Abstract
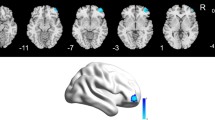
Psychical and functional disturbances of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO) patients are drawing increasingly attention, despite the characterized ophthalmic symptoms. We aimed to investigate the alterations of structural complexity using fractal dimension (FD) analysis in patients with TAO. Thirty-nine TAO patients and 25 healthy controls underwent high-resolution 3.0 T structural brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). FD values of brain regions were calculated by Computational Anatomy Toolbox (CAT12) and compared between groups. The associations between clinical variables and FD values were further estimated. We found that TAO patients exhibited significantly decreased FD values in right caudal anterior cingulate cortex, right lingual gyrus, right pars orbitalis and right cuneus cortex (FDR corrected p < 0.05). FD values of right cuneus cortex were positively correlated with visual acuity, and FD values of right caudal anterior cingulate cortex were also positively correlated with cognitive performance. Meanwhile, FD values of right lingual gyrus were found to be negatively correlated with emotional function. Our study indicated disturbed cortical complexity in brain regions corresponding to known functional deficits of vision, emotion and cognition in TAO. FD might be a potential marker for reflecting the underlying neurobiological basis of TAO.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, HH, upon reasonable request.
References
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007
Bartalena, L., Baldeschi, L., Boboridis, K., Eckstein, A., Kahaly, G. J., Marcocci, C., et al. (2016). The 2016 European Thyroid Association/European Group on Graves’ Orbitopathy Guidelines for the Management of Graves’ Orbitopathy. European Thyroid Journal, 5(1), 9–26. https://doi.org/10.1159/000443828
Bearden, C. E., van Erp, T. G., Dutton, R. A., Lee, A. D., Simon, T. J., Cannon, T. D., Emanuel, B. S., McDonald-McGinn, D., Zackai, E. H., & Thompson, P. M. (2009). Alterations in midline cortical thickness and gyrification patterns mapped in children with 22q11.2 deletions. Cerebral Cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991), 19(1), 115–126. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhn064
Bruscolini, A., Sacchetti, M., La Cava, M., Nebbioso, M., Iannitelli, A., Quartini, A., Lambiase, A., Ralli, M., de Virgilio, A., & Greco, A. (2018). Quality of life and neuropsychiatric disorders in patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy: Current concepts. Autoimmunity Reviews, 17(7), 639–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.12.012
Cha, J., DeDora, D., Nedic, S., Ide, J., Greenberg, T., Hajcak, G., & Mujica-Parodi, L. R. (2016). Clinically anxious individuals show disrupted feedback between inferior frontal gyrus and prefrontal-limbic control circuit. The Journal of Neuroscience : The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 36(17), 4708–4718. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1092-15.2016
Chen, Q. F., Zhang, X. H., Zou, T. X., Huang, N. X., & Chen, H. J. (2020). Reduced cortical complexity in cirrhotic patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Neural Plasticity, 2020, 7364649. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7364649
Choi, J. S., Kang, D. H., Kim, J. J., Ha, T. H., Roh, K. S., Youn, T., & Kwon, J. S. (2005). Decreased caudal anterior cingulate gyrus volume and positive symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 139(3), 239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2004.05.008
Coulter, I., Frewin, S., Krassas, G. E., & Perros, P. (2007). Psychological implications of Graves’ orbitopathy. European Journal of Endocrinology, 157(2), 127–131. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-07-0205
Dahnke, R., Yotter, R. A., & Gaser, C. (2013). Cortical thickness and central surface estimation. NeuroImage, 65, 336–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.050
Davis, K. D., Taylor, K. S., Hutchison, W. D., Dostrovsky, J. O., McAndrews, M. P., Richter, E. O., & Lozano, A. M. (2005). Human anterior cingulate cortex neurons encode cognitive and emotional demands. The Journal of Neuroscience : The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 25(37), 8402–8406. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2315-05.2005
Desikan, R. S., Ségonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., Buckner, R. L., Dale, A. M., Maguire, R. P., Hyman, B. T., Albert, M. S., & Killiany, R. J. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021
Gerding, M. N., Terwee, C. B., Dekker, F. W., Koornneef, L., Prummel, M. F., & Wiersinga, W. M. (1997). Quality of life in patients with Graves’ ophthalmopathy is markedly decreased: Measurement by the medical outcomes study instrument. Thyroid : Official Journal of the American Thyroid Association, 7(6), 885–889. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.1997.7.885
Huang, X., Li, D., Li, H. J., Zhong, Y. L., Freeberg, S., Bao, J., Zeng, X. J., & Shao, Y. (2017). Abnormal regional spontaneous neural activity in visual pathway in retinal detachment patients: A resting-state functional MRI study. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 13, 2849–2854. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S147645
Im, K., Lee, J. M., Yoon, U., Shin, Y. W., Hong, S. B., Kim, I. Y., Kwon, J. S., & Kim, S. I. (2006). Fractal dimension in human cortical surface: Multiple regression analysis with cortical thickness, sulcal depth, and folding area. Human Brain Mapping, 27(12), 994–1003. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20238
Jung, J., Kang, J., Won, E., Nam, K., Lee, M. S., Tae, W. S., & Ham, B. J. (2014). Impact of lingual gyrus volume on antidepressant response and neurocognitive functions in Major Depressive Disorder: A voxel-based morphometry study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 169, 179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.08.018
Kahaly, G. J., Petrak, F., Hardt, J., Pitz, S., & Egle, U. T. (2005). Psychosocial morbidity of Graves’ orbitopathy. Clinical Endocrinology, 63(4), 395–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02352.x
Keedwell, P., Drapier, D., Surguladze, S., Giampietro, V., Brammer, M., & Phillips, M. (2009). Neural markers of symptomatic improvement during antidepressant therapy in severe depression: Subgenual cingulate and visual cortical responses to sad, but not happy, facial stimuli are correlated with changes in symptom score. Journal of Psychopharmacology (oxford, England), 23(7), 775–788. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881108093589
Killen, A., Firbank, M. J., Collerton, D., Clarke, M., Jefferis, J. M., Taylor, J. P., McKeith, I. G., & Mosimann, U. P. (2013). The assessment of cognition in visually impaired older adults. Age and Ageing, 42(1), 98–102. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afs157
King, R. D., Brown, B., Hwang, M., Jeon, T., George, A. T., & Initiative, A. D. N. (2010). Fractal dimension analysis of the cortical ribbon in mild Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 53(2), 471–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.050
Kiselev, V. G., Hahn, K. R., & Auer, D. P. (2003). Is the brain cortex a fractal? NeuroImage, 20(3), 1765–1774. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00380-x
Liu, C. H., Ma, X., Song, L. P., Fan, J., Wang, W. D., Lv, X. Y., Zhang, Y., Li, F., Wang, L., & Wang, C. Y. (2015). Abnormal spontaneous neural activity in the anterior insular and anterior cingulate cortices in anxious depression. Behavioural Brain Research, 281, 339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.11.047
Madan, C. R., & Kensinger, E. A. (2016). Cortical complexity as a measure of age-related brain atrophy. NeuroImage, 134, 617–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.04.029
Maller, J. J., Thomson, R. H., Pannek, K., Bailey, N., Lewis, P. M., & Fitzgerald, P. B. (2014). Volumetrics relate to the development of depression after traumatic brain injury. Behavioural Brain Research, 271, 147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.05.047
Merkley, T. L., Larson, M. J., Bigler, E. D., Good, D. A., & Perlstein, W. M. (2013). Structural and functional changes of the cingulate gyrus following traumatic brain injury: Relation to attention and executive skills. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society: JINS, 19(8), 899–910. https://doi.org/10.1017/S135561771300074X
Nenadic, I., Yotter, R. A., Dietzek, M., Langbein, K., Sauer, H., & Gaser, C. (2017). Cortical complexity in bipolar disorder applying a spherical harmonics approach. Psychiatry Research. Neuroimaging, 263, 44–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.02.007
Posner, M. I., & Rothbart, M. K. (1998). Attention, self-regulation and consciousness. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 353(1377), 1915–1927. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1998.0344
Prasad, S., & Galetta, S. L. (2011). Anatomy and physiology of the afferent visual system. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 102, 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52903-9.00007-8
Rajagopalan, V., Das, A., Zhang, L., Hillary, F., Wylie, G. R., & Yue, G. H. (2019). Fractal dimension brain morphometry: A novel approach to quantify white matter in traumatic brain injury. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 13(4), 914–924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9892-2
Reishofer, G., Studencnik, F., Koschutnig, K., Deutschmann, H., Ahammer, H., & Wood, G. (2018). Age is reflected in the fractal dimensionality of MRI diffusion based tractography. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 5431. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23769-6
Riguetto, C. M., Neto, A. M., Tambascia, M. A., & Zantut-Wittmann, D. E. (2019). The relationship between quality of life, cognition, and thyroid status in Graves’ disease. Endocrine, 63(1), 87–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1733-y
Roberts, G., Green, M. J., Breakspear, M., McCormack, C., Frankland, A., Wright, A., Levy, F., Lenroot, R., Chan, H. N., & Mitchell, P. B. (2013). Reduced inferior frontal gyrus activation during response inhibition to emotional stimuli in youth at high risk of bipolar disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 74(1), 55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.11.004
Rosen, M. L., Sheridan, M. A., Sambrook, K. A., Peverill, M. R., Meltzoff, A. N., & McLaughlin, K. A. (2018). The role of visual association cortex in associative memory formation across development. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 30(3), 365–380. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_01202
Silkiss, R. Z., & Wade, A. R. (2016). Neuroanatomic variations in Graves’ Dysthyroid ophthalmopathy as studied with MRI. Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society, 114, T9.
Swienton, D. J., & Thomas, A. G. (2014). The visual pathway–functional anatomy and pathology. Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MR, 35(5), 487–503. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sult.2014.06.007
Tao, H., Guo, S., Ge, T., Kendrick, K. M., Xue, Z., Liu, Z., & Feng, J. (2013). Depression uncouples brain hate circuit. Molecular Psychiatry, 18(1), 101–111. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.127
Vanni, S., Tanskanen, T., Seppä, M., Uutela, K., & Hari, R. (2001). Coinciding early activation of the human primary visual cortex and anteromedial cuneus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(5), 2776–2780. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.041600898
Veer, I. M., Beckmann, C. F., van Tol, M. J., Ferrarini, L., Milles, J., Veltman, D. J., Aleman, A., van Buchem, M. A., van der Wee, N. J., & Rombouts, S. A. (2010). Whole brain resting-state analysis reveals decreased functional connectivity in major depression. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 41. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2010.00041
Wang, L., Dai, Z., Peng, H., Tan, L., Ding, Y., He, Z., Zhang, Y., Xia, M., Li, Z., Li, W., Cai, Y., Lu, S., Liao, M., Zhang, L., Wu, W., He, Y., & Li, L. (2014). Overlapping and segregated resting-state functional connectivity in patients with major depressive disorder with and without childhood neglect. Human Brain Mapping, 35(4), 1154–1166. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22241
Wu, Q., Hu, H., Chen, W., Chen, H. H., Chen, L., Xu, X. Q., & Wu, F. Y. (2020). Morphological and microstructural brain changes in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: A combined voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging study. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, 43(11), 1591–1598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-020-01242-4
Wyble, B., & Swan, G. (2015). Mapping the spatiotemporal dynamics of interference between two visual targets. Attention, Perception & Psychophysics, 77(7), 2331–2343. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-015-0938-x
Ye, L., Wei, R., Huang, X., Shi, W. Q., Yang, Q. C., Yuan, Q., Zhu, P. W., Jiang, N., Li, B., Zhou, Q., Zhou, F. Q., & Shao, Y. (2018). Reduction in interhemispheric functional connectivity in the dorsal visual pathway in unilateral acute open globe injury patients: a resting-state fMRI study. International Journal of Ophthalmology, 11(6), 1056–1060. https://doi.org/10.18240/ijo.2018.06.26
Yotter, R. A., Dahnke, R., Thompson, P. M., & Gaser, C. (2011a). Topological correction of brain surface meshes using spherical harmonics. Human Brain Mapping, 32(7), 1109–1124. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21095
Yotter, R. A., Nenadic, I., Ziegler, G., Thompson, P. M., & Gaser, C. (2011b). Local cortical surface complexity maps from spherical harmonic reconstructions. NeuroImage, 56(3), 961–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.02.007
Yotter, R. A., Thompson, P. M., & Gaser, C. (2011c). Algorithms to improve the reparameterization of spherical mappings of brain surface meshes. Journal of Neuroimaging : Official Journal of the American Society of Neuroimaging, 21(2), e134–e147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2010.00484.x
Yu, Y., Lan, D. Y., Tang, L. Y., Su, T., Li, B., Jiang, N., Liang, R. B., Ge, Q. M., Li, Q. Y., & Shao, Y. (2020). Intrinsic functional connectivity alterations of the primary visual cortex in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy: A seed-based resting-state fMRI study. Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 11, 2042018820960296. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042018820960296
Zeng, L. L., Shen, H., Liu, L., Wang, L., Li, B., Fang, P., Zhou, Z., Li, Y., & Hu, D. (2012). Identifying major depression using whole-brain functional connectivity: A multivariate pattern analysis. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 135(Pt 5), 1498–1507. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws059
Zhao, G., Denisova, K., Sehatpour, P., Long, J., Gui, W., Qiao, J., Javitt, D. C., & Wang, Z. (2016). Fractal dimension analysis of subcortical gray matter structures in schizophrenia. PLoS ONE, 11(5), e0155415. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155415
Zheng, D. D., Swenor, B. K., Christ, S. L., West, S. K., Lam, B. L., & Lee, D. J. (2018). Longitudinal associations between visual impairment and cognitive functioning: The Salisbury eye evaluation study. JAMA Ophthalmology, 136(9), 989–995. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2018.2493
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81801659 to Hao Hu) and Clinical Capability Promotion Project of Jiangsu Province Hospital (to Xiao-Quan Xu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and study design (WFY, HH, CHH and LH), data collection or acquisition (ZJ, WQ and CL), statistical analysis (ZJ and CW), interpretation of results (ZJ, WFY, XXQ and HH), drafting the manuscript work or revising it critically for important intellectual content (ZJ, XXQ and HH) and approval of final version to be published and agreement to be accountable for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work (All authors).
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Chen, W., Wu, Q. et al. Reduced cortical complexity in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 2133–2140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00683-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00683-0