistry of Fruit Ripening. (Chapman & Hall, London, 1993)
V.E. Nambi, K. Thangavel, K.A. Rajeswari, A. Manickavasagan, V. Geetha, Texture and rheological changes of Indian mango cultivars during ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 117, 152–160 (2016)
F. Charles, V. Vidal, F. Olive, H. Filgueiras, H. Sallanon (2013) Pulsed light treatment as new method to maintain physical and nutritional quality of fresh-cut mangoes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 18, 190–195
B. Salinas-Roca, R. Soliva-Fortuny, J. Welti-Chanes, O. Martín-Belloso, Combined effect of pulsed light, edible coating and malic acid dipping to improve fresh-cut mango safety and quality. Food Control 66, 190–197 (2016)
X.B. Xu, H.H. Lei, X.Y. Ma, T.F. Lai, H.M. Song, X.Q. Shi, J.K. Li, Antifungal activity of 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) against anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) inpostharvestmangofruit and its possible mechanisms of action. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 241, 1–6 (2017)
M.-J. Kim, C.H. Tang, W.S. Bang, H.-G. Yuk, Antibacterial effect of 405 ± 5 nm light emitting diode illumination against Escherichia coli O157:H7, Listeria monocytogenes, and Salmonella on the surface of fresh-cut mango and its influence on fruit quality. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 244, 82–89 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2017C31010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Hui Guohua has received research grant from Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2017C31010).
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
(If not applicable on the study) Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lihuan, S., Liu, W., Xiaohong, Z. et al. Fabrication of electronic nose system and exploration on its applications in mango fruit (M. indica cv. Datainong) quality rapid determination. Food Measure 11, 1969–1977 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9579-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9579-1