Abstract
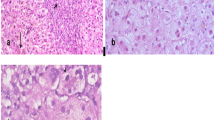
In order to analyze the causative drugs, clinical manifestation and pathological characteristics of the patients with acute drug-induced liver disease, from January 2000 to December 2005, 275 cases diagnosed as acute drug-induced liver diseases according to Maria Criterion and hospitalized in Zhongshan Hospital of Fudan University were retrospectively reviewed. Each was determined by drug history, clinical symptoms and signs, laboratory tests and therapeutic effects. In 41 cases, the diagnosis was confirmed by liver biopsy. The proportion of acute drug-induced liver disease among all of the acute liver injuries was annually increased. The most common drugs which induced acute liver injuries were traditional Chinese herb medicine (23.3%, 64/275 cases), antineoplastic (15.3%, 42/275), hormones and other immunosuppressant agents (13.8%, 38/275), antihypertensive drugs and other cardiovascular drugs (10.2%, 28/275), NSAIDs (8.7%, 24/275) respectively. Hepatocellular injury was the predominant type in these cases (132 cases, 48%). The principal clinical manifestation included nausea (54.8%), fatigue (50.2%), jaundice (35.6%). 27.9% patients were asymptomatic. Most patients were cured with good prognosis. The total effective rate was 94.2% after treatment. The clinicians should pay attention to the prevention, diagnosis and therapy of drug-induced liver disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilinps S J, Carter B L. Miberfradil withdram from the market. Ann Pharmacother, 1998, 32: 841–847
Vasco A, Maria J, Rui M M. Development and validation of a clinical scale for the diagnosis of a drug-induced hepatitis. Hepatology, 1997, 26(3): 664–669
Beinchou C. Criteria of Drug-induced liver disorders. Report of an international consensus meeting. J Hepatol, 1990, 11(2): 272–276
Haller C A, Dyer J E, Ko R, Olson K R. Making a diagnosis of herbal-related toxic hepatitis. West J Med, 2002, 176(1): 39–44
Liu P. Lay stress on the problem of liver injury induced by traditional Chinese medicine. J Chin Liv Dis (Chinese), 2004, 12(4): 243–246
Dominique L. Drug-induced liver disease. J Hepatol, 2002, 32(Suppl 1): 177–188
Hussain I, Kar P, Husain S A. Antituberculosis drug-induced hepatitis: Risk factors, prevention and management. Indian J Exp Biol, 2003, 41(11): 1126–1132
Neil K. Drug-induced liver disorders. Drug Safety, 2001, 24(7): 483–490
Larrey D, Vial T, Micaleff A, Babany G, Morichau-Beauchant M, Michel H, Benhamou J P. Hepatitis associated with amoxicillinclavulanic acid combination, report of 15 cases. Gut, 1992, 33(3): 368–371
Hoyumpa A M, Schenker S. Is glucurenidation truly preserved in patients with liver disease? Herpetology, 1991, 13: 786–795
Willis C, Maddrey M D. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2005, 29: S83–S89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Jiang, W. & Wang, J. Clinical analysis of 275 cases of acute drug-induced liver disease. Front. Med. China 1, 58–61 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0012-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0012-8