Abstract
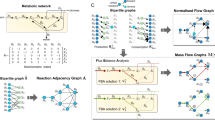
Metabolism forms an integral part of all cells and its study is important to understand the functioning of the system, to understand alterations that occur in disease state and hence for subsequent applications in drug discovery. Reconstruction of genome-scale metabolic graphs from genomics and other molecular or biochemical data is now feasible. Few methods have also been reported for inferring biochemical pathways from these networks. However, given the large scale and complex inter-connections in the networks, the problem of identifying biochemical routes is not trivial and some questions still remain open. In particular, how a given path is altered in perturbed conditions remains a difficult problem, warranting development of improved methods. Here we report a comparison of 6 different weighting schemes to derive node and edge weights for a metabolic graph, weights reflecting various kinetic, thermodynamic parameters as well as abundances inferred from transcriptome data. Using a network of 50 nodes and 107 edges of carbohydrate metabolism, we show that kinetic parameter derived weighting schemes \(\left[ {\left( {\frac{{K_{M}^{S} }}{{ K_{M}^{P } }}} \right){\text{ and }}\left( { \frac{{K_{M} }}{{K_{cat} }} } \right)} \right]\) fare best. However, these are limited by their extent of availability, highlighting the usefulness of omics data under such conditions. Interestingly, transcriptome derived weights yield paths with best scores, but are inadequate to discriminate the theoretical paths. The method is tested on a system of Escherichia coli stress response. The approach illustrated here is generic in nature and can be used in the analysis for metabolic network from any species and perhaps more importantly for comparing condition-specific networks.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña V, Ferreira C, Freire A, Moreno E (2011) Solving the maximum edge biclique packing problem on unbalanced bipartite graphs. Discret Appl Math. doi:10.1016/j.dam.2011.09.019
Aittokallio T, Schwikowski B (2006) Graph-based methods for analysing networks in cell biology. Brief Bioinform 7(3):243–255
Arita M (2012) From metabolic reactions to networks and pathways. Bact Mol Netw, Springer 804:93–106
Batenkov D (2011) Boosting productivity with the boost graph library. XRDS Crossroads ACM Mag Stud 17(3):31–32
Cornish-Bowden A, Cárdenas ML (2003) Metabolic analysis in drug design. C R Biol 326(5):509–515
Croes D, Couche F, Wodak SJ, van Helden J (2005) Metabolic PathFinding: inferring relevant pathways in biochemical networks. Nucleic Acids Res 33(suppl 2):W326–W330
Croes D, Couche F, Wodak SJ, van Helden J (2006) Inferring meaningful pathways in weighted metabolic networks. J Mol Biol 356(1):222–236
Dreyfuss JM, Zucker JD, Hood HM, Ocasio LR, Sachs MS, Galagan JE (2013) Reconstruction and validation of a genome-scale metabolic model for the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa using FARM. PLoS Comput Biol 9(7):e1003126
Flight MH (2010) Drug screening: shifting energy metabolism. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(4):272
Floyd RW (1962) Algorithm 97: shortest path. Commun ACM 5(6):345
Gleich DF (2009) Models and algorithms for pagerank sensitivity. Stanford University
Hawick KA (2011) Applying enumerative, spectral and hybrid graph analyses to biological network data. Small 15:16
Ideker T, Thorsson V, Ranish JA, Christmas R, Buhler J, Eng JK, Bumgarner R, Goodlett DR, Aebersold R, Hood L (2001) Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of a systematically perturbed metabolic network. Science 292(5518):929–934
Ideker T, Ozier O, Schwikowski B, Siegel AF (2002) Discovering regulatory and signalling circuits in molecular interaction networks. Bioinformatics 18(suppl 1):S233–S240
Jozefczuk S, Klie S, Catchpole G, Szymanski J, Cuadros-Inostroza A, Steinhauser D, Selbig J, Willmitzer L (2010) Metabolomic and transcriptomic stress response of Escherichia coli. Mol Syst Biol 6:364
Kayser A, Weber J, Hecht V, Rinas U (2005) Metabolic flux analysis of Escherichia coli in glucose-limited continuous culture. I. Growth-rate-dependent metabolic efficiency at steady state. Microbiology 151(3):693–706
Liebermeister W, Klipp E (2006) Bringing metabolic networks to life: integration of kinetic, metabolic, and proteomic data. Theor Biol Med Model 3(1):42
Ma’ayan A (2009) Insights into the organization of biochemical regulatory networks using graph theory analyses. J Biol Chem 284(9):5451–5455
Mavrovouniotis ML (1990) Group contributions for estimating standard gibbs energies of formation of biochemical compounds in aqueous solution. Biotechnol Bioeng 36(10):1070–1082
Milo R, Jorgensen P, Moran U, Weber G, Springer M (2010) BioNumbers—the database of key numbers in molecular and cell biology. Nucleic Acids Res 38(suppl 1):D750–D753
Noirel J, Ow SY, Sanguinetti G, Jaramillo A, Wright PC (2008) Automated extraction of meaningful pathways from quantitative proteomics data. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 7(2):136–146
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono H, Kanehisa M (1999) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 27(1):29–34
Palsson B (2000) The challenges of in silico biology. Nat Biotechnol 18(11):1147–1150
Pitkänen E, Jouhten P, Rousu J (2009) Inferring branching pathways in genome-scale metabolic networks. BMC Syst Biol 3(1):103
Scheer M, Grote A, Chang A, Schomburg I, Munaretto C, Rother M, Söhngen C, Stelzer M, Thiele J, Schomburg D (2011) BRENDA, the enzyme information system in 2011. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl 1):D670–D676
Scott MS, Perkins T, Bunnell S, Pepin F, Thomas DY, Hallett M (2005) Identifying regulatory subnetworks for a set of genes. Mol Cell Proteomics 4(5):683–692
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504
Tennant DA, Durán RV, Gottlieb E (2010) Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 10(4):267–277
Verkhedkar KD, Raman K, Chandra NR, Vishveshwara S (2007) Metabolome based reaction graphs of M. tuberculosis and M. leprae: a comparative network analysis. PLoS ONE 2(9):e881
Zien A, Kuffner R, Zimmer R, Lengauer T (2000) Analysis of gene expression data with pathway scores. Proceedings of the 8th international conference intelligent systems molecular biology (ISMB) 8:407–417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Baloni, P., Vishveshwara, S. et al. Weighting schemes in metabolic graphs for identifying biochemical routes. Syst Synth Biol 8, 47–57 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-013-9128-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-013-9128-0