Abstract
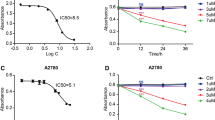
The aim of this article is to explore the effect of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) on the proliferation and apoptosis of myeloma cell line U266 and its relationship with the expression variation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The viability and apoptosis of U266 cells were observed by methylthiazolyl-tetrazolium (MTT) assay and terminal-deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL). The effect of As2O3 on the VEGF expression of U266 cells were tested by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis. We found that As2O3 could significantly inhibit the growth of U266 cells, and the concentration for 50% growth inhibition (IC50) was 2 μmol/L. After treatment with 2, 5, 10 μmol/L As2O3 for 36 hours, dose-dependent apoptosis of U266 cells was observed. After treatment with 2, 5, 10 μmol/L As2O3 for 72 hours, a dose-dependent reduction of VEGF in the supernatant of U266 cells culture was found. As far as single cells are concerned, nevertheless, the expression of VEGF mRNA did not vary. So we draw the conclusion that As2O3 could induce the apoptosis of U266 cells and inhibit their proliferation, decrease the tumor load, and lead to the reduction of VEGF in the culture supernatant, but not change the expression of VEGF in single U266 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munshi N C, Tricot G, Desikan R, Badros A, Zangari M, Toor A, Morris C, Anaissie E, Barlogie B. Clinical activity ofarsenic trioxide for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Leukemia, 2002, 16(9): 1835–1837
Podar K, Anderson K C. The pathophysiologic role of VEGF in hematologic malignancies: Therapeutic implications. Blood, 2005, 105(4): 1383–1395
Amadori S, Fenaux P, Ludwig H, O’dwyer M, Sanz M. Use of arsenic trioxide in haematological malignancies: insight into the clinical development of a novel agent. Curr Med Res Opin, 2005, 21(3): 403–411
Grad J M, Bahlis N J, Reis I, Oshiro M M, Dalton W S, Boise L H. Ascorbic acid enhances arsenic trioxide-induced cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma cells. Blood, 2001, 98(3): 805–813
Rousselot P, Larghero J, Labaume S, Poupon J, Chopin M, Dosquet C, Marolleau J P, Janin A, Brouet J C, Fermand J P. Arsenic trioxide is effective in the treatment of multiple myeloma in SCID mice. Eur J Haematol, 2004, 72(3): 166–171
Bellamy W T, Richter L, Frutiger Y, Grogan T M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in hematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Res, 1999, 59(3): 728–733
Podar K, Tai Y T, Davies F E, Lentzsch S, Sattler M, Hideshima T, Lin B K, Gupta D, Shima Y, Chauhan D, Mitsiades C, Raje N, Richardson P, Anderson K C. Vascular endothelial growth factor triggers signaling cascades mediating multiple myeloma cell growth and migration. Blood, 2001, 98(2): 428–435
Le Gouill S, Podar K, Amiot M, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Ishitsuka K, Kumar S, Raje N, Richardson P G, Harousseau J L, Anderson K C. VEGF induces MCL-1 upregulation and protects multiple myeloma cells against apoptosis. Blood, 2004, 104(9): 2886–2892
Gabrilovich D I, Chen H L, Girgis K R, Cunningham H T, Meny G M, Nadaf S, Kavanaugh D, Carbone D P. Production of vascular endothelial growth factor by human tumors inhibits the functional maturation of dendritic cells. Nat Med, 1996, 2(10): 1096–1103
Nakagawa M, Kaneda T, Arakawa T, Morita S, Sato T, Yomada T, Hanada K, Kumegawa M, Hakeda Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) directly enhances osteoclastic bone resorption and survival of mature osteoclasts. FEBS Lett, 2000, 473(2): 161–164
Henriksen K, Karsdal M, Delaisse J M, Engsig MT. RANKL and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induce osteoclast chemotaxis through an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(49): 48745–48753
Hayashi T, Hideshima T, Akiyama M, Raje N, Richardson P, Chauhan D, Anderson K C. Ex vivo induction of multiple myeloma-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood, 2003, 102(4): 1435–1442
Podar K, Catley L P, Tai Y T, Shringarpure R, Carvalho P, Hayashi T, Burger R, Schlossman R L, Richardson P G, Pandite L N, Kumar R, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Anderson K C. GW654652, the pan-inhibitor of VEGF receptors, blocks the growth and migration of multiple myeloma cells in the bone marrow microenvironment. Blood, 2004, 103(9): 3474–3479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of Fujian Medical University, 2007, 41(6): 491–494 [译自: 福建医科大学学报]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, R., Yu, Q. & Huang, H. Effect of arsenic trioxide on proliferation and apoptosis of U266 cells and its relationship with the expression variation of VEGF. Front. Med. China 2, 356–360 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0068-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0068-0