Abstract
Purpose
Blastocystis sp. is one of the most prevalent intestinal protozoa found in humans and many other animals. The present study aimed to examine the distribution and genetic diversity of Blastocystis sp. in stool samples from patients with gastrointestinal complaints in İzmir, Turkey.
Methods
All stool samples of 439 patients with gastrointestinal complaints were examined by native-Lugol and trichrome staining. To investigate the presence of Blastocystis sp. in stool samples, DNA was isolated, and PCR was performed with the barcode region in the SSU rRNA gene. PCR positive samples were sequenced to identify subtypes and alleles of Blastocystis sp.
Results
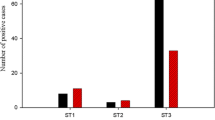
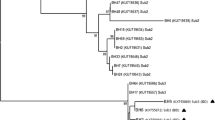
The prevalence of Blastocystis sp. was found to be 16.6% (73/439) in patients with gastrointestinal complaints in İzmir, Turkey. Three different Blastocystis sp. subtypes were identified. ST3 (28/55; 51.0%) was the most common subtype followed by ST2 (19/55; 34.5%) and ST1 (8/55; 14.5%). Itching and diarrhea were the most prominent clinical symptoms in Blastocystis sp. positive patients. When clinical symptoms and subtypes were compared, diarrhea was found in 62.5%, 47.4%, and 46.4% of patients with ST1, ST2, and ST3 subtypes, respectively. In addition, itching was found in 37.5%, 32.1%, and 21.1% of patients with ST1, ST3, and ST2, respectively. Six distinct alleles were identified by allele analysis of Blastocystis 18S rRNA gene: allele 4 for ST1, alleles 9, 11, and 12 for ST2, and alleles 34 and 36 for ST3. In this study, Blastocystis sp. was detected in 16 of 21 districts, including the central and rural districts of İzmir. Although ST1 was detected in central districts, it was not found in rural districts.
Conclusion
This study provides comprehensive data on the prevalence and molecular epidemiology of the genetic diversity at the level of subtypes and alleles of Blastocystis sp. in different districts of İzmir province in Turkey. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study which evaluates the distribution of subtypes and alleles of Blastocystis sp. according to PCR and SSU rRNA gene sequencing in patients with gastrointestinal complaints in different districts of İzmir province in Turkey.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. New molecular sequences produced for the study are available in GenBank.
References
Stensvold CR, Clark CG (2016) Current status of Blastocystis: a personal view. Parasitol Int 65(6):763–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2016.05.015
Stensvold CR, Suresh GK, Tan KS, Thompson RC, Traub RJ, Viscogliosi E et al (2007) Terminology for Blastocystis subtypes—a consensus. Trends Parasitol 23(3):93–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2007.01.004
Alexeieff A (1911) Sur la nature des formations dites kystes de Trichomonas intestinalis. CR Soc Biol 71:296–298
Brumpt E (1912) Blastocystis hominis n. sp. et formes voisines. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 5:725–730
Zierdt CH (1991) Blastocystis hominis—past and future. Clin Microbiol Rev 4(1):61–79. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.4.1.61
Parija SC, Jeremiah S (2013) Blastocystis: taxonomy, biology and virulence. Trop Parasitol 3(1):17. https://doi.org/10.4103/2229-5070.113894
Ramirez JD, Sanchez A, Hernandez C, Florez C, Bernal MC, Giraldo JC et al (2016) Geographic distribution of human Blastocystis subtypes in South America. Infect Genet Evol 41:32–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2016.03.017
Valenca Barbosa C, de Jesus BR, Pereira Igreja R, d’Avila Levy CM, Werneck de Macedo H, Carneiro Santos HL (2017) Distribution of Blastocystis subtypes isolated from humans from an urban community in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Parasit Vectors 10(1):518. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2458-0
Mohamed RT, El-Bali MA, Mohamed AA, Abdel-Fatah MA, El-Malky MA, Mowafy NM et al (2017) Subtyping of Blastocystis sp. isolated from symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Parasit Vectors 10(1):174. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2114-8
Tan KS (2008) New insights on classification, identification, and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Clin Microbiol Rev 21(4):639–665. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00022-08
Parkar U, Traub RJ, Vitali S, Elliot A, Levecke B, Robertson I et al (2010) Molecular characterization of Blastocystis isolates from zoo animals and their animal-keepers. Vet Parasitol 169(1):8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.12.032
Stensvold CR, Lewis HC, Hammerum AM, Porsbo LJ, Nielsen SS, Olsen KE et al (2009) Blastocystis: unravelling potential risk factors and clinical significance of a common but neglected parasite. Epidemiol Infect 137(11):1655–1663. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268809002672
Alfellani MA, Jacob AS, Perea NO, Krecek RC, Taner-Mulla D, Verweij JJ et al (2013) Diversity and distribution of Blastocystis sp. subtypes in non-human primates. Parasitology 140(8):966–971. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182013000255
Casero RD, Mongi F, Sanchez A, Ramirez JD (2015) Blastocystis and urticaria: examination of subtypes and morphotypes in an unusual clinical manifestation. Acta Trop 148:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2015.05.004
Dogruman-Al F, Kustimur S, Yoshikawa H, Tuncer C, Simsek Z, Tanyuksel M et al (2009) Blastocystis subtypes in irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease in Ankara, Turkey. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104(5):724–727. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02762009000500011
Abdel-Hafeez EH, Ahmad AK, Abdelgelil NH, Abdellatif MZ, Kamal AM, Hassanin KM et al (2016) Immunopathological assessments of human Blastocystis spp. in experimentally infected immunocompetent and immunosuppresed mice. Parasitol Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4951-3
Hussein EM, Hussein AM, Eida MM, Atwa MM (2008) Pathophysiological variability of different genotypes of human Blastocystis hominis Egyptian isolates in experimentally infected rats. Parasitol Res 102(5):853–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0833-z
Stensvold CR, Clark CG (2020) Pre-empting Pandora’s box: Blastocystis subtypes revisited. Trends Parasitol 36(3):229–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2019.12.009
Maloney JG, Da Cunha MJR, Molokin A, Cury MC, Santin M (2021) Next-generation sequencing reveals wide genetic diversity of Blastocystis subtypes in chickens including potentially zoonotic subtypes. Parasitol Res 120(6):2219–2231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07170-3
Stensvold CR, Tan KSW, Clark CG (2020) Blastocystis. Trends Parasitol 36(3):315–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2019.12.008
Stensvold CR, Clark CG (2016) Molecular identification and subtype analysis of Blastocystis. Curr Protoc Microbiol 43:20A22 21-20A 2210. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpmc.17
Ramirez JD, Sanchez LV, Bautista DC, Corredor AF, Florez AC, Stensvold CR (2014) Blastocystis subtypes detected in humans and animals from Colombia. Infect Genet Evol 22:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2013.07.020
Poirier P, Wawrzyniak I, Vivares CP, Delbac F, El Alaoui H (2012) New insights into Blastocystis spp.: a potential link with irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS Pathog 8(3):e1002545. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002545
Roberts T, Ellis J, Harkness J, Marriott D, Stark D (2014) Treatment failure in patients with chronic Blastocystis infection. J Med Microbiol 63(Pt 2):252–257. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.065508-0
Verma R, Delfanian K (2013) Blastocystis hominis associated acute urticaria. Am J Med Sci 346(1):80–81. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3182801478
Cakir F, Cicek M, Yildirim IH (2019) Determination the subtypes of Blastocystis sp. and evaluate the effect of these subtypes on pathogenicity. Acta Parasitol 64(1):7–12. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-018-00002-y
Bahrami F, Babaei E, Badirzadeh A, Riabi TR, Abdoli A (2019) Blastocystis, urticaria, and skin disorders: review of the current evidences. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39(6):1027–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03793-8
Aydin M, Yazici M, Demirkazik M, Koltas I, Cikman A, Gulhan B et al (2019) Molecular characterization and subtyping of Blastocystis in urticarial patients in Turkey. Asian Pac J Trop Med 12(10):450–456. https://doi.org/10.4103/1995-7645.269905
Gulhan B, Aydin M, Demirkazik M, Koltas IS, Cikman A, Turkmen K et al (2020) Subtype distribution and molecular characterization of Blastocystis from hemodialysis patients in Turkey. J Infect Dev Ctries 14(12):1448–1454. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.12650
Dogan N, Aydin M, Tuzemen NU, Dinleyici EC, Oguz I, Dogruman-Al F (2017) Subtype distribution of Blastocystis spp. isolated from children in Eskisehir, Turkey. Parasitol Int 66(1):948–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2016.10.008
Stensvold CR (2013) Comparison of sequencing (barcode region) and sequence-tagged-site PCR for Blastocystis subtyping. J Clin Microbiol 51(1):190–194. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.02541-12
Scicluna SM, Tawari B, Clark CG (2006) DNA barcoding of blastocystis. Protist 157(1):77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protis.2005.12.001
Aykur M, Caliskan Kurt C, Dirim Erdogan D, Biray Avci C, Vardar R, Aydemir S et al (2019) Investigation of Dientamoeba fragilis prevalence and evaluation of sociodemographic and clinical features in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. Acta Parasitol 64(1):162–170. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-018-00017-5
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Alfellani MA, Stensvold CR, Vidal-Lapiedra A, Onuoha ES, Fagbenro-Beyioku AF, Clark CG (2013) Variable geographic distribution of Blastocystis subtypes and its potential implications. Acta Trop 126(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.12.011
Stensvold CR, Alfellani M, Clark CG (2012) Levels of genetic diversity vary dramatically between Blastocystis subtypes. Infect Genet Evol 12(2):263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2011.11.002
Scanlan PD, Stensvold CR (2013) Blastocystis: getting to grips with our guileful guest. Trends Parasitol 29(11):523–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2013.08.006
Tan KS, Mirza H, Teo JD, Wu B, MacAry PA (2010) Current views on the clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Curr Infect Dis Rep 12(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11908-009-0073-8
Clark CG, van der Giezen M, Alfellani MA, Stensvold CR (2013) Recent developments in Blastocystis research. Adv Parasitol 82:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407706-5.00001-0
Mulayim S, Aykur M, Dagci H, Dalkilic S, Aksoy A, Kaplan M (2021) Investigation of isolated Blastocystis subtypes from cancer patients in Turkey. Acta Parasitol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-020-00322-y
Yersal O, Malatyali E, Ertabaklar H, Oktay E, Barutca S, Ertug S (2016) Blastocystis subtypes in cancer patients: analysis of possible risk factors and clinical characteristics. Parasitol Int 65(6 Pt B):792–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2016.02.010
Beyhan YE, Yilmaz H, Cengiz ZT, Ekici A (2015) Clinical significance and prevalence of Blastocystis hominis in Van, Turkey. Saudi Med J 36(9):1118. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2015.9.12444
Ulusan Ö, Zorbozan O, Kardelen I, Töz S, Ünver A, Turgay N (2019) The distribution of the intestinal parasites detected in Ege University Medical Faculty Parasitology Direct Diagnosis Laboratory; 10-years evaluation. Türk Mikrobiyol Cemiyeti Dergisi 49(2):86–91. https://doi.org/10.5222/TMCD.2019.086
Cengiz ZT, Yılmaz H, Beyhan YE, Çiçek M (2019) A comprehensive retrospective study: intestinal parasites in human in Van Province. Turk Parazitol Dergisi 43(2):70. https://doi.org/10.4274/tpd.galenos.2019.5997
Dagci H, Kurt O, Demirel M, Ostan I, Azizi NR, Mandiracioglu A et al (2008) The prevalence of intestinal parasites in the province of Izmir, Turkey. Parasitol Res 103(4):839–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1065-6
Stensvold CR (2013) Blastocystis: genetic diversity and molecular methods for diagnosis and epidemiology. Trop Parasitol 3(1):26–34. https://doi.org/10.4103/2229-5070.113896
Yoshikawa H, Iwamasa A (2016) Human Blastocystis subtyping with subtype-specific primers developed from unique sequences of the SSU rRNA gene. Parasitol Int 65(6 Pt B):785–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2016.03.002
Sankur F, Ayturan S, Malatyalı E, Ertabaklar H, Ertug S (2017) The distribution of Blastocystis subtypes among school-aged children in Mugla, Turkey Iran. J Parasitol 12(4):580
Aykur M, Camyar A, Turk BG, Sin AZ, Dagci H (2022) Evaluation of association with subtypes and alleles of Blastocystis with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Acta Trop 231:106455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2022.106455
Nemati S, Falahati Anbaran M, Mohammad Rahimi H, Hosseini MS, Aghaei S, Khalili N et al (2021) Evolutionary and phylogenetic analyses of the barcoding region suggest geographical relationships among Blastocystis sp., ST3 in humans. Infect Genet Evolut 96:105151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105151
Popruk S, Adao DEV, Rivera WL (2021) Epidemiology and subtype distribution of Blastocystis in humans: a review. Infect Genet Evolut 95:105085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105085
Dagci H, Kurt O, Demirel M, Mandiracioglu A, Aydemir S, Saz U et al (2014) Epidemiological and diagnostic features of Blastocystis infection in symptomatic patients in Izmir Province, Turkey Iran. J Parasitol 9(4):519–529
Yowang A, Tsaousis AD, Chumphonsuk T, Thongsin N, Kullawong N, Popluechai S et al (2018) High diversity of Blastocystis subtypes isolated from asymptomatic adults living in Chiang Rai, Thailand. Infect Genet Evol 65:270–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2018.08.010
Vogelberg C, Stensvold CR, Monecke S, Ditzen A, Stopsack K, Heinrich-Grafe U et al (2010) Blastocystis sp. subtype 2 detection during recurrence of gastrointestinal and urticarial symptoms. Parasitol Int 59(3):469–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2010.03.009
El Safadi D, Gaayeb L, Meloni D, Cian A, Poirier P, Wawrzyniak I et al (2014) Children of Senegal River Basin show the highest prevalence of Blastocystis sp. ever observed worldwide. BMC Infect Dis 14(1):164. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-14-164
Poirier P, Wawrzyniak I, Albert A, El Alaoui H, Delbac F, Livrelli V (2011) Development and evaluation of a real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of Blastocystis parasites in human stool samples: prospective study of patients with hematological malignancies. J Clin Microbiol 49(3):975–983. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.01392-10
Ramirez JD, Florez C, Olivera M, Bernal MC, Giraldo JC (2017) Blastocystis subtyping and its association with intestinal parasites in children from different geographical regions of Colombia. PLoS ONE 12(2):e0172586. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172586
WHO (2011) Microbial fact sheets. World Health Organization guidelines for drinking-water quality (WHO GDWQ) 271–273
Li LH, Zhou XN, Du ZW, Wang XZ, Wang LB, Jiang JY et al (2007) Molecular epidemiology of human Blastocystis in a village in Yunnan province, China. Parasitol Int 56(4):281–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2007.06.001
Lee LI, Chye TT, Karmacharya BM, Govind SK (2012) Blastocystis sp.: waterborne zoonotic organism, a possibility? Parasit Vectors 5(1):130. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-5-130
Leelayoova S, Siripattanapipong S, Thathaisong U, Naaglor T, Taamasri P, Piyaraj P et al (2008) Drinking water: a possible source of Blastocystis spp. subtype 1 infection in schoolchildren of a rural community in central Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 79(3):401–406. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2008.79.401
Suresh K, Tan T (2009) Blastocystis in water-need for screening? Water Pract Technol. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2009.072
Koloren Z, Gulabi BB, Karanis P (2018) Molecular identification of Blastocystis sp. subtypes in water samples collected from Black sea, Turkey. Acta Trop 180:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.12.029
Noradilah SA, Moktar N, Anuar TS, Lee IL, Salleh FM, Manap S et al (2017) Molecular epidemiology of blastocystosis in Malaysia: does seasonal variation play an important role in determining the distribution and risk factors of Blastocystis subtype infections in the Aboriginal community? Parasit Vectors 10(1):360. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2294-2
Noradilah SA, Lee IL, Anuar TS, Salleh FM, Manap SNAA, Mohtar NSHM et al (2016) Occurrence of Blastocystis sp. in water catchments at Malay villages and Aboriginal settlement during wet and dry seasons in Peninsular Malaysia. PeerJ 4:e2541. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2541
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients who participated in the study. This study was partly supported by the grant given by the Scientific Research Projects Branch Directorate of Ege University, Turkey (Grant number: 13-TIP-092).
Funding
This study was partly supported by the grant given by the Scientific Research Projects Branch Directorate of Ege University, Turkey (Grant number: 13-TIP-092).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by Dokuz Eylül University Clinical Research Ethics Committee (Protocol no.: 2013/16-02).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aykur, M., Calıskan Kurt, C., Dirim Erdogan, D. et al. Distribution and Phylogenetic Analysis of Subtypes and Alleles of Blastocystis sp. in the Stool Samples Collected from Patients with Gastrointestinal Complaints in İzmir, Turkey. Acta Parasit. 68, 304–316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-023-00665-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-023-00665-2