Abstract
Purpose
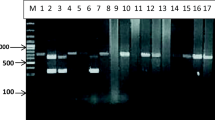
Identification of different genotypes of echinococcal cyst in various domestic herbivores and humans within the target area was the principal aim of the present study, performed using sequence data of cox1 and nad1 mitochondrial genes.
Methods
A total of 57 cystic echinococcosis (CE) cysts were isolated from indigenous livestock including 45 cattle, 9 sheep and 3 goats from several slaughterhouses in Guilan Province. Moreover, 12 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) CE cyst tissues from humans were also included, obtained from the archives of several hospitals in Rasht, the capital of Guilan. Genetic sequencing was conducted using mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (cox1) and NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (nad1) genes.
Results
Our results found that E. granulosus sensu stricto (s.s.) and E. ortleppi were present in 92.7% and 7.2% isolates, respectively. E. granulosus s.s. (genotypes G1 and G3) and E. ortleppi were isolated from various livestock whereas all CE cysts isolated from humans were E. granulosus s.s. G1 genotype.
Conclusion
We found that E. granulosus s.s. G1 was the predominant genotype within the study region. This is the first study to report E. ortleppi in cattle in Iran.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moro P, Schantz PM (2009) Echinococcosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis 13(2):125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2008.03.037
Rahimi MT, Sharifdini M, Ahmadi A, Laktarashi B, Mahdavi SA, Kia EB (2011) Hydatidosis in human and slaughtered herbivores in Mazandaran province, northern Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 1:212–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2222-1808(11)60031-5
Rokni M (2009) Echinococcosis/hydatidosis in Iran. Iran J Parasitol 4:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1201-9712(09)60564-6
McManus DP (2013) Current status of the genetics and molecular taxonomy of Echinococcus species. Parasitology 140:1617–1623. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182013000802
Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP (1992) Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 54:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6851(92)90109-W
Le TH, Pearson MS, Blair D, Dai N, Zhang LH, McManus DP (2002) Complete mitochondrial genomes confirm the distinctiveness of the horse-dog and sheep-dog strains of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitology 124:97–112. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182001008976
Huttner M, Nakao M, Wassermann T, Siefert L, Boomker JD, Dinkel A, Sako Y, Mackenstedt U, Romig T, Ito A (2008) Genetic characterization and phylogenetic position of Echinococcus felidis (Cestoda: Taeniidae) from the African lion. Int J Parasitol 38:861–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.10.013
Lavikainen A, Lehtinen MJ, Meri T, Hirvela-Koski V, Meri S (2003) Molecular genetic characterization of the Fennoscandian cervid strain, a new genotypic group (G10) of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitology 127:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182003003780
Saarma U, Jogisalu I, Moks E, Varcasia A, Lavikainen A, Oksanen A, Simsek S, Andresiuk V, Denegri G, Gonzalez LM, Ferrer E, Garate T, Rinaldi L, Maravilla P (2009) A novel phylogeny for the genus Echinococcus, based on nuclear data, challenges relationships based on mitochondrial evidence. Parasitology 136:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182008005453
Rojas CAA, Romig T, Lightowlers MW (2014) Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes infecting humans–review of current knowledge. Int J Parasitol 44:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.08.008
Kinkar L, Laurimäe T, Sharbatkhori M, Mirhendi H, Kia EB, Ponce-Gordo F, Andresiuk V, Simsek S, Lavikainen A, Irshadullah M (2017) New mitogenome and nuclear evidence on the phylogeny and taxonomy of the highly zoonotic tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto. Infect Genet Evol 52:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2017.04.023
Deplazes P, Rinaldi L, Rojas CA, Torgerson P, Harandi M, Romig T, Antolova D, Schurer J, Lahmar S, Cringoli G (2017) Global distribution of alveolar and cystic echinococcosis. Adv Parasitol 95:315–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apar.2016.11.001
Dousti M, Abdi J, Bakhtiyari S, Mohebali M, Mirhendi S, Rokni M (2013) Genotyping of hydatid cyst isolated from human and domestic animals in Ilam Province, Western Iran Using PCR-RFLP. Iran J Parasitol 8:47–52
Nikmanesh B, Mirhendi H, Mahmoudi S, Rokni MB (2017) Multilocus sequence analysis of Echinococcus granulosus strains isolated from humans and animals in Iran. Exp Parasitol 183:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2017.10.002
Sharbatkhori M, Fasihi Harandi M, Mirhendi H, Hajialilo E, Kia EB (2011) Sequence analysis of cox1 and nad1 genes in Echinococcus granulosus G3 genotype in camels (Camelus dromedarius) from central Iran. Parasitol Res 108(3):521–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2092-7
Sharbatkhori M, Mirhendi H, Jex AR, Pangasa A, Campbell BE, Kia EB, Eshraghian MR, Harandi MF, Gasser RB (2009) Genetic categorization of Echinococcus granulosus from humans and herbivorous hosts in Iran using an integrated mutation scanning-phylogenetic approach. Electrophoresis 30:2648–2655. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200900145
Matini M, Fallah M, Maghsood AH, Saidijam M, Fasihi Harandi M (2019) Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in livestock and human in Hamadan, western Iran. Iran J Parasitol 14:288–296
Rostami S, Shariat Torbaghan S, Dabiri S, Babaei Z, Ali Mohammadi M, Sharbatkhori M, Fasihi Harandi M (2015) Genetic characterization of Echinococcus granulosus from a large number of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples of human isolates in Iran. Am J Trop Med Hyg 92:588–594. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0585
Parsa F, Fasihi Harandi M, Rostami S, Sharbatkhori M (2012) Genotyping Echinococcus granulosus from dogs from western Iran. Exp Parasitol 132(2):308–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2012.07.010
Shariatzadeh SA, Spotin A, Gholami S, Fallah E, Hazratian T, Mahami-Oskouei M, Montazeri F, Moslemzadeh HR, Shahbazi A (2015) The first morphometric and phylogenetic perspective on molecular epidemiology of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato in stray dogs in a hyperendemic Middle East focus, northwestern Iran. Parasit Vectors 8:409. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-1025-9
Heidari Z, Sharbatkhori M, Mobedi I, Mirhendi SH, Nikmanesh B, Sharifdini M, Mohebali M, Zarei Z, Arzamani K, Kia EB (2019) Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus in canines in North-Khorasan Province, northeastern Iran, identified using morphology and genetic characterization of mitochondrial DNA. Parasit Vectors 12:606. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3859-z
Ebrahimipour M, Sadjjadi SM, Yousofi Darani H, Najjari M (2017) Molecular Studies on Cystic Echinococcosis of Camel (Camelus dromedarius) and Report of Echinococcus ortleppi in Iran. Iran J Parasitol 12(3):323–331
Hajialilo E, Harandi MF, Sharbatkhori M, Mirhendi H, Rostami S (2012) Genetic characterization of Echinococcus granulosus in camels, cattle and sheep from the south-east of Iran indicates the presence of the G3 genotype. J Helminthol 86:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X11000320
Nikmanesh B, Mirhendi H, Ghalavand Z, Alebouyeh M, Sharbatkhori M, Kia E, Mohebali M, Eghbali M, Rokni MB (2014) Genotyping of Echinococcus granulosus isolates from human clinical samples based on sequencing of mitochondrial genes in Iran, Tehran. Iran J Parasitol 9:20–27
Pezeshki A, Akhlaghi L, Sharbatkhori M, Razmjou E, Oormazdi H, Mohebali M, Meamar AR (2013) Genotyping of Echinococcus granulosus from domestic animals and humans from Ardabil Province, northwest Iran. J Helminthol 87:387–391. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X1200051X
Sharbatkhori M, Tanzifi A, Rostami S, Rostami M, Harandi MF (2016) Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes in domestic livestock and humans in Golestan Province. Iran Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 58:38. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1678-9946201658038
Khademvatan S, Yousefi E, Rafiei A, Rahdar M, Saki J (2013) Molecular characterization of livestock and human isolates of Echinococcus granulosus from south-west Iran. J Helminthol 87:240–244. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X12000296
Berenji F, Shamsian SA, Nouri Daloee M, Fattahi Masoom SH, Moghaddas E (2019) Genotyping of Echinococcus granulosus isolates from human in khorasan province, north-eastern Iran. Iran J Parasitol 14(1):52–58
Hammad SJ, Cavallero S, Milardi GL, Gabrielli S, Al-Nasiri FS (2018) Molecular genotyping of Echinococcus granulosus in the north of Iraq. Vet Parasitol 249:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.11.010
Eryıldız C, Şakru N (2012) Molecular characterization of human and animal isolates of Echinococcus granulosus in the Thrace region. Turkey Balk Med J 29:261. https://doi.org/10.5152/balkanmedj.2012.072
Casulli A, Manfredi MT, La Rosa G, Cerbo AR, Genchi C, Pozio E (2008) Echinococcus ortleppi and E. granulosus G1, G2 and G3 genotypes in Italian bovines. Vet Parasitol 155:168–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.04.004
Varcasia A, Canu S, Kogkos A, Pipia AP, Scala A, Garippa G, Seimenis A (2007) Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus in sheep and goats of Peloponnesus, Greece. Parasitol Res 101:1135–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0568-x
Bowles J, McManus DP (1993) Molecular variation in Echinococcus. Acta Trop 53:291–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-706X(93)90035-A
Busi M, Šnábel V, Varcasia A, Garippa G, Perrone V, De Liberato C, D’Amelio S (2007) Genetic variation within and between G1 and G3 genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus in Italy revealed by multilocus DNA sequencing. Vet Parasitol 150:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.09.003
Mario L, Takano K, Brochado JF, Costa CV, Soares AG, Yamano K, Yagi K, Katoh Y, Takahashi K (2011) Infection of humans and animals with Echinococcus granulosus (G1 and G3 strains) and E. ortleppi in southern Brazil. Vet Parasitol 177:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.11.018
Sharma M, Sehgal R, Fomda BA, Malhotra A, Malla N (2013) Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus cysts in north Indian patients: identification of G1, G3, G5 and G6 genotypes. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7:e2262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002262
Jafari R, Sanei B, Baradaran A, Spotin A, Bagherpour B, Darani HY (2017) Genetic characterization of Echinococcus granulosus strains isolated from humans based on nad1 and cox1 gene analysis in Isfahan, central Iran. J Helminthol 92:696–702. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X17000967
Romig T, Deplazes P, Jenkins D, Giraudoux P, Massolo A, Craig PS, Wassermann M, Takahashi K, De La Rue M (2017) Ecology and life cycle patterns of Echinococcus species. Adv Parasitol 95:213–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apar.2016.11.002
Pednekar RP, Gatne ML, Thompson RC, Traub RJ (2009) Molecular and morphological characterisation of Echinococcus from food producing animals in India. Vet Parasitol 165:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.06.021
Addy F, Wassermann M, Banda F, Mbaya H, Aschenborn J, Aschenborn O (2017) Genetic polymorphism and population structure of Echinococcus ortleppi. Parasitology 144:450–458. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182016001840
Mbaya H, Magambo J, Njenga S, Zeyhle E, Mbae C, Mulinge E, Wassermann M, Kern P, Romig T (2014) Echinococcus spp. in central Kenya: a different story. Parasitol Res 113:3789–3794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4045-z
Ahmed ME, Eltom KH, Musa NO, Ali IA, Elamin FM, Grobusch MP, Aradaib IE (2013) First report on circulation of Echinococcus ortleppi in the one humped camel (Camelus dromedaries). Sudan BMC Vet Res 9:127. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-6148-9-127
Hodžić A, Alić A, Šupić J, Škapur V, Duscher GG (2018) Echinococcus ortleppi, the cattle strain in a crested porcupine (Hystrix cristata): A new host record. Vet Parasitol 256:32–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.05.004
Boufana B, Stidworthy M, Bell S, Chantrey J, Masters N, Unwin S, Wood R, Lawrence R, Potter A, McGarry J (2012) Echinococcus and Taenia spp. from captive mammals in the United Kingdom. Vet Parasitol 190:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.05.023
Alvi MA, Ohiolei JA, Saqib M, Li L, Tayyab MH, Alvi AA, Wu Y-T, Fu B-Q, Yan H-B, Jia W-Z (2020) Echinococcus granulosus (sensu stricto)(G1, G3) and E. ortleppi (G5) in Pakistan: phylogeny, genetic diversity and population structural analysis based on mitochondrial DNA. Parasit Vectors 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105470
Monteiro DU, de Azevedo MI, Weiblen C, Ribeiro TC, Emmanouilidis J, Tonin AA, de Avila BS, de la Rue ML (2016) Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto, Echinococcus canadensis (G7), and Echinococcus ortleppi in fertile hydatid cysts isolated from cattle in southern Brazil. Acta Trop 164:41–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.08.017
Ali V, Martinez E, Duran P, Seláez M, Barragan M, Nogales P, y Lillo AP, Castañares M, Claros Y, Deplazes P, (2020) Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto, Echinococcus ortleppi; and E. intermedius (G7) are present in Bolivia. Parasitology 147:949–956. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182020000529
Thapa NK, Armua-Fernandez MT, Kinzang D, Gurung RB, Wangdi P, Deplazes P (2017) Detection of Echinococcus granulosus and Echinococcus ortleppi in Bhutan. Parasitol Int 66:139–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2016.12.010
Grenouillet F, Umhang G, Arbez-Gindre F, Mantion G, Delabrousse E, Millon L, Boué F (2014) Echinococcus ortleppi infections in humans and cattle, France. Emerg Infect Dis 20:2100–2102. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2012.140641
Omer R, Dinkel A, Romig T, Mackenstedt U, Elnahas A, Aradaib I, Ahmed M, Elmalik K, Adam A (2010) A molecular survey of cystic echinococcosis in Sudan. Vet Parasitol 169:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.01.004
Corrêa F, Stoore C, Horlacher P, Jiménez M, Hidalgo C, Alvarez Rojas CA, Figueiredo Barros G, Bunselmeyer Ferreira H, Hernández M, Cabrera G (2018) First description of Echinococcus ortleppi and cystic echinococcosis infection status in Chile. PLoS ONE 13(5):e0197620. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197620
Kamenetzky L, Gutierrez AM, Canova SG, Haag KL, Guarnera EA, Parra A, Garcı́aRosenzvit GEMC (2002) Several strains of Echinococcus granulosus infect livestock and humans in Argentina. Infect Genet Evol 2:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1567-1348(02)00131-4
Dybicz M, Borkowski PK, Jonas M, Wasiak D, Małkowski P (2019) First Report of Echinococcus ortleppi in human cases of cystic echinococcosis in Poland. BioMed Res Int 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2013.03.005
Bowles J, Van Knapen F, Mcmanus D (1992) Cattle strain of Echinococcus granulosus and human infection. Lancet 339:1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(92)92003-x
Maravilla P, Thompson RA, Palacios-Ruiz JA, Estcourt A, Ramirez-Solis E, Mondragon-de-la-Peña C, Moreno-Moller M, Cardenas-Mejia A, Mata-Miranda P, Aguirre-Alcantara M-T (2004) Echinococcus granulosus cattle strain identification in an autochthonous case of cystic echinococcosis in central Mexico. Acta Trop 92:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2004.07.001
Mogoye BK, Menezes CN, Wong ML, Stacey S, von Delft D, Wahlers K, Wassermann M, Romig T, Kern P, Grobusch MP (2013) First insights into species and genotypes of Echinococcus in South Africa. Vet Parasitol 196:427–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.03.033
Van De N, Minh PN, Le Van Duyet NNB, Son TN, Jung B-K, Chai J-Y (2020) Two human cases of Echinococcus ortleppi infection in the lung and heart in Vietnam. Korean J Parasitol 8:45–51. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2020.58.4.451
Shi Y, Wan X, Wang Z, Li J, Jiang Z, Yang Y (2019) First description of Echinococcus ortleppi infection in China. Parasit Vectors 12:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3653-y
Nakao M, McManus DP, Schantz PM, Craig PS, Ito A (2007) A molecular phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus inferred from complete mitochondrial genomes. Parasitology 134:713–722. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182006001934
Zhang L, Hu M, Jones A, Allsopp BA, Beveridge I, Schindler AR et al (2007) Characterization of Taenia madoquae and Taenia regis from carnivores in Kenya using genetic markers in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and their relationships with other selected taeniids. Mol Cell Probes 21:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2007.05.003
Funding
This study has been financially supported by Research Deputy of Guilan University of Medical Sciences, with project No. 95110216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS, KA, BM and EBK conceived and designed the study. AZ and KN provided the samples. KN performed the molecular experiments. MS supervised molecular phylogenetic analyses and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Guilan University of Medical Sciences with ethics number of IR.GUMS.REC.1395.345.
Informed Consent
Formal consent and permission for research use of human CE cysts samples were obtained from both Ethics Committee of Guilan University of Medical Sciences and the responsible authorities of the referral hospitals (Razi and Poursina) in Rasht, Guilan, Iran.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nematdoost, K., Ashrafi, K., Majidi-Shad, B. et al. Genetic Characterization of Echinococcus granulosus Sensu Lato in Livestock and Human Isolates from North of Iran Indicates the Presence of E. ortleppi in Cattle. Acta Parasit. 66, 446–454 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-020-00293-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-020-00293-0