Abstract
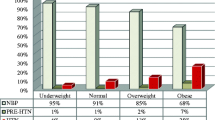
The association of metabolic syndrome (MS) with arterial compliance in children and adolescents was explored. 337 subjects (188 men and 149 women) aged 6–18 (10.95 ± 3.01) years, out of “Beijing Child Metabolic Syndrome Study”, were divided into three case groups (one component, two components, three & more components of MS) and one control group based on the Cook’s MS definition in children and adolescents. Measurements including anthropometry, blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose and insulin, serum lipid profile were done. Homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index was calculated for estimating individual insulin resistance. Arterial compliance was measured using digital pulse wave analyzing method from the pulse trace machine (Micro medical, London), and then the stiffness index (SI) was determined. The mean value of SI in MS group was significant higher than that in control group [(7.69 ± 1.63) vs (6.25 ± 0.86) m/s, P<0.01]. With the increase of the clustering of MS components, SI and HOMA-IR were gradually increased. After taking account of gender, age and pubertal development, the partial correlation analysis showed that the amount of components of MS and HOMA-IR were positively correlated with SI (both P values were less than 0.05). The arterial compliance of MS group was significantly lowered in children and adolescents, and with the increase of the clustering of MS components, arterial compliance was gradually decreased. It was suggested that arterial compliance assessment in children and adolescents was important for early prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bots M L, Dijk J M, Oren A, Grobbee D E. Carotid intima-media thickness, arterial stiffness and risk of cardiovascular disease: current evidence. J Hypertens, 2002, 20(12): 2317–2325
Guerin A P, Blacher J, Pannier B, Marchais S J, Safar M E, London G M. Impact of aortic stiffness attenuation on survival of patients in end-stage renal failure. Circulation, 2001, 103(7): 987–992
Bots M L. Use of intermediate cardiovascular endpoints in intervention studies: not as easy as it seems? Neth J Med, 2004, 62(7): 214–215
McGrath B P, Liang Y L, Kotsopoulos D, Cameron J D. Impact of physical and physiological factors on arterial function. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2001, 28(12): 1104–1107
Slyper A H. Childhood obesity, adipose tissue distribution, and the pediatric practitioner. Pediatrics, 1998, 102(1): e4
Tounian P, Aggoun Y, Dubern B, Varille V, Guy-Grand B, Sidi D, Girardet J P, Bonnet D. Presence of increased stiffness of the common carotid artery and endothelial dysfunction in severely obese children: a prospective study. Lancet, 2001, 358(9291): 1400–1404
Cook S, Weitzman M, Auinger P, Nguyen M, Dietz W H. Prevalence of a metabolic syndrome phenotype in adolescents: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, 2003, 157(8): 821–827
Ji C Y, Sun J L, Chen T J. Dynamic analysis on the prevalence of obesity and overweight school-age children and adolescents in recent 15 years in China. Chin J Epidemiol, 2004, 25(2): 103–108
Li J, Li J Y, Liang Y C, Wang H L, Wu M C, Yu Z F, Fang Q, Zhong M Y. A cross-sectional survey for blood pressure in children and adolescents. Chin J Pediatrics, 1991, 29(1): 34–38
Li M, Wu C Y, Song A L, Zhang K. Development and preliminary application of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for human net insulin in serum. Chin J Endocrin Metabol, 1997, 11(4): 215–217
Woodman R J, Watts G F, Kingwell B A, Dart A M. Interpretation of the digital volume pulse: its relationship with large and small artery compliance. Clin Sci (Lond), 2003, 104(3): 283–285
Millasseau S C, Kelly R P, Ritter J M, Chowienczyk P J. Determination of age-related increases in large artery stiffness by digital pulse contour analysis. Clin Sci (Lond), 2002, 103(4): 371–377
Zhang L, Zhang Z K, Jiang B Y, Chen X Q, Mi J. Digital pulse wave analyzing method in evaluating arterial compliance based on population study in Chinese 415 adults. Chin J Prevent Med, 2006, 40(2): 113–115
Cohun J N. Arteries, myocardium, blood pressure and cardiovascular risk: towards a revised definition of hypertension. J Hypertens, 1998, 16(12 Pt 2): 2117–2124
Arnett D K, Evans G W, Riley W A. Arterial stiffness: a new cardiovascular risk factor? Am J Epidemiol, 1994, 140(8): 669–682
Cohn J N, Finkelstein S, McVeigh G, Morgan D, LeMay L, Robinson J, Mock J. Noninvasive pulse wave analysis for the early detection of vascular disease. Hypertension, 1995, 26(3): 503–508
Blacher J, Guerin A P, Pannier B, Marchais S J, Safar M E, London G M. Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease. Circulation, 1999, 99(18): 2434–2439
Mackey R H, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Vaitkevicius P V, Sakkinen P A, Lyles M F, Spurgeon H A, Lakatta E G, Kuller L H. Correlates of aortic stiffness in elderly individuals: a subgroup of the Cardiovascular Health Study. Am J Hypertens, 2002, 15(1 Pt 1): 16–23
Benetos A, Waeber B, Izzo J, Mitchell G, Resnick L, Asmar R, Safar M. Influence of age, risk factors, and cardiovascular and renal disease on arterial stiffness: clinical applications. Am J Hypertens, 2002, 15(12): 1101–1108
Scuteri A, Najjar S S, Muller D C, Andres R, Hougaku H, Metter E J, Lakatta E G. Metabolic syndrome amplifies the age-associated increases in vascular thickness and stiffness. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2004, 43(8): 1388–1395
Nakanishi N, Suzuki K, Tatara K. Clustered features of the metabolic syndrome and the risk for increased aortic pulse wave velocity in middle-aged Japanese men. Angiology, 2003, 54(5): 551–559
Kupari M, Hekali P, Keto P, Poutanen V P, Tikkanen M J, Standerstkjold-Nordenstam C G. Relation of aortic stiffness to factors modifying the risk of atherosclerosis in healthy people. Arterioscler Thromb, 1994, 14(3): 386–394
Neutel J M, Smith D H, Graettinger W F, Weber M A. Dependency of arterial compliance on circulating neuroendocrine and metabolic factors in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol, 1992, 69(16): 1340–1344
van Popele N M, Westendorp I C, Bots M L, Reneman R S, Hoeks A P, Hofman A, Grobbee D E, Witteman J C. Variables of the insulin resistance syndrome are associated with reduced arterial distensibility in healthy non-diabetic middle-aged women. Diabetologia, 2000, 43(5): 665–672
Khan B V, Harrison D G, Olbrych M T, Alexander R W, Medford R M. Nitric oxide regulates vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 gene expression and redox-sensitive transcriptional events in human vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93(17): 9114–9119
Reaven G M. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes, 1988, 37(12): 1595–1607
Stern M P, Morales P A, Haffner S M, Valdez R A. Hyperdynamic circulation and the insulin resistance syndrome (”syndrome X”). Hypertension, 1992, 20(6): 802–808
Wilkinson I B, Qasem A, McEniery C M, Webb D J, Avolio A P, Cockcroft J R. Nitric oxide regulates local arterial distensibility in vivo. Circulation, 2002, 105(2): 213–217
Kizu A, Koyama H, Tanaka S, Maeno T, Komatsu M, Fukumoto S, Emoto M, Shoji T, Inaba M, Shioi A, Miki T, Nishizawa Y. Arterial wall stiffness is associated with peripheral circulation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis, 2003, 170(1): 87–91
O’Rourke M F, Staessen J A, Vlachopoulos C, Duprez D, Plante G E. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference value. Am J Hypertens, 2002, 15(5): 426–444
Ji C Y, Sun J L. Analysis of the epidemiological status of overweight and obesity in Chinese students and the prevalence changes in recent 15 years. J Peking Univ (Health Sciences), 2004, 36(2): 194–197
Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Asmar R, Gautier I, Laloux B, Guize L, Ducimetiere P, Benetos A. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension, 2001, 37(5): 1236–1241
Tedesco M A, Ratti G, Di S G, Natale F. Does the angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan improve cognitive function? Drugs Aging, 2002, 19(10): 723–732
Fitchett D H, Simkus G J, Beaudry J P, Marpole D G. Reflected pressure waves in the ascending aorta: effect of glyceryl trinitrate. Cardiovasc Res, 1988, 22(7): 494–500
Boutouyrie P, Tropeano A I, Asmar R, Gautier I, Benetos A, Lacolley P, Laurent S. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of primary coronary events in hypertensive patients: a longitudinal study. Hypertension, 2002, 39(1): 10–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Chin J Evid Based Pediatr, 2006, 1(1): 14–19 [译自: 中国循证儿科杂志]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Mi, J., Li, M. et al. Association of metabolic syndrome with arterial compliance in children and adolescents. Front. Med. China 1, 68–73 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0014-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0014-6