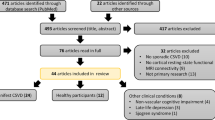
Abstract
Beyond causing local injury, stroke disrupts structural and functional organization of the brain networks, exposing patients to a high risk of cognitive impairment by affecting the neural network activity. However, the impact of these pathological changes on cognition-related neural circuits is not well understood. In this study, we mainly focused on structures and directed functional connectivity within the Papez circuit in subacute stroke patients. Forty-five stroke patients and thirty-four age-, sex-matched healthy controls were included in our study. The Papez circuit gray matter were measured to explore ischemia-induced structural alterations. And Granger causality analysis with the hippocampus as seed regions was performed to identify alterations of directional functional connectivity within the neural circuit. We also explored the associations between cerebral changes with cognitive status. Compared with healthy controls, stroke patients revealed marked atrophy in gray matter of the Papez circuit, including ipsilateral hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, and caudal anterior cingulate gyrus. Additionally, there are alterations in the directed functional connections between the bilateral hippocampus and cingulate gyrus within the Papez circuit. These altered effective connectivities were correlated with cognitive function after cerebrovascular event. Taken together, in the early post-stroke period, disruptions of the Papez circuit in both architecture and directed functional connectivity have already occurred and might affect the cognitive function. These findings have prompted researchers to better understand the potential mechanisms underlying vascular cognitive impairment and to investigate new therapeutic targets that could reduce cognitive burden.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aggleton, J. P., Pralus, A., Nelson, A. J., & Hornberger, M. (2016). Thalamic pathology and memory loss in early Alzheimer’s disease: Moving the focus from the medial temporal lobe to Papez circuit. Brain, 139(Pt 7), 1877–1890. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww083
Blum, S., Luchsinger, J. A., Manly, J. J., Schupf, N., Stern, Y., Brown, T. R., . . . Brickman, A. M. (2012). Memory after silent stroke: hippocampus and infarcts both matter. Neurology, 78(1), 38-46. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31823ed0cc
Brainin, M., Tuomilehto, J., Heiss, W. D., Bornstein, N. M., Bath, P. M., Teuschl, Y., . . . Post Stroke Cognition Study, G. (2015). Post-stroke cognitive decline: an update and perspectives for clinical research. European Journal of Neurology, 22(2), 229–238, e213–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12626
Campbell, B. C. V., De Silva, D. A., Macleod, M. R., Coutts, S. B., Schwamm, L. H., Davis, S. M., & Donnan, G. A. (2019). Ischaemic stroke. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 5(1), 70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0118-8
Carter, A. R., Astafiev, S. V., Lang, C. E., Connor, L. T., Rengachary, J., Strube, M. J., . . . Corbetta, M. (2009). Resting state inter-hemispheric fMRI connectivity predicts performance after stroke. Annals of Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21905
Chen, Y. C., Xia, W., Chen, H., Feng, Y., Xu, J. J., Gu, J. P., . . . Yin, X. (2017). Tinnitus distress is linked to enhanced resting-state functional connectivity from the limbic system to the auditory cortex. Human Brain Mapping, 38(5), 2384-2397. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23525
Crofts, J. J., Higham, D. J., Bosnell, R., Jbabdi, S., Matthews, P. M., Behrens, T. E. J., & Johansen-Berg, H. (2011). Network analysis detects changes in the contralesional hemisphere following stroke. NeuroImage, 54(1), 161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.08.032
Dacosta-Aguayo, R., Grana, M., Savio, A., Fernandez-Andujar, M., Millan, M., Lopez-Cancio, E., . . . Mataro, M. (2014a). Prognostic value of changes in resting-state functional connectivity patterns in cognitive recovery after stroke: A 3T fMRI pilot study. Human Brain Mapping, 35(8), 3819-3831. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22439
Dacosta‐Aguayo, R., Graña, M., Iturria‐Medina, Y., Fernández‐Andújar, M., López‐Cancio, E., Cáceres, C., . . . Mataró, M. (2014b). Impairment of functional integration of the default mode network correlates with cognitive outcome at three months after stroke. Human Brain Mapping, 36(2), 577-590. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22648
Debette, S., Seshadri, S., Beiser, A., Au, R., Himali, J. J., Palumbo, C., . . . DeCarli, C. (2011). Midlife vascular risk factor exposure accelerates structural brain aging and cognitive decline. Neurology, 77(5), 461-468. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318227b227
Delattre, C., Bournonville, C., Auger, F., Lopes, R., Delmaire, C., Henon, H., . . . Bastide, M. (2018). Hippocampal deformations and entorhinal cortex atrophy as an anatomical signature of long-term cognitive impairment: from the MCAO rat model to the stroke patient. Translational Stroke Research, 9(3), 294-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-017-0576-9
Desikan, R. S., Segonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., . . . Killiany, R. J. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968-980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021
Ding, X., Li, C. Y., Wang, Q. S., Du, F. Z., Ke, Z. W., Peng, F., . . . Chen, L. (2014). Patterns in default-mode network connectivity for determining outcomes in cognitive function in acute stroke patients. Neuroscience, 277, 637-646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.060
Florin, E., & Baillet, S. (2015). The brain’s resting-state activity is shaped by synchronized cross-frequency coupling of neural oscillations. NeuroImage, 111, 26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.01.054
Gemmell, E., Bosomworth, H., Allan, L., Hall, R., Khundakar, A., Oakley, A. E., . . . Kalaria, R. N. (2012). Hippocampal neuronal atrophy and cognitive function in delayed poststroke and aging-related dementias. Stroke, 43(3), 808-814. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636498
Gorelick, P. B., Scuteri, A., Black, S. E., Decarli, C., Greenberg, S. M., Iadecola, C., . . . Seshadri, S. (2011). Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke, 42(9), 2672-2713. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e3182299496
Guo, W., Liu, F., Zhang, Z., Liu, J., Yu, M., Zhang, J., . . . Zhao, J. (2015). Unidirectionally affected causal connectivity of cortico-limbic-cerebellar circuit by structural deficits in drug-naive major depressive disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 172, 410-416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.10.019
Haque, M. E., Gabr, R. E., Hasan, K. M., George, S., Arevalo, O. D., Zha, A., . . . Savitz, S. (2019). Ongoing secondary degeneration of the limbic system in patients with ischemic stroke: A longitudinal MRI study. Frontiers in Neurology, 10, 154. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00154
Hewlett, K. A., Kelly, M. H., & Corbett, D. (2014). “Not-so-minor” stroke: Lasting psychosocial consequences of anterior cingulate cortical ischemia in the rat. Experimental Neurology, 261, 543–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.07.024
Hornberger, M., Wong, S., Tan, R., Irish, M., Piguet, O., Kril, J., . . . Halliday, G. (2012). In vivo and post-mortem memory circuit integrity in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain, 135(10), 3015-3025. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws239
Jankowski, M. M., Ronnqvist, K. C., Tsanov, M., Vann, S. D., Wright, N. F., Erichsen, J. T., . . . O'Mara, S. M. (2013). The anterior thalamus provides a subcortical circuit supporting memory and spatial navigation. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 7, 45. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2013.00045
Ji, Y., Xie, Y., Wang, T., Cao, D., Li, J., Han, J., . . . Kang, Z. (2020). Four patients with infarction in key areas of the Papez circuit, with anterograde amnesia as the main manifestation. Journal of International Medical Research, 48(7), 300060520939369. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060520939369
Jiang, L., Geng, W., Chen, H., Zhang, H., Bo, F., Mao, C. N., . . . Yin, X. (2018). Decreased functional connectivity within the default-mode network in acute brainstem ischemic stroke. European Journal of Radiology, 105, 221-226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.06.018
Jokinen, H., Melkas, S., Ylikoski, R., Pohjasvaara, T., Kaste, M., Erkinjuntti, T., & Hietanen, M. (2015). Post-stroke cognitive impairment is common even after successful clinical recovery. European Journal of Neurology, 22(9), 1288–1294. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12743
Jung, J., Laverick, R., Nader, K., Brown, T., Morris, H., Wilson, M., . . . Hosseini, A. A. (2021). Altered hippocampal functional connectivity patterns in patients with cognitive impairments following ischaemic stroke: A resting-state fMRI study. Neuroimage Clinical, 32, 102742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102742
Kliper, E., Bashat, D. B., Bornstein, N. M., Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S., Hallevi, H., Auriel, E., . . . Assayag, E. B. (2013). Cognitive decline after stroke: relation to inflammatory biomarkers and hippocampal volume. Stroke, 44(5), 1433-1435. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000536
Krajcovicova, L., Marecek, R., Mikl, M., & Rektorova, I. (2014). Disruption of resting functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s patients and at-risk subjects. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports, 14(10), 491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-014-0491-3
Mandeville, E. T., Ayata, C., Zheng, Y., & Mandeville, J. B. (2017). Translational MR neuroimaging of stroke and recovery. Translational Stroke Research, 8(1), 22–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0497-z
Matsuoka, K., Yasuno, F., Taguchi, A., Yamamoto, A., Kajimoto, K., Kazui, H., . . . Nagatsuka, K. (2015). Delayed atrophy in posterior cingulate cortex and apathy after stroke. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 30(6), 566-572. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.4185
Mehrabian, S., Raycheva, M., Petrova, N., Janyan, A., Petrova, M., & Traykov, L. (2015). Neuropsychological and neuroimaging markers in prediction of cognitive impairment after ischemic stroke: A prospective follow-up study. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 11, 2711–2719. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S86366
Ovadia-Caro, S., Villringer, K., Fiebach, J., Jungehulsing, G. J., van der Meer, E., Margulies, D. S., & Villringer, A. (2013). Longitudinal effects of lesions on functional networks after stroke. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 33(8), 1279–1285. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.80
Pendlebury, S. T., & Rothwell, P. M. (2009). Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Neurology, 8(11), 1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70236-4
Rehme, A. K., & Grefkes, C. (2013). Cerebral network disorders after stroke: Evidence from imaging-based connectivity analyses of active and resting brain states in humans. Journal of Physiology, 591(1), 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.243469
Schmahmann, J. D. (2003). Vascular syndromes of the thalamus. Stroke, 34(9), 2264–2278. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Str.0000087786.38997.9e
Snaphaan, L., & de Leeuw, F. E. (2007). Poststroke memory function in nondemented patients: A systematic review on frequency and neuroimaging correlates. Stroke, 38(1), 198–203. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000251842.34322.8f
Vicentini, J. E., Weiler, M., Casseb, R. F., Almeida, S. R., Valler, L., de Campos, B. M., & Li, L. M. (2021). Subacute functional connectivity correlates with cognitive recovery six months after stroke. Neuroimage Clinical, 29, 102538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102538
Wang, J., Ke, J., Zhou, C., & Yin, C. (2018). Amnesia due to the injury of Papez circuit following isolated fornix column infarction. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 27(5), 1431–1433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.12.040
Werden, E., Cumming, T., Li, Q., Bird, L., Veldsman, M., Pardoe, H. R., . . . Brodtmann, A. (2017). Structural MRI markers of brain aging early after ischemic stroke. Neurology, 89(2), 116-124. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004086
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: data processing & analysis for (Resting-State) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14(3), 339–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-016-9299-4
Yang, S., Jiang, C., Ye, H., Tao, J., Huang, J., Gao, Y., . . . Chen, L. (2014). Effect of integrated cognitive therapy on hippocampal functional connectivity patterns in stroke patients with cognitive dysfunction: a resting-state FMRI study. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2014, 962304. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/962304
Yao, G., Li, J., Liu, S., Wang, J., Cao, X., Li, X., . . . Xu, Y. (2020). Alterations of functional connectivity in stroke patients with basal ganglia damage and cognitive impairment. Frontiers in Neurology, 11, 980. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00980
Zang, Z. X., Yan, C. G., Dong, Z. Y., Huang, J., & Zang, Y. F. (2012). Granger causality analysis implementation on MATLAB: A graphic user interface toolkit for fMRI data processing. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 203(2), 418–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.10.006
Zhao, L., Biesbroek, J. M., Shi, L., Liu, W., Kuijf, H. J., Chu, W. W., . . . Wong, A. (2018). Strategic infarct location for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A multivariate lesion-symptom mapping study. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 38(8), 1299-1311. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678x17728162
Zhao, Z., Cai, H., Zheng, W., Liu, T., Sun, D., Han, G., . . . Wu, D. (2021). Atrophic pattern of hippocampal subfields in post-stroke demented patient. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 80(3), 1299-1309. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-200804
Zhong, Y., Huang, L., Cai, S., Zhang, Y., von Deneen, K. M., Ren, A., . . . Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging, I. (2014). Altered effective connectivity patterns of the default mode network in Alzheimer's disease: an fMRI study. Neuroscience Letters, 578, 171-175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.06.043
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the contribution of the patients and their families.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Funds of China (Grants No.81730049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SY preprocessed MRI images, performed statistical analyses, and completed the original draft; YL preprocessed MRI images and revised the manuscript; JL collected MRI images, diagnosed the patients, and performed clinical evaluations; TT supervised MRI preprocessing, and revised the manuscript; GZ, YZ and DW scanned MRI images, and performed clinical evaluation; SZ supervised MRI preprocessing and statistical analyses, and revised the manuscript; WZ conceived the study, gained the financial support, and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Tongji Hospital.
Consent to participant
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
This manuscript has not been published elsewhere and the authors agree to publication in the journal.
Competing interests
None of the authors have a conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Li, Y., Lu, J. et al. Structural and functional alterations within the Papez circuit in subacute stroke patients. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 2681–2689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00727-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00727-5