Abstract
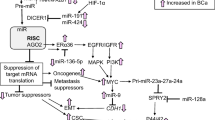
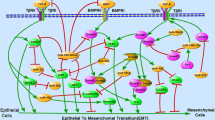
Breast cancer metastasis is a complex and still weakly understood process that involves diverse cellular pathways. It accounts for the majority of deaths from breast cancer. Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs), small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally, have been shown to be involved in breast cancer metastasis. In particular, in a recent work it has been found that miR-429 may have a role in the inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Its target gene CRKL has been identified as a potential candidate. In this paper, by using systems biology tools we have shown that CRKL is involved in positive regulation of ERK1/2 signaling pathway and contribute to the regulation of LYN through a topological generalization of feed forward loop.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
IntAct is one of the largest available repositories for curated molecular interactions data, storing PPIs as well as interactions involving other molecules. It is hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute. IntAct has evolved into a multisource curation platform and many other databases curate into IntAct and make their data available through it (Sandra et al. 2014).
References
Alon U (2007) An introduction to systems biology design principles of biological circuits. Chapman & Hall/CRC, London
Bylgja H, Eirikur B, Jon Thor B, Magnus Karl M, Thorarinn G (2014) Functional role of the microRNA-200 family in breast morphogenesis and neoplasia. Genes 5:804–820
Emily SB, Morag P (2012) Models of crk adaptor proteins in cancer. Genes Cancer 3(5–6):341–352
Fathers K, Bell E, Rajadurai C, Cory S, Zhao H, Mourskaia A, Zuo D, Madore J, Monast A, Mes-Masson A, Grosset A, Gaboury L, Hallet M, Siegel P, Park M (2012) Crk adaptor proteins act as key signaling integrators for breast tumorigenesis. Breast Cancer Res 14(3):R74
Ganapathy S, Raymond BB (2010) Emerging roles for crk in human cancer. Genes Cancer 1(11):1132–1139
Hui G, Zhichao Z, Gary EG, Shu-Fang J, Jaime M, Anil KS, Seth JC, Eugenie SK (2008) Targeting LYN inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in Ewing’s sarcoma. Mol Cancer Ther 7(7):1807–1816
Ingley E (2012) Functions of the LYN tyrosine kinase in health and disease. Cell Commun Signal 10(1):21
Jun L, Gad G, Eric AM, Ezequiel A-S, Justin L, David P, Alejandro S-C, Benjamin LE, Raymond HM, Adolfo AF, James RD, Tyler J (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838
Lee R, Feinbaum R, Ambros V (1993) The c. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small rnas with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843
Li L, Zhang C, Liu L, Yi C, Lu S, Zhou X, Zhang Z, Peng Y, Yang Y, Yun J (2014) mir-720 inhibits tumor invasion and migration in breast cancer by targeting twist1. Carcinogenesis 35(2):469–78
Maere S, Heymans K, Kuiper M (2005) BiNGO: a cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics 21:3448–3449
Malik Y, Jens A (eds) (2014) miRNomics: microRNA biology and computational analysis. Springer, London
Manav K, sther SL, Guohong H, Yibin K (2008) The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283(22):14910–14914
Masood u R K, Mahmood AK, Faraz AM, Faryal R (2011) Role of miRNAs in breast cancer. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev 12:3175–3180
Olivia JS, Boon-Huat B, George Y, Yingnan Y (2012) Breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 9:311–320
Sandra O, Mais A, Bruno A, Lionel B, Leonardo B, Fiona B-C, Nancy HC, Gayatri C, Carol C, Noemi d-T, Margaret D, Marine D, Eugenia G, Ursula H, Marta I, Sruthi J, Rafael J, Jyoti K, Astrid L, Luana L, Ruth C,L, Birgit M, Anna N,M, Mila M, Daniele P, Livia P, Pablo P, Arathi R, Sylvie R-B, Bernd R, Andre S, Michael T, Kim v R, Gianni C, Henning H (2014) The MIntAct project-IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D358–D363
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga N, Wang J, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504
Stefanie S, Eric AM, Carlos C (2008) MicroRNA—implications for cancer. Virchows Archiv 452:1–10
Sun-Mi P, Arti BG, Ernst L, Marcus EP (2008) The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 22:894–907
Tsuda M, Tanaka S (2012) Roles for crk in cancer metastasis and invasion. Genes Cancer 3(5–6):334–340
Victoria JF (2010) MicroRNAs and breast cancer. Open Cancer J 3:55–61
Vlachos IS, Paraskevopoulou MD, Karagkouni D, Georgakilas G, Vergoulis T, Kanellos I, Anastasopoulos IL, Maniou S, Karathanou K, Kalfakakou D, Fevgas A, Dalamagas T, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2015) DIANA-TarBase v7.0: indexing more than half a million experimentally supported miRNA:mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D153–D159
Wang C, Bian Z, Wei D, JG Z (2011) mir-29b regulates migration of human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 352:197–207
Wen-Sheng W, Chi-Tan H (eds) (2010) Signal transduction in cancer metastasis. Springer, London
Ye Z, Ma G, Zhao Y, Xiao Y, Zhan Y, Jing C, Gao K, Liu Z, SJ Y (2015) mir-429 inhibits migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro. Int J Oncol 46(2):531–538
Yoon-La C, Melanie B, Mi JK, Young KS, Seok JN, Jung-Hyun Y, Jessica K, Andrew KG, Jonathan RP (2010) LYN is a mediator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and target of dasatinib in breast cancer. Cancer Res 70(6):2296–2306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chafik, A. The role of CRKL in breast cancer metastasis: insights from systems biology. Syst Synth Biol 9, 141–146 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-015-9180-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-015-9180-z