Abstract
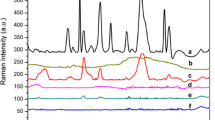
This study reports the feasibility of citrate-reduced colloidal silver surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) for differentiating three important food borne pathogens, E. coli, Listeria, and Salmonella. FT-Raman and SERS spectra of both silver colloids and colloid-K3PO4 mixtures were collected and analyzed to evaluate the reproducibility and stability of silver colloids fabricated in a batch-production process. The results suggest that the reproducibility of the colloids over the batch process is high and that their binding effectiveness remains consistent over a 60-day storage period. Two specific SERS bands at 712 and 390 cm−1 were identified and used to develop simple 2-band ratios for differentiating E. coli-, Listeria-, and Salmonella-colloid mixtures with a 100% success. These results indicate that colloidal silver SERS technique may be a practical alternative method suitable for routine and rapid screening of E. coli, Listeria, and Salmonella bacteria.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Moskovits, Rev. Mod. Phys. 57, 783 (1985). doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.57.783
E. Podstawka, Y. Ozaki, L.M. Proniewicz, Appl. Spectrosc. 58, 570 (2004). doi:10.1366/000370204774103408
S. Farquharson, A. Gift, P. Maksymiuk, F. Inscore, Appl. Spectrosc. 59, 654 (2005). doi:10.1366/0003702053946100
J.C. Hoogvliet, M. Dijksma, B. Kamp, W.P. van Bennekom, Anal. Chem. 72, 2016 (2000)
L.A. Lyon, M.D. Musick, M.J. Natan, Anal. Chem. 70, 5177 (1998). doi:10.1021/ac9809940
R.M. Jarvis, R. Goodacre, Anal. Chem. 76, 40 (2004). doi:10.1021/ac034689c
M.L. Laucks, A. Sengupta, K. Junge, E.J. Davis, B.D. Swanson, Appl. Spectrosc. 59, 1222 (2005). doi:10.1366/000370205774430891
L. Zeiri, B.V. Bronk, Y. Shabtai, J. Czege, S. Efrima, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 208, 357 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(02)00162-0
H. Li, B.M. Cullum, Appl. Spectrosc. 59, 410 (2005). doi:10.1366/000370205775142593
S. Shanmukh, L. Jones, J. Driskell, Y. Zhao, R. Dluhy, R.A. Tripp, Nano. Lett. 6, 2630 (2006). doi:10.1021/nl061666f
R. Keir, D. Sadler, W.E. Smith, Appl. Spectrosc. 56, 551 (2002). doi:10.1366/0003702021955259
Y. Liu, Y.R. Chen, X. Nou, X.K. Chao, Appl. Spectrosc. 61, 824 (2007). doi:10.1366/000370207781540060
C.A. Batt, in Listeria, Listeriosis, and Food Safety, 2nd edn., ed. by T. Ryser, E.H. Marth (Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1999), pp. 261–278
T. Geng, J. Uknalis, S.I. Tu, A.K. Bhunia, Sensors 6, 796 (2006). doi:10.3390/s6080796
P.C. Lee, D. Meisel, J. Phys. Chem. 86, 3391 (1982). doi:10.1021/j100214a025
W. Ke, D. Zhou, J. Wu, J.,K. Ji, Appl. Spectrosc. 59, 418 (2005)
J. Baran, T. Lis, H. Ratajczak, J. Mol. Struct. 195, 159 (1989). doi:10.1016/0022-2860(89)80166-8
H. Tsuda, J. Arends, J. Dent. Res. 72, 1609 (1993)
X. Li, W. Xu, H. Jia, X. Wang, B. Zhao, B. Li, Y. Ozaki, Appl. Spectrosc. 58, 26 (2004). doi:10.1366/000370204322729432
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Chao, K., Nou, X. et al. Feasibility of colloidal silver SERS for rapid bacterial screening. Sens. & Instrumen. Food Qual. 3, 100–107 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-008-9064-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-008-9064-y