Abstract
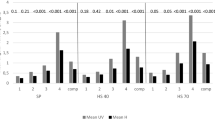
The postural balance is a important aspect of assessment in vestibular rehabilitation therapy. As the computerized dynamic posturography, the foam posturography performed by using foam in posturography is a useful measurement tool for postural balance. Then, the reliability of foam posturography is critical in clinic. To our knowledge, there is no report about the test-retest reliability of foam posturography in the patients with vertigo in China. The foam posturography was taken on the patients with vertigo in stable state and repeated in 3 to 5 days. In the two assessments of test and retest, all subjects stood under 4 sensory conditions, such as firm surface with eyes open (T1), firm surface with eyes closed (T2), foam surface with eyes open (T3) and foam surface with eyes closed (T4) for 30 seconds respectively. The average sway velocity (SV) of center of pressure (COP) under feet of upright standing was recorded as research parameter. The results of patients with vertigo were compared with those of normal subjects. It demonstrated that all normal subjects did not fall in the two assessments. There were 10 of 34 patients with vertigo at least fell one time during the two assessments, and the SVs of these subjects did not taken the analysis of test-retest reliability. The results showed that: (1) The interclass correlation coefficients (ICC) of all 49 subjects including normal subjects and patients without falling were 0.887–0.973 according to the T1–T4 between two assessment. (2) The SVs between the normal subjects and patients were significantly different in the T2 (t = 2.018, P = 0.049) and T4 (t = 3.905, P < 0.001) in the first assessment and in the T4 (t = 3.715, P = 50.001) in the second. And (3) the cases of falling between two assessments were not significant different (χ 2 = 0.073, P = 0.787) in the patients with vertigo. It is concluded from this study that the foam posturography has high test-retest reliability to assess the postural balance in the patients with vertigo in stable state, indicating the foam posturography can be used as the valid means to assess the improvement of postural balance for patients with vertigo in the vestibular rehabilitation therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Neill D, Gill-Body K M, Kerbs D E. Posturography changes do not predict functional performance changes. Am J Otol, 1998, 19(6): 797–803
Herdman S J. Vestibular rehabilitation. 2nd. Philadelphia (PA): F. A. Davis Co, 1994: 247–286
Liu B, Kong W J, Lai C Q, Hu Y J, Wu Y Y. Timed balance test and static posturography in the patients with unilateral vestibular hypofunction. Zhonghua Erkexue Zazhi, 2007, 42(3): 165–168 (in Chinese)
Weber P C, Cass S P. Clinical assessment of postural stability. Am J Otol, 1993, 14(6): 566–569
Nashner L M, Peters J F. Dynamic posturography in the diagnosis and management of dizziness and balance disorders. Neurol Clin, 1990, 8(2): 331–349
Shumway-Cook A, Horak F B. Assessing the influence of sensory integration on balance: suggestions from the field. Phys Ther, 1986, 66(10): 1548–1550
Cohen H, Blatchly C A, Gombash L L. A study of the clinical test of sensory interaction and balance. Phys Ther, 1993, 73(6): 346–351
Baloh R W, Jacobson K M, Beykirch K, Honrubia V. Static and dynamic posturography in patients with vestibular and cerebellar lesions. Arch Neurol, 1998, 55(5): 649–654
Norre M E. Sensory interaction testing in plat posturography. J Laryngol Otol, 1993, 107(6): 496–501
Editorial board of Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Chinese Otolaryngology of Chinese Medical Association. Diagnosis basis and curative effect appraisal of Meniere’s disease. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi, 1997, 32: 71 (in Chinese)
Kong W J, Liu B, Wu Q, Wu Y Y. Postural characteristics of healthy subjects under different thickness of foam. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Waike Zazhi, 2007, 42(10): 721–725 (in Chinese)
Horak F B, Jones-Rycewicz C, Black F O, Shumway-Cook A. Effects of vestibular rehabilitation on dizziness and imbalance. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1992, 106(2): 175–180
Cass S P, Borello-France D, Furman J M. Functional outcome of vestibular rehabilitation in patients with abnormal sensoryorganization testing. Am J Otol, 1996, 17(4): 581–594
Black F O, Angel C R, Pesznecker S C, Gianna C. Outcome analysis of individualized vestibular rehabilitation protocols. Am J Otol, 2000, 21(4): 543–551
Kong W J, Liu B, Leng Y M. Individualized integrated therapy on patients with vertigo. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Waike Zazhi, 2008, 22(4):145–149 (in Chinese)
Horak F B. Clinical assessment of balance disorder. Gait Posture, 1997, 6(1): 76–84
Pyykkö I, Enbom H, Magnusson M, Schalén L. Effect of proprioceptor stimulation on postural stability in patients with peripheral or central vestibular lesion. Acta Otolaryngol, 1991, 111(1): 27–35
El-Kahky A M, Kingma H, Dolmans M, de Jong I. Balance control near the limit of stability in various sensory conditions in healthy subjects and patients suffering from vertigo or balance disorders: impact of sensory input on balance control. Acta Otolaryngol, 2000, 120(4): 508–516
Girardi M, Konrad H R, Amin M, Hughes L F. Predicting fall risks in an elderly population: computer dynamic posturography versus electronystagmography test results. Laryngoscope, 2001, 111(9): 1528–1532
Jin D M, Yan T B, Zen H H. Validity and reliability of Berg balance scale on assessing balance function. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi, 2003, 18(1): 25–27 (in Chinese)
Jin D M, Yan T B, Tan W J. Reliability of balance performance monitor in the assessment of balance function. Zhonghua Wuli Yixue Yu Kangfu Zazhi, 2002, 24(4): 203–205 (in Chinese)
Loughran S, Tennant N, Kishore A, Swan I R. Interobserver reliability in evaluating postural stability between clinicians and posturography. Clin Otolaryngol, 2005, 30(3): 255–257
Kantner R M, Rubin A M, Armstrong C W, Cummings V. Stabilometry in balance assessment of dizzy and normal subjects. Am J Otolaryngol, 1991, 12(4): 196–204
Evans M K, Krebs D E. Posturography does not test vestibulospinal function. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1999, 120(2): 164–173
Winter D A. Human balance and postural control during standing and walking. Gait Posture, 1995, 3(4): 193–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Kong, W. Reliability of foam posturography in assessment of postural balance in the patients with vertigo. Front. Med. China 2, 361–365 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0069-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0069-z