Abstract
Purpose
This comprehensive global meta-analysis reviews the parasitism levels of tick genera and species, life stages, seasonality, attachment sites, the global mean ranks of tick species parasitism rates and records, and their distribution and role as vectors.
Methods
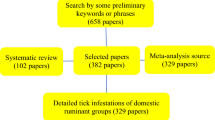
From the 418 papers identified, 390 papers were selected to become part of the study.
Results
The genera recorded as infesting domestic ruminants were Rhipicephalus (42 species), Haemaphysalis (32 species), Hyalomma (19 species), Amblyomma (18 species), Ixodes (10 species), Dermacentor (8 species), Margaropus and Nosomma (1 species). Globally, domestic ruminants are more infested by adult females and males than by the nymphal and larval stages of the tick species. The global tick species parasitism levels at the attachment sites of domestic ruminants were, in order, tail and anal region, neck and dewlap, scrotum or udder, ear region, thigh and abdomen, and dorsal surface.
Conclusions
Among 131 species of eight genera of hard ticks recorded infesting domestic ruminants, 42 species had mean ranks of tick species parasitism rates up to 10%, and 37 species had mean ranks of tick species parasitism up to 10 records. Briefly, the higher the indexes of tick species parasitism rates and records, the more important their role as vectors. In addition, the majority of them are found among tick species-infested humans with nearly high ranks of tick species parasitism rates and records that double their medical, veterinary, and zoonotic importance to be the most common vectors and reservoirs of bacterial, protozoan, and viral pathogenic microorganisms, causing severe infectious diseases, and as a result, can be more dangerous to humans and domestic ruminants.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The author declares that he has satisfy for availability of data and materials online.
References
Abbasi F, Abbasi IHR, Nissa TF, Bhutto ZA, Arain MA, Soomro RN, Siyal FA, Fazlani SA (2017) Epidemiological study of tick infestation in buffalo of various regions of district Khairpur, Pakistan. Vet World 10(6):688–694
Abdela N (2016) Important cattle ticks and tick born haemoparasitic disease in Ethiopia: a review. Acta Parasitol Globalis 7(1):12–20. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.apg.2016.7.1.102140
Abdullah S, Helps C, Tasker S, Newbury H, Wall R (2016) Ticks infesting domestic dogs in the UK: a large-scale surveillance programme. Parasites Vectors 9:391. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1673-4
Abdullahi YM, Magami IM, Audu A, Mainasara MM (2018) Prevalence of ticks on camels and cattle brought to Dodoru Market Kebbi State, Nigeria. Path Sci 4:3001–3004. https://doi.org/10.22178/pos.33-4
Abebe R, Fantahun T, Abera M, Bekele J (2010) Survey of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting cattle in two districts of Somali Regional State, Ethiopia. Vet World 3(12):539–543
Abebe R, Tatek M, Megersa B, Sheferaw D (2011) Prevalence of small ruminant ectoparasites and associated risk factors in selected districts of Tigray region, Ethiopia. Glob Vet 7(5):433–437
Abed MJ, Hasso SA (2019) Molecular detection of Babesia bigemina in ticks infesting water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) in Iraq. Al-Qadisiyah J Vet Med Sci 18(1):15–22
Abera M, Mohammed T, Abebe R, Aragaw K, Bekele J (2010) Survey of ixodid ticks in domestic ruminants in Bedelle district, Southwestern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 42:1677–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9620-4
Abiso M, Yohannes B, Alemu B (2019) Ixodidae ticks of bovine; prevalence and major species identification in Soddo Zuria Districts of Wolaita Zone, Ethiopia. Approaches Poultry Dairy Vet Sci 6(2):APDV.000632. https://doi.org/10.31031/APDV.2019.06.000632
Abunna F, Kasasa D, Shelima B, Megersa B, Regassa A, Amenu K (2009) Survey of tick infestation in small ruminants of Miesso district, West Harergie, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 41:969–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-008-9286-3
Abunna F, Tura J, Regassa A (2012) Status of tick infestation in small ruminants of Bedelle district, Oromia region, Ethiopia. Glob Vet 8(5):459–462
Ahmed BM, El Hussein A, El Khider A (2005) Some observations on ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting sheep in River Nile Province of Northern Sudan. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 72:239–243
Ahmed S, Numan M, Manzoor AW, Ali FA (2012) Investigations into Ixodidae ticks in cattle in Lahore, Pakistan. Vet Ital 48(2):185–191
Aktas M, Dumanli N, Angin M (2004) Cattle infestation by Hyalomma ticks and prevalence of Theileria in Hyalomma species in the east of Turkey. Vet Parasitol 119:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2003.10.013
Aktas M, Altay K, Ozubek S, Dumanli N (2012) A survey of ixodid ticks feeding on cattle and prevalence of tick-borne pathogens in the Black Sea region of Turkey. Vet Parasitol 187:567–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.01.035
Al-Asgah NA, Hussein HS, Al-Khalifa MS, Diab FM (1985) Hyalomma schulzei (the Large Camel Tick): distribution in Saudi Arabia. J Med Entomol 22(2):230–231
Al-Husseini MT (2019) Morphological study of the cattle ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting on sheep in Alnnajaf province-Iraq. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. IOP Publishing, pp 571. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/571/1/012061
Al-Mayah SH, Hatem AN (2018) Species diversity, prevalences and some ecological aspects of Ectoparasites of buffalo Bubalus bubalis in Basrah Province, Iraq. J Entomol Zool Stud 6:390–394
Al-Shaibani IR (2012) Preliminary study on hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) of sheep in some areas of Thamar Governorate, Yemen. Thamar Univ J Nat Appl Sci 5(5):21–31. https://doi.org/10.59167/tujnas.v5i5.1304
Alajmi R, Ayaad T, Al-Harbi H, Shaurub E, Al-Musawi Z (2019) Molecular identification of ticks infesting camels and the detection of their natural infections with Rickettsia and Borrelia in Riyadh province, Saudi Arabia. Trop Biomed 36(3):758–765
Alayande M, Mayaki A, Lawal M, Bandi N, Ibrahim D, Talabi A (2015) Pattern of tick infestation on one humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Sokoto, Nigeria. Bull Anim Health Prod Afr 63:349–354
Ali A, Khan MA, Zahid H, Yaseen PM, Khan MQ, Nawab J, Rehman ZU, Ateeq M, Khan S, Ibrahim M (2019) Seasonal dynamics, record of ticks infesting humans, wild and domestic animals and molecular phylogeny of Rhipicephalus microplus in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Front Physiol 10:793. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00793
AlKhalifa MS, Khalil GM, Diab FM (2007) A two years study of ticks infesting goats and sheep in Abha, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Biol Sci 14:83–91
Amante M, Alelgn Z, Hirpa E (2014) Prevalence of ixodid ticks on cattle in and around Diga Town, West Ethiopia. Eur J Biol Sci 6:25–32. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ejbs.2014.6.01.85154
Amuamuta A, Kassahun A, Fentahun T (2012) Occurrence of small ruminant ectoparasites in and around Bahir Dar, Northwest Ethiopia. Adv Biol Res 6(5):170–176. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.abr.2012.6.5.6628
Anderson K, Ezenwa VO, Jolles AE (2013) Tick infestation patterns in free ranging African buffalo (Syncercus caffer): effects of host innate immunity and niche segregation among tick species. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl 2:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2012.11.002
Asmaa NM, ElBably MA, Shokier KA (2014) Studies on prevalence, risk indicators and control options for tick infestation in ruminants. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 3:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2014.02.009
Asrate S, Yalew A (2012) Prevalence of cattle tick infestation in and around Haramaya district, Eastern Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 4:84–88. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH12.035
Awad A, Abudl-Hussein M (2005) Epidemiological study on the hard ticks of some domestic animals in Basrah. Basrah J Sci 23:93–108
Ayalew T, Hailu Y, Kumsa B (2014) Ixodid ticks infesting cattle in three agroecological zones in central Oromia: species composition, seasonal variation, and control practices. Comp Clin Pathol 23:1103–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-013-1748-y
Aydin MF, Aktas M, Dumanli N (2015) Molecular identification of Theileria and Babesia in ticks collected from sheep and goats in the Black Sea region of Turkey. Parasitol Res 114:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4160-x
Ayele T, Mohammed M, Abrham F (2013) Prevalence and identification of camel ticks in eastern Ethiopia. Online J Vet Res 17:64–72
Bala AE, Abakar AD, Mohammed MS, Mohammed MA, Tigani MAE (2018) Seasonal prevalence and geographical distribution of ticks of camels (Camelus dromedaries) in four states of Great Butana, Sudan. J Entomol Zool Stud 6(3):1212–1220
Balinandi S, Chitimia-Dobler L, Grandi G, Nakayiki T, Kabasa W, Bbira J, Lutwama JJ, Bakkes DK, Malmberg M, Mugisha L (2020) Morphological and molecular identification of ixodid tick species (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting cattle in Uganda. Parasitol Res 119:2411–2420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06742-z
Barghash S, Hafez A, Darwish A, El-Naga T (2016) Molecular detection of pathogens in ticks infesting camels in Matrouh Governorate, Egypt. J Bacteriol Parasitol 7:259. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9597.1000269
Batista HR, Sarturi C, Stelmachtchuk FN, Oliveira DR, Morini AC, Gennari SM, Marcili A, Bastos FAN, Barata LES, Minervino AHH (2018) Prevalence and risk factors associated with ectoparasite infestation of buffaloes in an Amazonian ecosystem. Parasites Vectors 11:335. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2917-2
Batool M, Nasir S, Rafique A, Yousaf I, Yousaf M (2019) Prevalence of tick infestation in farm animals from Punjab, Pakistan. Pak Vet J 39(3):406–410. https://doi.org/10.29261/pakvetj/2019.089
Bayou K, Asegdew A (2017) Prevalence and identification of Ixodid ticks on cattle in Kimbibit district, North Shoa Zone, Ethiopia. Adv Biol Res 11(5):271–277
Bazarusanga T, Geysen D, Vercruysse J, Madder M (2007) An update on the ecological distribution of Ixodid ticks infesting cattle in Rwanda: countrywide cross-sectional survey in the wet and the dry season. Exp Appl Acarol 43:279–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-007-9121-y
Bedada H, Gizaw F, Fekadu G, Negash W (2017) Identification of major ectoparasites infesting sheep in Aba Jima District, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Int J Curr Res Biol Med 2(11):42–29. https://doi.org/10.22192/ijcrbm
Bedasso M, Abebe B, Degefu H (2014) Species composition, prevalence and seasonal variations of ixodid cattle ticks in and around Haramaya town, Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 6(5):131–137. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH2014.0275
Bekele J, Tariku M, Abebe R (2011) External parasites infestations in small ruminants in Wolmera district of Oromia region, central Ethiopia. J Anim Vet Adv 10(4):518–523. https://doi.org/10.3923/javaa.2011.518.523
Beyecha K, Kumsa B, Beyene D (2014) Ectoparasites of goats in three agroecologies in central Oromia, Ethiopia. Comp Clin Pathol 23:21–28
Bibi S, Rafique N, Kareem A, Taj MK, Iqbl K, Bibi A, Shafiq M, Ghafoor G, Ghafoor A, Ijaz A (2020) Prevalence and taxonomic identification of hard ticks (Ixodidea) found in livestock of Harnai District, Balochistan, Pakistan. Pure Appl Biol 9:2330–2338. https://doi.org/10.19045/bspab.2020.90247
Biglari P, Chinikar S, Belqeiszadeh H, Telmadarraiy Z, Mostafavi E, Ghaffari M, Javaherizadeh S, Nowotny N, Fooks AR, Shahhosseini N (2016) Phylogeny of tick-derived Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus strains in Iran. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 7:1216–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2016.07.012
Boka O, Achi L, Adakal H, Azokou A, Yao P, Yapi Y, Kone M, Dagnogo K, Kaboret Y (2017) Review of cattle ticks (Acari, Ixodida) in Ivory Coast and geographic distribution of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, an emerging tick in West Africa. Exp Appl Acarol 71:355–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-017-0129-7
Bouattour A, Darghouth M, Miled LB (1996) Cattle infestation by Hyalomma ticks and prevalence of Theileria in H. detritum species in Tunisia. Vet Parasitol 65(3–4):233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4017(96)00951-x
Bouhous A, Aissi M, Harhoura K (2011) Prevalence of Ixodidae in sheep brought for slaughter in Adrar municipal abattoir, Southwest Algeria. Sci Parasitol 12(4):197–201
Bryson N, Tice G, Horak I, Stewart C, Du Plessis B (2002) Ixodid ticks on cattle belonging to small-scale farmers at 4 communal grazing areas in South Africa. J S Afr Vet Assoc 73(3):98–103. https://doi.org/10.4102/jsava.v73i3.568
Castellà J, Estrada-Peña A, Almería S, Ferrer D, Gutiérrez J, Ortuño A (2001) A survey of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) on dairy cattle on the island of Menorca in Spain. Exp Appl Acarol 25(10–11):899–908. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020482017140
Chae J-B, Cho Y-S, Cho Y-K, Kang J-G, Shin N-S, Chae J-S (2019) Epidemiological investigation of tick species from near domestic animal farms and cattle, goat, and wild boar in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 57(3):319–324. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2019.57.3.319
Champour M, Mohammadi GR, Chinikar S, Razmi GR, Mostafavi E, Jalali T (2013) Frequency of hard-ticks and the influence of age and sex of camel on ticks’ infestation rates in one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) population in the northeast of Iran. Sci Parasitol 14(2):89–93
Champour M, Chinikar S, Mohammadi G, Razmi G, Shah-Hosseini N, Khakifirouz S, Mostafavi E, Jalali T (2016) Molecular epidemiology of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus detected from ticks of one humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) population in northeastern Iran. J Parasit Dis 40(1):110–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0458-y
Cicculli V, Capai L, Quilichini Y, Masse S, Fernández-Alvarez A, Minodier L, Bompard P, Charrel R, Falchi A (2019) Molecular investigation of tick-borne pathogens in ixodid ticks infesting domestic animals (cattle and sheep) and small rodents (black rats) of Corsica, France. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 10:606–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2019.02.007
Coronel-Benedett KC, Ojeda-Robertos NF, González-Garduño R, Ibañez FM, Rodríguez-Vivas RI (2018) Prevalence, intensity and population dynamics of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) on sheep in the humid tropics of Mexico. Exp Appl Acarol 74:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-017-0195-x
Dabaja MF, Tempesta M, Bayan A, Vesco G, Greco G, Torina A, Blanda V, La Russa F, Scimeca S, Lelli R (2017) Diversity and distribution of ticks from domestic ruminants in Lebanon. Vet Ital 53:147–155. https://doi.org/10.12834/VetIt.1171.6503.2
Davari B, Alam FN, Nasirian H, Nazari M, Abdigoudarzi M, Salehzadeh A (2017) Seasonal distribution and faunistic of ticks in the Alashtar county (Lorestan Province), Iran. Pan Afr Med J 27:284. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.12017.11627.11284.10341
Davari B, Barik-Abi S, Nasirian H, Zahirnia AH, Mohammadi Y, Salehzadeh A (2023) Comparative efficacy of topical dimethicone and permethrin for the treatment of head lice infestation in students. Chulalongkorn Med J 67(3):161–165. https://doi.org/10.14456/clmj.2023.XX
Davoudi J, Hoghooghi-Rad N, Golzar-Adabi S (2008) Ixodid tick species infesting cows and buffaloes and their seasonality in West Azerbaijan. Res J Parasitol 3(3):98–103
De Matos C, Sitoe C, Neves L, Nöthling J, Horak IG (2009) The comparative prevalence of five ixodid tick species infesting cattle and goats in Maputo Province, Mozambique. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 76(2):201–208. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v76i2.45
Deger MS, Bicek K, Oguz B (2016) Infestation rate and distribution of hard ticks on cattle in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. Sci Parasitol 17(3–4):76–82
Dehaghi MM, Fathi S, Asl EN (2011) Prevalence of ixodid ticks on cattle and sheep southeast of Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 43:459–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9715-y
Dehuri M, Panda MR, Mohanty B, Hembram A, Mahapatra T, Sahu A (2017) Ixodid ticks infesting cattle and associated risk factors in coastal districts of Odisha. J Entomol Zool Stud 5(4):129–132
Desalegn T, Fikru A, Kasaye S (2015) Survey of tick infestation in domestic ruminants of Haramaya District, Eastern Hararghe, Ethiopia. J Bacteriol Parasitol 6(5):246. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9597.1000246
Dinka A, Eyerusalem B, Yacob H (2010) A study on major ectoparasites of camel in and around Dire Dawa, Eastern Ethiopia. Rev Med Vet 161:498–501
Dioli M, Jean-Baptiste S, Fox M (2001) Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) of the one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) in Kenya and southern Ethiopia: species composition, attachment sites, sex ratio and seasonal incidence. Rev Elev Méd Vét Pays Trop 54:115–122
Diyes G, Rajakaruna R (2015) Diversity and distribution of tick species infesting goats with two new host records from Sri Lanka. J Natl Sci Found 43(3):225–234. https://doi.org/10.4038/jnsfsr.v43i3.7951
Dreyer K, Fourie L, Kok D (1998) Tick diversity, abundance and seasonal dynamics in a resource-poor urban environment in the Free State Province. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 65(4):305–316
Dumitrache M, Gherman C, Cozma V, Mircean V, Györke A, Sándor A, Mihalca A (2012) Hard ticks (Ixodidae) in Romania: surveillance, host associations, and possible risks for tick-borne diseases. Parasitol Res 110:2067–2070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2703-y
El-Azazy OME, Scrimgeour EM (1997) Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus infection in the Western Province of Saudi Arabia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 91(3):275–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0035-9203(97)90072-9
El-Seify M, Mahran O, El-Aal A (2011) Epidemiological studies on hard ticks and tick borne parasites, in Shalatin City, red sea governorate, Egypt. Assiut Vet Med J 57:305–332
El Tigani MA, Mohammed A (2010) Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting camels in El Butana area Mid-Central Sudan. Sudan J Vet Res 25:51–54
Elati K, Khbou AAAMK, Gharbi MJMRM (2018) Population dynamics of ticks infesting sheep in the arid steppes of Tunisia. Rev Elev Méd Vét Pays Trop 71(3):131–135. https://doi.org/10.19182/remvt.31641
Elghali A, Hassan S (2009) Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting camels (Camelus dromedarius) in northern Sudan. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 76(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v76i2.43
Eyob E, Matios L (2014) Preliminary survey on the distribution of Ixodid ticks in small ruminants of Dhas District of Borena pastoral area, Southern Rangelands of Ethiopia. Adv Bio Res 5(1):87–91. https://doi.org/10.15515/abr.0976-4585.5.87-91
Fakoorziba MR, Golmohammadi P, Moradzadeh R, Moemenbellah-Fard MD, Azizi K, Davari B, Alipour H, Ahmadnia S, Chinikar S (2012) Reverse transcription PCR-based detection of crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus isolated from ticks of domestic ruminants in Kurdistan Province of Iran. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis 12(9):794–799. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2011.0743
Fakoorziba MR, Naddaf-Sani AA, Moemenbellah-Fard MD, Azizi K, Ahmadnia S, Chinikar S (2015) First phylogenetic analysis of a Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus genome in naturally infected Rhipicephalus appendiculatus ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Arch Virol 160:1197–1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2379-1
Fanos T, Gezali A, Sisay G, Bersissa K, Tariku J (2012) Identification of tick species and their preferred site on cattle’s body in and around Mizan Teferi, Southwestern Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 4(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH11.039
Farah Isse AS, Ali M (2017) Hard tick distribution of camels in and around Galkaio District, Somalia. Glob J Med Res 17(1):6–11
Farahi A, Ebrahimzade E, Nabian S, Hanafi-Bojd AA, Akbarzadeh K, Bahonar A (2016) Temporal and spatial distribution and species diversity of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in the eastern region of Caspian sea. Acta Trop 164:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.08.013
Farhadpour F, Telmadarraiy Z, Chinikar S, Akbarzadeh K, Moemenbellah-Fard M, Faghihi F, Fakoorziba M, Jalali T, Mostafavi E, Shahhosseini N (2016) Molecular detection of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in ticks collected from infested livestock populations in a New Endemic Area, South of Iran. Trop Med Int Health 21(3):340–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/tmi.12667
Farooqi SH, Ijaz M, Saleem MH, Rashid MI, Oneeb M, Khan A, Aqib AI, Mahmood S (2017) Distribution of ixodid tick species and associated risk factors in temporal zones of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Pak J Zool 49(6):2011–2017. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjz/2017.49.6.2011.2017
Farzinnia B, Saghafipour A, Telmadarreyi Z (2012) Survey of tick species distribution in sheep and camel in Qom city, Iran, 2010–2011. J North Khorasan Univ Med Sci 4(3):391–398
Fatemian Z, Salehzadeh A, Sedaghat M, Telmadarraiy Z, Hanafi-Bojd A, Zahirnia A (2018) Hard tick (Acari: Ixodidae) species of livestock and their seasonal activity in Boyer-Ahmad and Dena cities of Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, Southwest of Iran. Vet World 11(9):1357–1363. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjz/2017.49.6.2011.2017
Fayazkhoo F, Zahirnia AH, Telmadarraiy Z (2017) Distribution and seasonal activity of hard ticks (Acari: Ixododae) infesting domestic ruminants in Famenin county, Hamadan province, Iran. Avicenna J Clin Med 24(3):221–228. https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.ajcm.24.3.221
Feleke A, Petros B, Lemecha H, Wossene A, Mulatu W, Rege EJ (2008) Study on monthly dynamics of ticks and seroprevalence of Anaplasma marginale, Babesia bigemina and Theileria mutans in four indigenous breeds of cattle in Ghibe Valley, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Sci 31(1):11–20
Feyera T, Megersa M, Maalin K, Gizaw Y, Asmare T (2017) Major ectoparasites infesting Camelus dromedarius in three districts of Somali Regional State, Eastern Ethiopia. World Appl Sci J 35(1):96–103. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2017.96.103
Fourie L, Horak I (1991) The seasonal activity of adult ixodid ticks on Angora goats in the south western Orange Free State. J S Afr Vet Assoc 62(3):104–106
Fourie L, Kok D, Heyne H (1996) Adult ixodid ticks on two cattle breeds in the south-western Free State, and their seasonal dynamics. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 63(1):19–23
Ganjali M, Dabirzadeh M, Sargolzaie M (2014) Species diversity and distribution of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Zabol County, eastern Iran. J Arthropod-Borne Dis 8(2):219–223
Ghafar A, Gasser RB, Rashid I, Ghafoor A, Jabbar A (2020) Exploring the prevalence and diversity of bovine ticks in five agro-ecological zones of Pakistan using phenetic and genetic tools. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 11:101472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101472
Ghafar A, Khan A, Cabezas-Cruz A, Gauci CG, Niaz S, Ayaz S, Mateos-Hernández L, Galon C, Nasreen N, Moutailler S (2020) An assessment of the molecular diversity of ticks and tick-borne microorganisms of small ruminants in Pakistan. Microorganisms 8:1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091428
Gharbi M, Moussi N, Jedidi M, Mhadhbi M, Sassi L, Darghouth MA (2013) Population dynamics of ticks infesting the one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) in central Tunisia. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 4:488–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.06.004
Gharekhani J, Gerami-Sadeghian A, Sadeghi-Dehkordi Z, Youssefi M (2015) Determination of hard tick species (Acarina: Ixodidae) on sheep and cattle in Hamedan Province, Iran. J Coastal Life Med 3:612–615
Ghashghaei O, Fard SRN, Khalili M, Sharifi H (2016) Abundance and associated risk factors of ixodid ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from one-humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Sistan and Balouchestan region, southeast of Iran. Persian J Acarol 5:219–227
Ghosh S, Bansal GC, Gupta SC, Ray D, Khan MQ, Irshad H, Shahiduzzaman M, Seitzer U, Ahmed JS (2007) Status of tick distribution in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. Parasitol Res 101(Suppl 2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0684-7
Ghosh S, Patra G, Borthakur SK, Behera P, Tolenkhomba T, Das M, Lalnunpuia C (2019) Prevalence of hard tick infestations in cattle of Mizoram, India. Biol Rhythm Res 50:564–574. https://doi.org/10.1080/09291016.2018.1474988
Gopalakrishnan A, Dimri U, Nandi A, Ajith Y, Joshi V, Jhambh R, Yatoo MI (2017) Prevalence study on tick infestations of goat in lower Shivalik region of Uttarakhand. Int J Livest Res 7(7):158–165. https://doi.org/10.5455/ijlr.20170513094814
Grech-Angelini S, Stachurski F, Lancelot R, Boissier J, Allienne J-F, Marco S, Maestrini O, Uilenberg G (2016) Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting cattle and some other domestic and wild hosts on the French Mediterranean island of Corsica. Parasites Vectors 9:582. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1876-8
Greenfield B (2011) Environmental parameters affecting tick (Ixodes ricinus) distribution during the summer season in Richmond Park, London. Biosci Horiz 4(2):140–148. https://doi.org/10.1093/biohorizons/hzr016
Gunes T, Poyraz O, Vatansever Z (2011) Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in ticks collected from humans, livestock, and picnic sites in the hyperendemic region of Turkey. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis 11(10):1411–1416. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2011.0651
Guo H, Moumouni PFA, Thekisoe O, Gao Y, Liu M, Li J, Galon EM, Efstratiou A, Wang G, Jirapattharasate C (2019) Genetic characterization of tick-borne pathogens in ticks infesting cattle and sheep from three South African provinces. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 10:875–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2019.04.008
Haque M, Singh N, Rath S, Ghosh S (2011) Epidemiology and seasonal dynamics of ixodid ticks of dairy animals of Punjab state, India. Indian J Anim Sci 81(7):661–664
Hasson RH (2012) Tick distribution and infestation among sheep and cattle in Baghdad’s south suburb. Kufa J Vet Med Sci 3(1):77–90
Hayati M, Hassan S, Ahmed S, Salih D (2020) Prevalence of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) and Theileria annulata infection of cattle in Gezira State, Sudan. Parasite Epidemiol Control 10:e00148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parepi.2020.e00148
Hlatshwayo M, Mbati P, Dipeolu O (2002) Seasonal abundance of adult ixodid ticks infesting cattle belonging to resource-limited farmers in the north-eastern Free State Province of South Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 69(1):1–6
Horak I, Macivor KDF, Greeff C (2001) Parasites of domestic and wild animals in South Africa. XXXIX. Helminth and arthropod parasites of Angora goats in the southern Karoo. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 68(1):27–35
Horak IG, Knight MM, Williams E (1991) Parasites of domestic and wild animals in South Africa. XXVIII. Helminth and arthropod parasites of Angora goats and kids in Valley Bushveld. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 58(4):253–260
Horak IG, Williams E, Van Schalkwyk P (1991) Parasites of domestic and wild animals in South Africa. XXV. Ixodid ticks on sheep in the north-eastern Orange Free State and in the eastern Cape Province. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 58(3):115–123
Horak IG, Nyangiwe N, De Matos C, Neves L (2009) Species composition and geographic distribution of ticks infesting cattle, goats and dogs in a temperate and in a subtropical region of south-east Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 76(3):263–276. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v76i3.28
Hornok S, Horváth G (2012) First report of adult Hyalomma marginatum rufipes (vector of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus) on cattle under a continental climate in Hungary. Parasites Vectors 5:170. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-5-170
Hornok S, Horváth G, Jongejan F, Farkas R (2012) Ixodid ticks on ruminants, with on-host initiated moulting (apolysis) of Ixodes, Haemaphysalis and Dermacentor larvae. Vet Parasitol 187(1–2):350–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.12.012
Hove T, Mukandi R, Bere M, Horak IG, Latif AA (2008) Ixodid ticks infesting domestic goats in communal land areas of Zimbabwe. J S Afr Vet Assoc 79(3):116–120. https://doi.org/10.4102/jsava.v79i3.257
Ica A, Inci A, Vatansever Z, Karaer Z (2007) Status of tick infestation of cattle in the Kayseri region of Turkey. Parasitol Res 101(Suppl 2):167–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0695-4
Inci A, Nalbantoğlu S, Çam Y, Atasever A, Karaer Z, Cakmak A, Sayin F, Yukari BA, Ica A, Deniz A (2003) Theileriosis and tick infestations in sheep and goats around Kayseri. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 27:57–60
Iqbal A, Sajid MS, Khan MN, Khan MK (2013) Frequency distribution of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting bubaline population of district Toba Tek Singh, Punjab, Pakistan. Parasitol Res 112:535–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3164-7
Iqbal A, Siddique F, Mahmood MS, Shamim A, Zafar T, Rasheed I, Saleem I, Ahmad W (2014) Prevalence and impacts of ectoparasitic fauna infesting goats (Capra hircus) of district Toba Tek Singh, Punjab Pakistan. Glob Vet 12(2):158–164. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.gv.2014.12.02.8286
Islam MK, Alim MA, Tsuji N, Mondal MMH (2006) An investigation into the distribution, host-preference and population density of ixodid ticks affecting domestic animals in Bangladesh. Trop Anim Health Prod 38(6):485–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-006-4381-9
Jadhao SG, Sanyal PK, Borkar SD, Chigure GM, Jadhav ND, Shirsikar PM, Kumar S (2020) Prevalence of ixodid ticks infesting in cattle of Chhattisgarh state, an east-central part of India. Int J Trop Insect Sci 40:951–954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00153-4
James-Rugu N, Jidayi S (2004) A survey on the ectoparasites of some livestock from some areas of Borno and Yobe States. Niger Vet J 25(2):48–55
Jameson LJ, Morgan PJ, Medlock JM, Watola G, Vaux AGC (2012) Importation of Hyalomma marginatum, vector of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus, into the United Kingdom by migratory birds. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 3:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2011.12.002
Jariko AA, Leghari RA, Gadahi JA, Memon MUR, Khaskheli AA, Koondhar MQ, Jariko RA, Jariko MA (2020) Prevalence of tick infestation in goats reared under semi-intensive system. Pure Appl Biol 9(1):1177–1183. https://doi.org/10.19045/bspab.2020.90123
Jayraw A, Mandloi U, Haque M, Jamra N (2016) Prevalence of ixodid ticks in cattle population of Indore, Madhya Pradesh. Indian J Vet Sci Biotechnol 12(2):62–65. https://doi.org/10.21887/ijvsbt.v12i2.3740
Jongejan F, Berger L, Busser S, Deetman I, Jochems M, Leenders T, De Sitter B, Van der Steen F, Wentzel J, Stoltsz H (2020) Amblyomma hebraeum is the predominant tick species on goats in the Mnisi Community Area of Mpumalanga Province South Africa and is co-infected with Ehrlichia ruminantium and Rickettsia africae. Parasites Vectors 13:172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-13020-04059-13075
Kabir M, Mondal M, Eliyas M, Mannan M, Hashem M, Debnath N, Miazi O, Kashem M, Islam M, Elahi M (2011) An epidemiological survey on investigation of tick infestation in cattle at Chittagong District, Bangladesh. Afr J Microbiol Res 5(4):346–352
Kadir M, Zangana I, Mustafa B (2012) A study on epidemiology of hard tick (Ixodidae) in sheep in Sulaimani governorate-Iraq. Iraqi J Vet Sci 26(4):95–103. https://doi.org/10.33899/ijvs.2012.168745
Kakar M, Khan M, Khan M, Ashraf K, Kakar M, Jan S, Razzaq A (2017) Prevalence of tick infestation in different breeds of cattle in Balochistan. J Anim Plant Sci 27(3):797–802
Kakeh-Khani A, Nazari M, Nasirian H (2020) Insecticide resistance studies on German cockroach (Blattella germanica) strains to malathion, propoxur and lambdacyhalothrin. Chulalongkorn Med J 64:357–365. https://doi.org/10.14456/clmj.2020.45
Kamal A, Uddin K, Islam M, Mondal M (1996) Prevalence of economically important ticks in cattle and goat at Chittagong hilly areas of Bangladesh. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 9(5):567–570. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.1996.567
Kariuki EK (2012) A survey of tick species on cattle and African buffaloes in the Tsavo Conservation Area, Kenya. University of Pretoria. Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree Magister Scientiae (Veterinary Tropical Diseases). https://repository.up.ac.za/handle/2263/31137
Kassiri H, Nasirian H (2021) New insights about human tick infestation features: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:17000–17028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-17021-13102-17006
Kaur D, Jaiswal K, Mishra S (2015) Studies on prevalence of ixodid ticks infesting cattle and their control by plant extracts. J Pharm Biol Sci 10(6):1–11. https://doi.org/10.9790/3008-10630111
Kebede N, Fetene T (2012) Population dynamics of cattle ectoparasites in Western Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 4(1):22–26. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH11.006
Kemal J, Muktar Y, Alemu S (2016) Distribution and prevalence of tick infestation in cattle in Babille district, eastern Ethiopia. Livest Res Rural Dev 28(12):232
Kerario II, Muleya W, Chenyambuga S, Koski M, Hwang S-G, Simuunza M (2017) Abundance and distribution of Ixodid tick species infesting cattle reared under traditional farming systems in Tanzania. Afr J Agric Res 12(4):286–299. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2016.12028
Kiros S, Awol N, Tsegaye Y, Hadush B (2014) Hard ticks of camel in Southern Zone of Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. J Parasitol Vector Biol 6(10):151–155. https://doi.org/10.5897/JPVB2014.0162
Kumsa B, Geloye M, Beyecha K (2012) Ectoparasites of sheep in three agro-ecological zones in central Oromia, Ethiopia. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 79(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v79i1.442
Kusiluka L, Kambarage D, Matthewman R, Daborn C, Harrison L (1995) Prevalence of ectoparasites of goats in Tanzania. J Appl Anim Res 7:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.1995.9706052
Kwak YS, Kim TY, Nam S-H, Lee I-Y, Kim H-P, Mduma S, Keyyu J, Fyumagwa R, Yong T-S (2014) Ixodid tick infestation in cattle and wild animals in Maswa and Iringa, Tanzania. Korean J Parasitol 52(5):565–568. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2014.52.5.565
Leblebicioglu H, Eroglu C, Erciyas-Yavuz K, Hokelek M, Acici M, Yilmaz H (2014) Role of migratory birds in spreading Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Turkey. Emerg Infect Dis 20:1331–1334. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2008.131547
Leblebicioglu H, Ozaras R, Erciyas-Yavuz K (2015) Emergence of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 109:676–678. https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/trv083
Leblebicioglu H, Ozaras R, Irmak H, Sencan I (2016) Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Turkey: current status and future challenges. Antiviral Res 126:21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.12.003
Liu M, Li T, Yang J, Li SS, Yu ZJ, Liu JZ (2020) Seasonal abundance and activity of the tick Dermacentor everestianus (Acari: Ixodidae) in the Tibetan Plateau, China. Exp Appl Acarol 81:609–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-020-00528-9
Liyanaarachchi D, Jinadasa H, Dilrukshi P, Rajapakse R (2013) Epidemiological study on ticks in farm animals in selected areas of Sri Lanka. Trop Agric Res 24:336–346
Liyanaarachchi DR, Rajakaruna RS, Dikkumbura AW, Rajapakse RP (2015) Ticks infesting wild and domestic animals and humans of Sri Lanka with new host records. Acta Trop 142:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2014.1011.1001
Loftis AD, Reeves WK, Szumlas DE, Abbassy MM, Helmy IM, Moriarity JR, Dasch GA (2006) Rickettsial agents in Egyptian ticks collected from domestic animals. Exp Appl Acarol 40:67–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-006-9025-2
Lorusso V, Picozzi K, de Bronsvoort BM, Majekodunmi A, Dongkum C, Balak G, Igweh A, Welburn SC (2013) Ixodid ticks of traditionally managed cattle in central Nigeria: where Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus does not dare (yet?). Parasites Vectors 6:171
Lotfollahzadeh S, NikbakhtBoroujeni GR, MokhberDezfouli MR, Bokaei S (2011) A Serosurvey of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in dairy cattle in Iran. Zoonoses Public Health 58:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1863-2378.2009.01269.x
Loui Monfared A, Mahmoodi M, Fattahi R (2015) Prevalence of ixodid ticks on cattle, sheep and goats in Ilam County, Ilam Province, Iran. J Parasit Dis 39(1):37–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-013-0267-8
Lu X, Lin X-D, Wang J-B, Qin X-C, Tian J-H, Guo W-P, Fan F-N, Shao R, Xu J, Zhang Y-Z (2013) Molecular survey of hard ticks in endemic areas of tick-borne diseases in China. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 4:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.01.003
Lutomiah J, Musila L, Makio A, Ochieng C, Koka H, Chepkorir E, Mutisya J, Mulwa F, Khamadi S, Miller BR (2014) Ticks and tick-borne viruses from livestock hosts in arid and semiarid regions of the eastern and northeastern parts of Kenya. J Med Entomol 51(1):269–277. https://doi.org/10.1603/ME13039
Lynen G, Zeman P, Bakuname C, Di Giulio G, Mtui P, Sanka P, Jongejan F (2007) Cattle ticks of the genera Rhipicephalus and Amblyomma of economic importance in Tanzania: distribution assessed with GIS based on an extensive field survey. Exp Appl Acarol 43:303–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-007-9123-9
Macivor KdF, Horak IG (2003) Ixodid ticks of Angora and Boer goats, grysbok, common duikers, kudus and scrub hares in Valley Bushveld in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 70(2):113–120
Mamak N, Gençer L, Ozkanlar YE, Ozçelik S (2006) Determination of tick species and treatment of cows, sheep and goats in the Sivas-Zara region. Turk Parazitol Derg 30(3):209–212
Mamoudou A, Nguetoum N, Zoli PA, Sevidzem S (2016) Identification and infestation of ticks on cattle in the peri-urban area of Ngaoundere, Cameroon. J Vet Sci Med Diagn 4:1000207
Mamun M, Begum N, Shahadat H, Mondal M (2010) Ectoparasites of buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) in Kurigram district of Bangladesh. J Bangladesh Agric Univ 8(1):61–66. https://doi.org/10.3329/JBAU.V8I1.6400
Marcellino WL, Julla II, Salih DA, El Hussein AR (2011) Ticks infesting cattle in the Central Equatoria region of South Sudan. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 78(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v78i1.336
Marufu MC, Chimonyo M, Mapiye C, Dzama K (2011) Tick loads in cattle raised on sweet and sour rangelands in the low-input farming areas of South Africa. Trop Anim Health Prod 43(2):307–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9690-3
Maya-Delgado A, Madder M, Benítez-Ortíz W, Saegerman C, Berkvens D, Ron-Garrido L (2020) Molecular screening of cattle ticks, tick-borne pathogens and amitraz resistance in ticks of Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas province in Ecuador. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 11:101492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101492
Megersa B, Damena A, Bekele J, Adane B, Sheferaw D (2012) Ticks and mange mites infesting camels of Boran pastoral areas and the associated risk factors, southern Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 4(5):71–77. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH12.029
Miranpuri G (1988) Ticks parasitising the Indian buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) and their possible role in disease transmission. Vet Parasitol 27(3–4):357–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4017(88)90050-7
Mirzaei M, Khedri J (2014) Ixodidae ticks in cattle and sheep in Sistan and Baluchestan Province (Iran). Vet Ital 50:65–68. https://doi.org/10.12834/VetIt.11018.12800
Moges N, Bogale B, Fentahun T (2012) Hard ticks (ixodidae): species composition, seasonal dynamics and body site distribution on cattle in Chilga District, Northwest Ethiopia. Asian J Agric Sci 4(5):341–345
Moghaddam AG, Seyed MR, Rasouli M, Hosseinzade S, Darvishi MM, Rakhshanpour A, Rahimi MT (2014) Survey on cattle ticks in Nur, north of Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 4(3):209–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(1014)60233-60231
Mohamed RAEH, Mohamed N, Aleanizy FS, Alqahtani FY, Khalaf AA, Al-Keridis LA (2017) Investigation of hemorrhagic fever viruses inside wild populations of ticks: One of the pioneer studies in Saudi Arabia. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 7(5):299–303. https://doi.org/10.12980/apjtd.7.2017D6-371
Mohammad MK, Jassim SY (2011) Distribution of hard tick species among sheep Ovis aries L. in Al-Anbar province, western desert of Iraq. Bull Iraq Nat History Museum 11(4):27–31
Mohammad MK (2016) Ixodiod tick fauna infesting sheep and goats in the middle and south of Iraq. Bull Iraq Nat History Museum 14(1):43–50
Mohammadi SM, Esmaeilnejad B, Jalilzadeh-Amin G (2017) Molecular detection, infection rate and vectors of Theileria lestoquardi in goats from West Azerbaijan province, Iran. Vet Res Forum 8(2):139–144
Mohammed M, Hassan S (2007) Distribution and population dynamics of ticks (Acari: ixodidae) infesting sheep in Sennar State, Sudan. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 74(4):301–306. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v74i4.116
Mohanta U, Mondal M (2011) Tick and tick borne protozoan diseases of livestock in the selected hilly areas of Bangladesh. Int J Agric Res Innovation Technol 1(1–2):60–63
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 4:1
Moshaverinia A, Dini M, Azizzadeh M (2012) Prevalence of ixodid tick infestation of sheep in the Arasbaran region of Iran. J Parasit Dis 36(2):230–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-012-0114-3
Moshaverinia A, Moghaddas E (2015) Prevalence of tick infestation in dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius) brought for slaughter in Mashhad abattoir, Iran. J Parasit Dis 39(3):452–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-013-0367-5
MotevalliHaghi F, Razmi G, Fakhar M, Mohammadpoor RA (2013) The hard ticks (Ixodidae) fauna of livestock in Sari suburb, Northern Iran. Comp Clin Pathol 22:5–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1361-x
Moyo DZ, Chakuya J, Sungirai M (2018) Ixodid ticks of African buffalo (Syncerus caffer), impala (Aepyceros melampus) and elephant (Loxodonta africana) in five protected park estates in the Zambezi valley, Zimbabwe. Exp Appl Acarol 75:409–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-018-0275-6
Muhanguzi D, Byaruhanga J, Amanyire W, Ndekezi C, Ochwo S, Nkamwesiga J, Mwiine FN, Tweyongyere R, Fourie J, Madder M (2020) Invasive cattle ticks in East Africa: morphological and molecular confirmation of the presence of Rhipicephalus microplus in south-eastern Uganda. Parasites Vectors 13:165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-13020-04043-z
Mulugeta Y, Yacob HT, Ashenafi H (2010) Ectoparasites of small ruminants in three selected agro-ecological sites of Tigray Region, Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 42:1219–1224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9551-0
Mustafa I, Shabbir RMK, Subhani M, Ahmad I, Aleem R, Jamil S, Muqaddas H, Shabbir RG, Ghani A, Mahmood T (2014) Seasonal activity of tick infestation in goats and buffalo of Punjab province (district Sargodha), Pakistan. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 20(5):655–662. https://doi.org/10.9775/kvfd.2014.10676
Mustafa ML, Ayazi E, Mohareb E, Yingst S, Zayed A, Rossi CA, Schoepp RJ, Mofleh J, Fiekert K, Akhbarian Z (2011) Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Afghanistan, 2009. Emerg Infect Dis 17(10):1940. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1710.110061
Najarnezhad V, Mishmast Z, Zabol I, Razmi G, Azad M (2009) Identification of Ixodidae ticks of imported camels in Zabol area. Vet J 83(2):35–39
Nasirian H, Ladonni H, Shayeghi M, Vatandoost H, Rassi Y, Ershadi MY, Rafinejad J, Basseri H (2006) Duration of fipronil WHO glass jar method toxicity against susceptible and feral German Cockroach strains. Pak J Biol Sci 9(10):1955–1959
Nasirian H (2013) Using insects for heavy metal contamination survey in Shadegan wetland. Thesis for fulfillment of the PhD Degree in Medical Entomology and Vector Control, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Nasirian H, Mahvi AH, Hosseini M, Vazirianzadeh B, Sadeghi SM, Nazmara S (2013) Study on the heavy metal bioconcentrations of the Shadegan international wetland mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis, by inductively coupled plasma technique. J Environ Health Sci Eng 11:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-1336X-1111-1122
Nasirian H (2014) Evaluation of water quality and organic pollution of Shadegan and Hawr Al Azim wetlands by biological indices using insects. J Entomol Zool Stud 2(5):193–200
Nasirian H, Sadeghi SMT, Vazirianzadeh B, Moosa-Kazemi SH (2014) New record of Aedes vittatus and Culiseta subochrea (Diptera: Culicidae) and their distribution from Shadegan Wetland, South Western Iran. J Entomol Zool Stud 2(5):271–275
Nasirian H, Vazirianzadeh B, Taghi Sadeghi SM, Nazmara S (2014) Culiseta subochrea as a bioindicator of metal contamination in Shadegan International Wetland, Iran (Diptera: Culicidae). J Insect Sci 14:258. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieu120
Nasirian H, Alimohammadi M, Kamandar M, SaikhBarahwie L, Mojadami Moghadam H, Sheikhi R, Asgari M, Hosseini SS, Farhani Ahmadi F (2015) Water quality evaluation of the Shadegan and Hawr Al Azim wetlands from Iran. Indian J Sci Res 6(2):11–24
Nasirian H, Nazmara S, Mahvi AH, Hosseini M, Shiri L, Vazirianzadeh B (2015) Assessment of some heavy metals in the Shadegan and Hawr Al Hawizea wetland waters from Iran. Indian J Sci Technol 8(33):1–9. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i33/53997
Nasirian H (2016) New aspects about Supella longipalpa (Blattaria: Blattellidae). Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 6:1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2016.1008.1017
Nasirian H, Irvine K, Sadeghi S, Mahvi A, Nazmara S (2016) Assessment of bed sediment metal contamination in the Shadegan and Hawr Al Azim wetlands, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-10016-15117-10666
Nasirian H (2017) Infestation of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) in the human dwelling environments: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop 167:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.1012.1019
Nasirian H (2017) Contamination of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) to medically fungi: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Mycol 27:427–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.1004.1012
Nasirian H, Irvine K (2017) Odonata larvae as a bioindicator of metal contamination in aquatic environments: application to ecologically important wetlands in Iran. Environ Monit Assess 189:436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-10017-16145-10666
Nasirian H (2019) Contamination of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) by medically important bacteriae: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Entomol 56:1534–1554. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjz1095
Nasirian H (2019) Recent cockroach bacterial contamination trend in the human dwelling environments: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bangladesh J Med Sci 18:540–545. https://doi.org/10.3329/BJMS.V3318I3323.41623
Nasirian H (2019) Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) seroprevalence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop 196:102–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.1005.1019
Nasirian H, Salehzadeh A (2019) Control of cockroaches (Blattaria) in sewers: a practical approach systematic review. J Med Entomol 56:181–191. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjy1205
Nasirian H, Salehzadeh A (2019) Effect of seasonality on the population density of wetland aquatic insects: a case study of the Hawr Al Azim and Shadegan wetlands, Iran. Vet World 12:584–592. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.12019.14584-14592
Nasirian H (2020) New aspects about Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) cases and associated fatality trends: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 69:101429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.102020.101429
Nasirian H, Saghafipour A (2021) Efficacy of several insecticide formulations against Periplaneta americana (L.) (Blattaria: Blattidae) in sewers. Bangladesh J Med Sci 20:569–585
Nasirian H, Zahirnia A (2021) Detailed infestation spectrums about biological stages of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae) in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Parasitol 66:770–796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-11021-00362-y
Nasirian H (2022) Ticks infected with Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV): a decision approach systematic review and meta-analysis regarding their role as vectors. Travel Med Infect Dis 47:102309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2022.102309
Nasirian H (2022) Detailed new insights about tick infestations in domestic ruminant groups: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. J Parasit Dis 46:526–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-021-01460-4
Nasirian H (2023) Monitoring the impact, trends, and impact levels of factors affecting Pediculus capitis infestation in primary school students: an illustrate scale evidence review. J Public Health 5:1–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-10023-01863-y
Nasirian H (2023) Reply to comment on “ticks infected with Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV): a decision approach systematic review and meta-analysis regarding their role as vectors.” Travel Med Infect Dis 51:102420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2022.102420
Nasirian H (2023) Monitoring of hard tick parasitism in domestic ruminants: a scale evidence for policymakers. Vet Parasitol 41:100878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vprsr.2023.100878
Nazifi S, Tamadon A, Behzadi M-A, Haddadi S, Raayat-Jahromi A-R (2011) One-humped camels (Camelus dromedaries) hard ticks infestation in Qeshm Island, Iran. Vet Res Forum 2(2):135–138
Ndhlovu DN, Makaya P, Penzhorn BL (2009) Tick infestation, and udder and teat damage in selected cattle herds of Matabeleland South, Zimbabwe. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 76(2):235–248. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v76i2.48
Noaman V (2012) Identification of hard ticks collected from sheep naturally infected with Anaplasma ovis in Isfahan province, central Iran. Comp Clin Pathol 21:367–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1438-1
NongaHezron E, Adrian M, Robinson M (2012) Tick infestations in extensively grazed cattle and efficacy trial of high-cis cypermethrin pour-on preparation for control of ticks in Mvomero district in Tanzania. BMC Vet Res 8:224. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-6148-8-224
NourollahiFard SR, Fathi S, Norouzi Asl E, AsgaryNazhad H, SalehzadehKazeroni S (2012) Hard ticks on one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) and their seasonal population dynamics in southeast, Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 44:197–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-011-9909-y
Nyangiwe N, Horak IG (2007) Goats as alternative hosts of cattle ticks. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 74(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.4102/ojvr.v74i1.133
Ofukwu R, Ogbaje C, Akwuobu C (2008) Preliminary study of the epidemiology of ectoparasite infestation of goats and sheep in Makurdi, north central Nigeria. Sokoto J Vet Sci 7(2):22–26
Ogden N, Swai E, Beauchamp G, Karimuribo E, Fitzpatrick J, Bryant M, Kambarage D, French N (2005) Risk factors for tick attachment to smallholder dairy cattle in Tanzania. Prev Vet Med 67(2–3):157–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2004.10.011
Oliveira AR, Cohnstaedt LW, Cernicchiaro N (2021) Unbiased approaches for reviewing entomology literature: a systematized review. Ann Entomol Soc Am 114:229–246. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/saaa058
Onu S, Shiferaw T (2013) Prevalence of ectoparasite infestations of cattle in Bench Maji zone, southwest Ethiopia. Vet World 6(6):291–294. https://doi.org/10.5455/vetworld.2013.291-294
Ouedraogo A, Luciani L, Zannou O, Biguezoton A, Pezzi L, Thirion L, Belem A, Saegerman C, Charrel R, Lempereur L (2020) Detection of two species of the genus Parapoxvirus (bovine papular stomatitis virus and Pseudocowpox virus) in ticks infesting cattle in Burkina Faso. Microorganisms 8:644. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050644
Papadopoulos B, Morel PC, Aeschlimann A (1996) Ticks of domestic animals in the Macedonia region of Greece. Vet Parasitol 63(1–2):25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4017(95)00877-2
Pasalary M, Arbabi M, Pashei S, Abdigoudarzi M (2017) Fauna of ticks (Acari: ixodidae) and their seasonal infestation rate on Camelus dromedarius (Mammalia: Camelidae) in Masileh region, Qom province, Iran. Persian J Acarol 6:31–37. https://doi.org/10.22073/pja.v22076i22071.15982
Pavlovic I, Ivanovic S, Zujovic M (2013) Tick fauna of goat and sheep in Belgrade area. Sci Works Ser C Vet Med 59:51–53
Pavlović I, Jovčevski S, Kukovska V, Dimitrić A (2014) Tick fauna of sheep and cattle at Kumanovo area (Macedonia) Lucr Stiint Univ Stiinte Agric Banatului Timisoara. Med Vet 47:88
Pavlovic I, Aleksandar D, Ana V, Bojana M, Mensur V, Slavica Z, Snežana I (2016) Tick population in goats and sheep in Šabac. Maced Vet Rev 39:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1515/macvetrev-2016-0077
Pegram RG, Hoogstraal H, Wassef HY (1981) Ticks (Acari: ixodoidea) of Ethiopia. I. Distribution, ecology and host relationships of species infesting livestock. Bull Entomol Res 71:339–359
Perveen F, Naqvi S, Yasmin N, Bibi N (2010) Ixodid ticks infestation in livestock and their traditional control in NWFP, Pakistan. Pak J Zool 42:43–54
Qamar M, Ayaz M, Nazir M (2019) Isolation and identification of ectoparasites in single humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) of Cholistan area, Pakistan. Iraqi J Vet Sci 32(2):291–297
Rafiq N, Kakar A, Ghani A, Iqbal A, Achakzai WM, Sadozai S, Shafiq M, Mengal MA (2017) Ixodid ticks (Arachnida: Acari) prevalence associated with risk factors in the bovine host in District Quetta, Balochistan. Pak J Zool 49:2113–2121
Ramzan M, Naeem-Ullah U, Abbas H, Adnan M, Rasheed Z, Khan S (2019) Diversity of hard ticks in goats and sheep in Multan, Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Agric Biol Res 35(2):7–9
Rasouli S, Rajabi E, Jafari K, Valizadeh E, Motalebi J, Etemad S (2010) Epidemiology and prevalence of hard ticks contaminate sheep in Maragheh city. J Vet Med 4(10):61–66
Razavi S, Seyfi S (2006) Identification of hard tick’s species (Ixodidae) in cattle of Amol area. J Vet Fac Univ Tehran 61:217–220
Razmi GR, Glinsharifodini M, Sarvi S (2007) Prevalence of ixodid ticks on cattle in Mazandaran province, Iran. Korean J Parasitol 45(4):307–310. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2007.45.4.307
Rashtibaf M, Najarnejad V, Razmi GR (2011) Determination the frequency of Ixodid ticks on the sheep in Khorasan Razavi province, Iran. Arch Razi Inst 66:129–132. https://doi.org/10.22092/ari.2016.103876
Regasa TD, KebedeTsegay A, Waktole H (2015) Prevalence of major ectoparasites of calves and associated risk factors in and around Bishoftu town. Afr J Agric Res 10(10):1127–1135. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2014.9380
Regassa A (2001) Tick infestation of Borana cattle in the Borana Province of Ethiopia. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 68(1):41–45
Regassa A, Awol N, Hadush B, Tsegaye Y, Sori T (2015) Internal and external parasites of camels (Camelus dromedarius) slaughtered at Addis Ababa Abattoir, Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 7:57–63. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH2014.0346
Rehman A, Nijhof AM, Sauter-Louis C, Schauer B, Staubach C, Conraths FJ (2017) Distribution of ticks infesting ruminants and risk factors associated with high tick prevalence in livestock farms in the semi-arid and arid agro-ecological zones of Pakistan. Parasites Vectors 10:190. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2138-0
Rezaei H, Mirzaei M, Nematollahi A, Ashrafihelan J (2011) Survey on ixodidae tick population in domestic ruminants in east Azerbaijan, Iran. Glob Vet 6(4):399–401
Riabi H, Atarodi A (2014) Faunistic study of hard ticks (Ixodidae) of domestic ruminants in the Southern Khorasan-e-Razavi in comparing with other regions of the province in 2012 Iran. J Vet Adv 4(5):508–515
Riaz M, Tasawar Z, Ullah M (2017) Epidemiological survey on diversity and seasonal distribution of hard ticks in sheep and goats in Multan, Pakistan. J Biodivers Environ Sci 10(3):50–61
Rinaldi L, Otranto D, Veneziano V, Milillo P, Buono V, Iori A, Di Giulio G, Cringoli G (2004) Cross-sectional survey of ticks (Acari: ixodidae) in sheep from an area of the southern Italian Apennines. Exp Appl Acarol 33:145–151
Rinaldi L, Morgoglione M, Noviello E, Bosco A, Prestera G, Cringoli G (2014) Ixodidae ticks in sheep and cattle in the Basilicata region (southern Italy). Parasites Vectors 7(Suppl 1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-S1-P8
Robson J, Robb JM (1967) Ticks (Ixodoidea) of domestic animals in Iraq spring and early summer infestations in the Liwas of Baghdad, Kut, Amara, and Basra. J Med Entomol 4(3):289–293. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/4.3.289
Rodríguez-Vivas RI, Apanaskevich DA, Ojeda-Chi MM, Trinidad-Martínez I, Reyes-Novelo E, Esteve-Gassent MD, Pérez de León AA (2016) Ticks collected from humans, domestic animals, and wildlife in Yucatan, Mexico. Vet Parasitol 215:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.11.010
Rony S, Mondal M, Begum N, Islam M, Affroze S (2010) Epidemiology of ectoparasitic infestations in cattle at Bhawal forest area, Gazipur. Bangladesh J Vet Med 8(1):27–33. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjvm.v8i1.7399
Rony S, Mondal M, Islam M, Begum N (2010) Prevalence of ectoparasites in goat at Gazipur in Bangladesh. Int J Bio Res 2(9):19–24
Roy B, Krücken J, Ahmed J, Majumder S, Baumann M, Clausen PH, Nijhof A (2018) Molecular identification of tick-borne pathogens infecting cattle in Mymensingh district of Bangladesh reveals emerging species of Anaplasma and Babesia. Transbound Emerg Dis 65(2):e231–e242. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.12745
Sahara A, Nugraheni YR, Patra G, Prastowo J, Priyowidodo D (2019) Ticks (Acari: ixodidae) infestation on cattle in various regions in Indonesia. Vet World 12(11):1755. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2019.1755-1759
Sajid MS, Iqbal Z, Khan MN, Muhammad G (2008) Point prevalence of hard ticks (Ixodids) infesting domestic ruminants of lower Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Agric Biol 10:349–351
Sajid MS, Kausar A, Iqbal A, Abbas H, Iqbal Z, Jones MK (2018) An insight into the ecobiology vector significance and control of Hyalomma ticks (Acari: ixodidae): a review. Acta Trop 187:229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.1008.1016
Salehzadeh A, Darvish Z, Davari B, Nasirian H (2020) The efficacy of baits containing abamectin, dinotefuran, imidacloprid and pyriproxyfen+abamectin against Blattella germanica (L.) (Blattaria: Blattellidae), the German cockroach. Afr Entomol 28(2):225–237. https://doi.org/10.4001/003.028.0225
Salim Abadi Y, Telmadarraiy Z, Vatandoost H, Chinikar S, Oshaghi M, Moradi M, MirabzadehArdakan E, Hekmat S, Nasiri A (2010) Hard ticks on domestic ruminants and their seasonal population dynamics in Yazd province, Iran. Iran J Arthropod-Borne Dis 4(1):66–71
Sang R, Lutomiah J, Koka H, Makio A, Chepkorir E, Ochieng C, Yalwala S, Mutisya J, Musila L, Richardson JH (2011) Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in Hyalommid ticks, northeastern Kenya. Emerg Infect Dis 17(5):1502–1505. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1708.102064
Saracho-Bottero MN, Tarragona EL, Sebastian PS, Venzal JM, Mangold AJ, Guglielmone AA, Nava S (2018) Ticks infesting cattle and humans in the Yungas biogeographic province of Argentina, with notes on the presence of tick-borne bacteria. Exp Appl Acarol 74:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-018-0208-4
Sarani M, Telmadarraiy Z, Moghaddam AS, Azam K, Sedaghat MM (2014) Distribution of ticks (Acari: ixodidae) infesting domestic ruminants in mountainous areas of Golestan Province, Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 4(Suppl 1):S246–S251. https://doi.org/10.12980/APJTB.4.2014C746
Sarkar M, Rahman S, Sarker B, Anisuzzaman A, Begum N, Mondal M (2010) Epidemiology and pathology of ectoparasitic infestations in black Bengal goats in Gaibandha and Mymensingh districts of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Vet Med 8(1):41–50. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjvm.v8i1.7718
Selmi R, Said MB, Mamlouk A, Yahia HB, Messadi L (2019) Molecular detection and genetic characterization of the potentially pathogenic Coxiella burnetii and the endosymbiotic Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii in ticks infesting camels (Camelus dromedarius) from Tunisia. Microb Pathog 136:103655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103655
Seo M-G, Kwon O-D, Kwak D (2020) Molecular and phylogenetic analysis of tick-borne pathogens in ticks parasitizing native Korean goats (Capra hircus coreanae) in South Korea. Pathogens 9:71. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020071
Shanavaz M, Zahirnia AH, Nasirian H (2023) Monitoring scorpionism in Shush County of Khuzestan Province in the first six months of 2019. J Isfahan Med Sch 41:319–325. https://doi.org/10.48305/jims.v41.i718.0319
Sharifah N, Heo CC, Ehlers J, Houssaini J, Tappe D (2020) Ticks and tick-borne pathogens in animals and humans in the island nations of Southeast Asia: a review. Acta Trop 209:105527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105527
Shemshad K, Rafinejad J, Kamali K, Piazak N, Sedaghat MM, Shemshad M, Biglarian A, Nourolahi F, Beigi EV, Enayati AA (2012) Species diversity and geographic distribution of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea: Ixodidae) infesting domestic ruminants, in Qazvin Province, Iran. Parasitol Res 110:373–380
Shubber H, Mohammed M, Al-Hassani N (2013) Ixodid ticks of water buffalo Bubalus bubalis in the middle and south of Iraq. Adv Bio Res 4:58–63
Silatsa BA, Simo G, Githaka N, Mwaura S, Kamga RM, Oumarou F, Keambou C, Bishop RP, Djikeng A, Kuiate J-R (2019) A comprehensive survey of the prevalence and spatial distribution of ticks infesting cattle in different agro-ecological zones of Cameroon. Parasites Vectors 12:489. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3738-7
Singh N, Rath S (2018) Epidemiology of ixodid ticks in buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) of Punjab, India. Buffalo Bull 35(3):347–353
Singh NK, Rath SS (2013) Epidemiology of ixodid ticks in cattle population of various agro-climatic zones of Punjab, India. Asian Pac J Trop Med 6(12):947–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(13)60169-8
Sofizadeh A, Telmadarraiy Z, Rahnama A, Gorganli-Davaji A, Hosseini-Chegeni A (2014) Hard tick species of livestock and their bioecology in Golestan province, north of Iran. J Arthropod-Borne Dis 8(1):108–116
Sohrabi S, Yakhchali M, Ghashghai O (2013) Hard ticks (Acarina: Ixodidae) diversity in the natural habitat of Iranian domestic ruminants: a provincial study in Kermanshah. J Vet Res 68(1):39–46
Taddese A, Mustefa M (2013) A study on camels ticks in and around Dire Dawa, Eastern Ethiopia. Acta Parasitol Glob 4(2):64–70. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.apg.2013.4.2.64173
Tadesse F, Abadfaji G, Girma S, Jibat T (2012) Identification of tick species and their preferred site on cattles body in and around Mizan Teferi, Southwestern Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 4(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH11.039
Tahmasebi F, Ghiasi SM, Mostafavi E, Moradi M, Piazak N, Mozafari A, Haeri A, Fooks A, Chinikar S (2010) Molecular epidemiology of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus genome isolated from ticks of Hamadan province of Iran. J Vector Borne Dis 47(4):211–216
Tamerat N, Erba F, Muktar Y, Kemal J (2015) Identification and prevalence of ixodid tick in bovine at Bedele district, Oromiyia Regional State, Western Ethiopia. J Parasitol Vector Biol 7(8):156–162. https://doi.org/10.5897/JPVB2015.0220
Tessema T, Gashaw A (2010) Prevalence of ticks on local and crossbreed cattle in and around Asela Town, South East, Ethiopia. Ethiopian Vet J 14(2):79–89. https://doi.org/10.4314/evj.v14i2.63886
Tiki B, Addis M (2011) Distribution of ixodid ticks on cattle in and around Holeta town, Ethiopia. Glob Vet 7(6):527–531
Tomassone L, Grego E, Callà G, Rodighiero P, Pressi G, Gebre S, Zeleke B, De Meneghi D (2012) Ticks and tick-borne pathogens in livestock from nomadic herds in the Somali Region, Ethiopia. Exp Appl Acarol 56(4):391–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-012-9528-y
Tongjura J, Amuga G, Ombugadu R, Azamu Y, Mafuiya H (2012) Ectoparasites infesting livestock in three local government areas (LGAs) of Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Sci World J 7(1):15–17
Torina A, Khoury C, Caracappa S, Maroli M (2006) Ticks infesting livestock on farms in Western Sicily, Italy. Exp Appl Acarol 38(1):75–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-005-5629-1
Tuama SJ, Al-Zihiry KJ, Al-Maliky HK (2007) Ticks infesting some domestic animals in thi-qar province, Southern Iraq. J Missan Res 4(7):1–12
Umar Y, George B, Ajanusi O (2010) Survey of hard ticks (Ixodidae) infesting camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Kano State, Nigeria. Anim Prod Res Adv 6:204–208
Wahba A (2001) Investigation of some tick species of cattle and buffaloes in Ismailia governorate. Egypt J Agric Res 79(3):1151–1162
Walker A, Koney E (1999) Distribution of ticks (Acari: ixodida) infesting domestic ruminants in Ghana. Bull Entomol Res 89(5):473–479
Wang Y-Z, Mu L-M, Zhang K, Yang M-H, Zhang L, Du J-Y, Liu Z-Q, Li Y-X, Lu W-H, Chen C-F (2015) A broad-range survey of ticks from livestock in Northern Xinjiang: changes in tick distribution and the isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto. Parasites Vectors 8:449. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-1021-0
Wasihun P, Doda D (2013) Study on prevalence and identification of ticks in Humbo district, Southern nations, nationalities, and peoples region (SNNPR), Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health 5(3):73–80. https://doi.org/10.5897/JVMAH12.040
Yacob H, Ataklty H, Kumsa B (2008) Major ectoparasites of cattle in and around Mekelle, northern Ethiopia. Entomol Res 38:126–130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-5967.2008.00148.x
Yaghfoori S, Razmi G, Heidarpour M (2013) Molecular detection of Theileria spp in sheep and vector ticks in Fasa and Kazeroun areas, Fars Province, Iran. Arch Razi Inst 68(2):159–164
Yagoub K, Abakar A, Bashar A, Mohammed S (2015) Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting sheep and goats in Nyala Town, South Darfur, Sudan. Sust J Agric Vet Sci 16(1):20–29
Yakhchali M, Hosseine A (2006) Prevalence and ectoparasites fauna of sheep and goats flocks in Urmia suburb, Iran. Veterinarski Arhiv 76:431–442
Yakhchali M, Rostami A, Esmaelzadeh M (2011) Diversity and seasonal distribution of ixodid ticks in the natural habitat of domestic ruminants in north and south of Iran. Rev Méd Vét 162(5):229–235
Yamane I, Nishiguchi A, Kobayashi S, Zeniya Y (2006) Cross-sectional survey of ixodid tick species on grazing cattle in Japan. Exp Appl Acarol 38(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-006-0005-3
Yassin SS, Abd El Baky S, Khalil MS, Allam NA (2016) Incidence of hard ticks infestations in ruminants settling Egyptian deserts regarding morpho-molecular characteristics. Bull Natl Res Cent 41:32–53
Yéo N, Bi ZFZ, Gragnon BG, Karamoko Y (2020) Prevalence and abundance of ticks infesting cattle and sheep in Poro Region (Côte d’Ivoire). Haya Saudi J Life Sci 5:10. https://doi.org/10.36348/sjls.2020.v05i05.00X
Yukari BA, Umur S (2002) The prevalance of tick species (Ixodoidea) in cattle, sheep and goats in the Burdur Region, Turkey. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 26:1263–1270
Yunus HA, Mamo YT, Yalew B, Mekonine A, Zeben E (2017) Identification of encountered bovine tick species in and around Gambela town. Am J Entomol 1(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.aje.20170101.11
Zahirnia A, Boroomand M, Nasirian H, Salehzadeh A, Soleimani-Asl S (2019) Comparing cytotoxicity of propoxur and Nepeta crispa (Lamiales: Lamiaceae) essential oil against invertebrate (Sf9) and vertebrate (L929) cell lines. Vet World 12:1698–1706. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2019.1698-1706
Zahirnia A, Boroomand M, Nasirian H, Soleimani-Asl S, Salehzadeh A, Dastan D (2019) The cytotoxicity of malathion and essential oil of Nepeta crispa (lamiales: lamiaceae) against vertebrate and invertebrate cell lines. Pan Afr Med J 33:285. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2019.33.285.18776
Zahirnia A, Aminpoor MA, Nasirian H (2021) The impact and trend of factors affecting the prevalence of head lice (Pediculus capitis) infestation in primary school students. Chulalongkorn Med J 65(4):357–365. https://doi.org/10.14456/clmj.2020.45
Zahirnia A, Seifi-Kar M, Nasirian H (2023) Evaluation of antifungal activity of hemolymph of American cockroaches against three human invasive fungal species: Aspergillus niger, Candida albicans and Penicillium oxalicum. Int J Trop Insect Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-023-01056-w
Zangana IK, Ali BA, Naqid IA (2013) Distribution of ectoparasites infested sheep and goats in Duhok province north Iraq. Basrah J Vet Res 12(1):54–64
Zeleke M, Bekele T (2004) Species of ticks on camels and their seasonal population dynamics in eastern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 36(3):225–231. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:trop.0000016830.30194.2a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and Funding
This work is a systematic and meta-analysis review that did not need ethical approval, did not receive any technical or financial support from any institution, and was done by the author at his own personal expense.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nasirian, H. Hard Tick Species Parasitism Levels in Domestic Ruminants with Their Distribution and Role as Vectors: A Detailed Global Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. Acta Parasit. 69, 1–105 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-023-00724-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-023-00724-8