Abstract
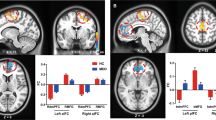
Although childhood maltreatment confers a high risk for the development of major depressive disorder, the neurobiological mechanisms underlying this connection remain unknown. The present study sought to identify the specific resting-state networks associated with childhood maltreatment. We recruited major depressive disorder patients with and without a history of childhood maltreatment (n = 31 and n = 30, respectively) and healthy subjects (n = 80). We used independent component analysis to compute inter- and intra- network connectivity. We found that individuals with major depressive disorder and childhood maltreatment could be characterized by the following network disconnectivity model relative to healthy subjects: (i) decreased intra-network connectivity in the left frontoparietal network and increased intra-network connectivity in the right frontoparietal network, (ii) decreased inter-network connectivity in the posterior default mode network—auditory network, posterior default mode network—limbic system, posterior default mode network—anterior default mode network, auditory network—medial visual network, lateral visual network - medial visual network, medial visual network—sensorimotor network, medial visual network - anterior default mode network, occipital pole visual network—dorsal attention network, and posterior default mode network—anterior default mode network, and (iii) increased inter-network connectivity in the sensorimotor network—ventral attention network, and dorsal attention network—ventral attention network. Moreover, we found significant correlations between the severity of childhood maltreatment and the intra-network connectivity of the frontoparietal network. Our study demonstrated that childhood maltreatment is integrally associated with aberrant network architecture in patients with major depressive disorder.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelnour, F., Dayan, M., Devinsky, O., Thesen, T., & Raj, A. (2018). Functional brain connectivity is predictable from anatomic network’s Laplacian eigen-structure. Neuroimage, 172, 728–739.
Arnsten, A. F., & Rubia, K. (2012). Neurobiological circuits regulating attention, cognitive control, motivation, and emotion: disruptions in neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 51, 356–367.
Bassett, D. S., & Sporns, O. (2017). Network neuroscience. Nature Neuroscience, 20, 353–364.
Bastos, C. R., Tovo-Rodrigues, L., Ardais, A. P., Xavier, J., Salerno, P., Camerini, L., Jansen, K., de Mattos, S. L., Da, S. R., Lara, D. R., & Ghisleni, G. (2020). The role of CACNA1C gene and childhood trauma interaction on bipolar disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 101, 109915.
Beckmann, C. F., DeLuca, M., Devlin, J. T., & Smith, S. M. (2005). Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 360, 1001–1013.
Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Woolrich, M. W., Smith, S. M., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., Boulby, P. A., Barker, G. J., Sillery, E. L., Sheehan, K., Ciccarelli, O., Thompson, A. J., Brady, J. M., & Matthews, P. M. (2003). Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nature Neuroscience, 6, 750–757.
Bell, A. J., & Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Computation, 7, 1129–1159.
Bernstein, D. P., Fink, L., Handelsman, L., Foote, J., Lovejoy, M., Wenzel, K., Sapareto, E., & Ruggiero, J. (1994). Initial reliability and validity of a new retrospective measure of child abuse and neglect. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 151, 1132–1136.
Bernstein, D. P., Ahluvalia, T., Pogge, D., & Handelsman, L. (1997). Validity of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire in an adolescent psychiatric population. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 340–348.
Biswal, B., Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34, 537–541.
Bressler, S. L., & Menon, V. (2010). Large-scale brain networks in cognition: emerging methods and principles. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14, 277–290.
Buckner, R. L., & Vincent, J. L. (2007). Unrest at rest: default activity and spontaneous network correlations. Neuroimage, 37(1091–1096), 1097–1099.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain's default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124, 1–38.
Calhoun, V. D., & Adali, T. (2012). Multisubject independent component analysis of fMRI: a decade of intrinsic networks, default mode, and neurodiagnostic discovery. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 5, 60–73.
Calhoun, V. D., Adali, T., Pearlson, G. D., & Pekar, J. J. (2001). A method for making group inferences from functional MRI data using independent component analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 14, 140–151.
Calhoun, V. D., Liu, J., & Adali, T. (2009). A review of group ICA for fMRI data and ICA for joint inference of imaging, genetic, and ERP data. Neuroimage, 45, S163–S172.
Cheng, B., Roberts, N., Zhou, Y., Wang, X., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Zhao, Y., Deng, P., Meng, Y., Deng, W., & Wang, J. (2022a). Social support mediates the influence of cerebellum functional connectivity strength on postpartum depression and postpartum depression with anxiety. Translational Psychiatry, 12, 54.
Cheng, B., Wang, X., Roberts, N., Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Deng, P., Meng, Y., Deng, W., & Wang, J. (2022b). Abnormal dynamics of resting-state functional activity and couplings in postpartum depression with and without anxiety. Cerebral Cortex.
Choi, J., Jeong, B., Rohan, M. L., Polcari, A. M., & Teicher, M. H. (2009). Preliminary evidence for white matter tract abnormalities in young adults exposed to parental verbal abuse. Biological Psychiatry, 65, 227–234.
Choi, J., Jeong, B., Polcari, A., Rohan, M. L., & Teicher, M. H. (2012). Reduced fractional anisotropy in the visual limbic pathway of young adults witnessing domestic violence in childhood. Neuroimage, 59, 1071–1079.
Cole, M. W., Repovs, G., & Anticevic, A. (2014). The frontoparietal control system: a central role in mental health. Neuroscientist, 20, 652–664.
Corbetta, M., & Shulman, G. L. (2002). Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 3, 201–215.
Damoiseaux, J. S., Rombouts, S. A., Barkhof, F., Scheltens, P., Stam, C. J., Smith, S. M., & Beckmann, C. F. (2006). Consistent resting-state networks across healthy subjects. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 13848–13853.
DeBettencourt, M. T., Cohen, J. D., Lee, R. F., Norman, K. A., & Turk-Browne, N. B. (2015). Closed-loop training of attention with real-time brain imaging. Nature Neuroscience, 18, 470–475.
Dichter, G. S., Gibbs, D., & Smoski, M. J. (2015). A systematic review of relations between resting-state functional-MRI and treatment response in major depressive disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 172, 8–17.
Dixon, M. L., De La Vega, A., Mills, C., Andrews-Hanna, J., Spreng, R. N., Cole, M. W., & Christoff, K. (2018). Heterogeneity within the frontoparietal control network and its relationship to the default and dorsal attention networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115, E1598–E1607.
Dixon, M. L., Moodie, C. A., Goldin, P. R., Farb, N., Heimberg, R. G., & Gross, J. J. (2020). Emotion Regulation in Social Anxiety Disorder: Reappraisal and Acceptance of Negative Self-beliefs. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 5, 119–129.
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Cohen, A. L., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2008). A dual-networks architecture of top-down control. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12, 99–105.
Drysdale, A. T., Grosenick, L., Downar, J., Dunlop, K., Mansouri, F., Meng, Y., Fetcho, R. N., Zebley, B., Oathes, D. J., Etkin, A., Schatzberg, A. F., Sudheimer, K., Keller, J., Mayberg, H. S., Gunning, F. M., Alexopoulos, G. S., Fox, M. D., Pascual-Leone, A., Voss, H. U., et al. (2017). Resting-state connectivity biomarkers define neurophysiological subtypes of depression. Nature Medicine, 23, 28–38.
Dunstan, D. A., Scott, N., & Todd, A. K. (2017). Screening for anxiety and depression: reassessing the utility of the Zung scales. BMC Psychiatry, 17, 329.
Duque, A., & Vazquez, C. (2015). Double attention bias for positive and negative emotional faces in clinical depression: evidence from an eye-tracking study. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 46, 107–114.
Erhardt, E. B., Rachakonda, S., Bedrick, E. J., Allen, E. A., Adali, T., & Calhoun, V. D. (2011). Comparison of multi-subject ICA methods for analysis of fMRI data. Human Brain Mapping, 32, 2075–2095.
Fair, D. A., Cohen, A. L., Dosenbach, N. U., Church, J. A., Miezin, F. M., Barch, D. M., Raichle, M. E., Petersen, S. E., & Schlaggar, B. L. (2008). The maturing architecture of the brain's default network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 4028–4032.
Fan, J., Liu, W., Xia, J., Li, S., Gao, F., Zhu, J., Han, Y., Zhou, H., Liao, H., Yi, J., Tan, C., & Zhu, X. (2021). Childhood trauma is associated with elevated anhedonia and altered core reward circuitry in major depression patients and controls. Human Brain Mapping, 42, 286–297.
Feurer, C., Jimmy, J., Chang, F., Langenecker, S. A., Phan, K. L., Ajilore, O., & Klumpp, H. (2021). Resting state functional connectivity correlates of rumination and worry in internalizing psychopathologies. Depression and Anxiety, 38, 488–497.
Fink, L. A., Bernstein, D., Handelsman, L., Foote, J., & Lovejoy, M. (1995). Initial reliability and validity of the childhood trauma interview: a new multidimensional measure of childhood interpersonal trauma. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 152, 1329–1335.
Fox, M. D., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 8, 700–711.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Vincent, J. L., Corbetta, M., Van Essen, D. C., & Raichle, M. E. (2005). The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 9673–9678.
Geng, L. Y., Ye, D. Q., Shi, Y. Y., Xu, Z., Pu, M. J., Li, Z. Y., Li, X. L., Li, Y., & Zhang, Z. J. (2014). Influence of genetic polymorphisms involved in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and their interactions with environmental factors on antidepressant response. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 20, 237–243.
Gilbert, R., Widom, C. S., Browne, K., Fergusson, D., Webb, E., & Janson, S. (2009). Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. Lancet, 373, 68–81.
Gong, J. B., Wang, Y., Lui, S., Cheung, E., & Chan, R. (2017). Childhood trauma is not a confounder of the overlap between autistic and schizotypal traits: A study in a non-clinical adult sample. Psychiatry Research, 257, 111–117.
Greicius, M. D., Srivastava, G., Reiss, A. L., & Menon, V. (2004). Default-mode network activity distinguishes Alzheimer's disease from healthy aging: evidence from functional MRI. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 4637–4642.
Greicius, M. D., Flores, B. H., Menon, V., Glover, G. H., Solvason, H. B., Kenna, H., Reiss, A. L., & Schatzberg, A. F. (2007). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biological Psychiatry, 62, 429–437.
Heim, C., Newport, D. J., Mletzko, T., Miller, A. H., & Nemeroff, C. B. (2008). The link between childhood trauma and depression: insights from HPA axis studies in humans. Psychoneuroendocrino, 33, 693–710.
Helmreich, I., Wagner, S., Mergl, R., Allgaier, A. K., Hautzinger, M., Henkel, V., Hegerl, U., & Tadic, A. (2012). Sensitivity to changes during antidepressant treatment: a comparison of unidimensional subscales of the Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (IDS-C) and the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) in patients with mild major, minor or subsyndromal depression. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 262, 291–304.
Hoffmann, F., Viding, E., Puetz, V. B., Gerin, M. I., Sethi, A., Rankin, G., & McCrory, E. J. (2018). Evidence for Depressogenic Spontaneous Thoughts and Altered Resting-State Connectivity in Adolescents With a Maltreatment History. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 57, 687–695.
Honey, C. J., Sporns, O., Cammoun, L., Gigandet, X., Thiran, J. P., Meuli, R., & Hagmann, P. (2009). Predicting human resting-state functional connectivity from structural connectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 2035–2040.
Hughes, K., Bellis, M. A., Hardcastle, K. A., Sethi, D., Butchart, A., Mikton, C., Jones, L., & Dunne, M. P. (2017). The effect of multiple adverse childhood experiences on health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Public Health, 2, e356–e366.
Jansen, K., Cardoso, T. A., Fries, G. R., Branco, J. C., Silva, R. A., Kauer-Sant'Anna, M., Kapczinski, F., & Magalhaes, P. V. (2016). Childhood trauma, family history, and their association with mood disorders in early adulthood. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 134, 281–286.
Johansen-Berg, H., Behrens, T. E., Sillery, E., Ciccarelli, O., Thompson, A. J., Smith, S. M., & Matthews, P. M. (2005). Functional-anatomical validation and individual variation of diffusion tractography-based segmentation of the human thalamus. Cerebral Cortex, 15, 31–39.
Kaiser, R. H., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Wager, T. D., & Pizzagalli, D. A. (2015). Large-Scale Network Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-analysis of Resting-State Functional Connectivity. JAMA Psychiatry, 72, 603–611.
Keller, A. S., Ball, T. M., & Williams, L. M. (2020). Deep phenotyping of attention impairments and the 'Inattention Biotype' in Major Depressive Disorder. Psychological Medicine, 50, 2203–2212.
Loewy, R. L., Corey, S., Amirfathi, F., Dabit, S., Fulford, D., Pearson, R., Hua, J., Schlosser, D., Stuart, B. K., Mathalon, D. H., & Vinogradov, S. (2019). Childhood trauma and clinical high risk for psychosis. Schizophrenia Research, 205, 10–14.
Luo, L., Wu, H., Xu, J., Chen, F., Wu, F., Wang, C., & Wang, J. (2021). Abnormal large-scale resting-state functional networks in drug-free major depressive disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 15, 96–106.
Luo, Q., Chen, J., Li, Y., Wu, Z., Lin, X., Yao, J., Yu, H., Peng, H., & Wu, H. (2022). Altered regional brain activity and functional connectivity patterns in major depressive disorder: A function of childhood trauma or diagnosis? Journal of Psychiatric Research, 147, 237–247.
McLaughlin, K. A., Colich, N. L., Rodman, A. M., & Weissman, D. G. (2020). Mechanisms linking childhood trauma exposure and psychopathology: a transdiagnostic model of risk and resilience. BMC Medicine, 18, 96.
Meng, C., Brandl, F., Tahmasian, M., Shao, J., Manoliu, A., Scherr, M., Schwerthoffer, D., Bauml, J., Forstl, H., Zimmer, C., Wohlschlager, A. M., Riedl, V., & Sorg, C. (2014). Aberrant topology of striatum's connectivity is associated with the number of episodes in depression. BRAIN, 137, 598–609.
Mirman, A., Bick, A. S., Kalla, C., Canetti, L., Segman, R., Dan, R., Ben, Y. A., Levin, N., & Bonne, O. (2021). The imprint of childhood adversity on emotional processing in high functioning young adults. Human Brain Mapping, 42, 615–625.
Misiak, B., Krefft, M., Bielawski, T., Moustafa, A. A., Sasiadek, M. M., & Frydecka, D. (2017). Toward a unified theory of childhood trauma and psychosis: A comprehensive review of epidemiological, clinical, neuropsychological and biological findings. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 75, 393–406.
Mulders, P. C., van Eijndhoven, P. F., Schene, A. H., Beckmann, C. F., & Tendolkar, I. (2015). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depressive disorder: A review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 56, 330–344.
Nelson, J., Klumparendt, A., Doebler, P., & Ehring, T. (2017). Childhood maltreatment and characteristics of adult depression: meta-analysis. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 210, 96–104.
Nelson, C. A., Scott, R. D., Bhutta, Z. A., Harris, N. B., Danese, A., & Samara, M. (2020). Adversity in childhood is linked to mental and physical health throughout life. BMJ, 371, m3048.
Nikkheslat, N., McLaughlin, A. P., Hastings, C., Zajkowska, Z., Nettis, M. A., Mariani, N., Enache, D., Lombardo, G., Pointon, L., Cowen, P. J., Cavanagh, J., Harrison, N. A., Bullmore, E. T., Pariante, C. M., & Mondelli, V. (2020). Childhood trauma, HPA axis activity and antidepressant response in patients with depression. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 87, 229–237.
Nogovitsyn, N., Addington, J., Souza, R., Placsko, T. J., Stowkowy, J., Wang, J., Goldstein, B. I., Bray, S., Lebel, C., Taylor, V. H., Kennedy, S. H., & MacQueen, G. (2020). Childhood trauma and amygdala nuclei volumes in youth at risk for mental illness. Psychological Medicine, 1–8.
Otte, C., Gold, S. M., Penninx, B. W., Pariante, C. M., Etkin, A., Fava, M., Mohr, D. C., & Schatzberg, A. F. (2016). Major depressive disorder. Nature Reviews. Disease Primers, 2, 16065.
Pang, Y., Zhao, S., Li, Z., Li, N., Yu, J., Zhang, R., Lu, F., Chen, H., Wu, F., Zheng, W., Gao, J., Yang, Y., Wu, H., & Wang, J. (2022). Enduring effect of abuse: Childhood maltreatment links to altered theory of mind network among adults. Human Brain Mapping.
Peng, W., Liu, Z., Liu, Q., Chu, J., Zheng, K., Wang, J., Wei, H., Zhong, M., Ling, Y., & Yi, J. (2021). Insecure attachment and maladaptive emotion regulation mediating the relationship between childhood trauma and borderline personality features. Depression and Anxiety, 38, 28–39.
Pico-Perez, M., Radua, J., Steward, T., Menchon, J. M., & Soriano-Mas, C. (2017). Emotion regulation in mood and anxiety disorders: A meta-analysis of fMRI cognitive reappraisal studies. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 79, 96–104.
Popovic, D., Ruef, A., Dwyer, D. B., Antonucci, L. A., Eder, J., Sanfelici, R., Kambeitz-Ilankovic, L., Oztuerk, O. F., Dong, M. S., Paul, R., Paolini, M., Hedderich, D., Haidl, T., Kambeitz, J., Ruhrmann, S., Chisholm, K., Schultze-Lutter, F., Falkai, P., Pergola, G., et al. (2020). Traces of Trauma: A Multivariate Pattern Analysis of Childhood Trauma, Brain Structure, and Clinical Phenotypes. Biological Psychiatry, 88, 829–842.
Ptak, R., & Schnider, A. (2010). The dorsal attention network mediates orienting toward behaviorally relevant stimuli in spatial neglect. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 12557–12565.
Rademacher, J., Morosan, P., Schormann, T., Schleicher, A., Werner, C., Freund, H. J., & Zilles, K. (2001). Probabilistic mapping and volume measurement of human primary auditory cortex. Neuroimage, 13, 669–683.
Raichle, M. E. (2015). The brain's default mode network. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 38, 433–447.
Raichle, M. E., MacLeod, A. M., Snyder, A. Z., Powers, W. J., Gusnard, D. A., & Shulman, G. L. (2001). A default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 676–682.
Rivier, F., & Clarke, S. (1997). Cytochrome oxidase, acetylcholinesterase, and NADPH-diaphorase staining in human supratemporal and insular cortex: evidence for multiple auditory areas. Neuroimage, 6, 288–304.
Sacchet, M. D., Ho, T. C., Connolly, C. G., Tymofiyeva, O., Lewinn, K. Z., Han, L. K., Blom, E. H., Tapert, S. F., Max, J. E., Frank, G. K., Paulus, M. P., Simmons, A. N., Gotlib, I. H., & Yang, T. T. (2016). Large-Scale Hypoconnectivity Between Resting-State Functional Networks in Unmedicated Adolescent Major Depressive Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol, 41, 2951–2960.
Sacchi, C., Vieno, A., & Simonelli, A. (2018). Italian validation of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire-Short Form on a college group. Psychological Trauma, 10, 563–571.
Saleh, A., Potter, G. G., McQuoid, D. R., Boyd, B., Turner, R., MacFall, J. R., & Taylor, W. D. (2017). Effects of early life stress on depression, cognitive performance and brain morphology. Psychological Medicine, 47, 171–181.
Scher, C. D., Stein, M. B., Asmundson, G. J., McCreary, D. R., & Forde, D. R. (2001). The childhood trauma questionnaire in a community sample: psychometric properties and normative data. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 14, 843–857.
Schmithorst, V. J., & Holland, S. K. (2004). Comparison of three methods for generating group statistical inferences from independent component analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging data. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 19, 365–368.
Shen, K., Misic, B., Cipollini, B. N., Bezgin, G., Buschkuehl, M., Hutchison, R. M., Jaeggi, S. M., Kross, E., Peltier, S. J., Everling, S., Jonides, J., McIntosh, A. R., & Berman, M. G. (2015). Stable long-range interhemispheric coordination is supported by direct anatomical projections. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112, 6473–6478.
Sikora, M., Heffernan, J., Avery, E. T., Mickey, B. J., Zubieta, J. K., & Pecina, M. (2016). Salience Network Functional Connectivity Predicts Placebo Effects in Major Depression. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 1, 68–76.
Smith, S. M., Fox, P. T., Miller, K. L., Glahn, D. C., Fox, P. M., Mackay, C. E., Filippini, N., Watkins, K. E., Toro, R., Laird, A. R., & Beckmann, C. F. (2009). Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 13040–13045.
Smith, S. M., Vidaurre, D., Beckmann, C. F., Glasser, M. F., Jenkinson, M., Miller, K. L., Nichols, T. E., Robinson, E. C., Salimi-Khorshidi, G., Woolrich, M. W., Barch, D. M., Ugurbil, K., & Van Essen, D. C. (2013). Functional connectomics from resting-state fMRI. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17, 666–682.
Sporns, O., Tononi, G., & Kotter, R. (2005). The human connectome: A structural description of the human brain. PLoS Computational Biology, 1, e42.
Teicher, M. H., & Samson, J. A. (2013). Childhood maltreatment and psychopathology: A case for ecophenotypic variants as clinically and neurobiologically distinct subtypes. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 170, 1114–1133.
Tomoda, A., Sheu, Y. S., Rabi, K., Suzuki, H., Navalta, C. P., Polcari, A., & Teicher, M. H. (2011). Exposure to parental verbal abuse is associated with increased gray matter volume in superior temporal gyrus. NEUROIMAGE, 54(Suppl 1), S280–S286.
Uys, J. D., Marais, L., Faure, J., Prevoo, D., Swart, P., Mohammed, A. H., Stein, D. J., & Daniels, W. M. (2006). Developmental trauma is associated with behavioral hyperarousal, altered HPA axis activity, and decreased hippocampal neurotrophin expression in the adult rat. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1071, 542–546.
van den Heuvel, M. P., & Hulshoff, P. H. (2010). Exploring the brain network: a review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 20, 519–534.
Vythilingam, M., Heim, C., Newport, J., Miller, A. H., Anderson, E., Bronen, R., Brummer, M., Staib, L., Vermetten, E., Charney, D. S., Nemeroff, C. B., & Bremner, J. D. (2002). Childhood trauma associated with smaller hippocampal volume in women with major depression. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 2072–2080.
Wang, D., Qin, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Jiang, T., & Yu, C. (2014). Altered resting-state network connectivity in congenital blind. Human Brain Mapping, 35, 2573–2581.
Wang, J., Wei, Q., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Bai, T., Cheng, L., Tian, Y., & Wang, K. (2018). Functional reorganization of intra- and internetwork connectivity in major depressive disorder after electroconvulsive therapy. Human Brain Mapping, 39, 1403–1411.
Wang, M., Chen, X., Hu, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, C., Zheng, W., Liu, W., Lan, X., Ning, Y., & Zhang, B. (2021a). Functional connectivity between the habenula and default mode network and its association with the antidepressant effect of ketamine. Depress Anxiety.
Wang, W., Kang, L., Zhang, N., Guo, X., Wang, P., Zong, X., Yao, L., Bai, H., Cheng, J., Tu, N., Feng, H., Wang, G., Bu, L., Wang, F., & Liu, Z. (2021b). The Interaction Effects of Suicidal Ideation and Childhood Abuse on Brain Structure and Function in Major Depressive Disorder Patients. Neural Plasticity, 2021, 7088856.
Weinberg, A., Perlman, G., Kotov, R., & Hajcak, G. (2016). Depression and reduced neural response to emotional images: Distinction from anxiety, and importance of symptom dimensions and age of onset. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 125, 26–39.
Weissman, D. G., Lambert, H. K., Rodman, A. M., Peverill, M., Sheridan, M. A., & McLaughlin, K. A. (2020). Reduced hippocampal and amygdala volume as a mechanism underlying stress sensitization to depression following childhood trauma. Depression and Anxiety, 37, 916–925.
Wessing, I., Rehbein, M. A., Romer, G., Achtergarde, S., Dobel, C., Zwitserlood, P., Furniss, T., & Junghofer, M. (2015). Cognitive emotion regulation in children: Reappraisal of emotional faces modulates neural source activity in a frontoparietal network. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 13, 1–10.
Williams, L. M. (2016). Precision psychiatry: a neural circuit taxonomy for depression and anxiety. Lancet Psychiatry, 3, 472–480.
Xie, P., Wu, K., Zheng, Y., Guo, Y., Yang, Y., He, J., Ding, Y., & Peng, H. (2018). Prevalence of childhood trauma and correlations between childhood trauma, suicidal ideation, and social support in patients with depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia in southern China. Journal of Affective Disorders, 228, 41–48.
Xu, Z., Zhang, Z., Shi, Y., Pu, M., Yuan, Y., Zhang, X., & Li, L. (2011). Influence and interaction of genetic polymorphisms in catecholamine neurotransmitter systems and early life stress on antidepressant drug response. Journal of Affective Disorders, 133, 165–173.
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (Resting-State) Brain Imaging. NEUROINFORMATICS, 14, 339–351.
Yang, Z., Gu, S., Honnorat, N., Linn, K. A., Shinohara, R. T., Aselcioglu, I., Bruce, S., Oathes, D. J., Davatzikos, C., Satterthwaite, T. D., Bassett, D. S., & Sheline, Y. I. (2018). Network changes associated with transdiagnostic depressive symptom improvement following cognitive behavioral therapy in MDD and PTSD. Molecular Psychiatry, 23, 2314–2323.
Yu, M., Linn, K. A., Shinohara, R. T., Oathes, D. J., Cook, P. A., Duprat, R., Moore, T. M., Oquendo, M. A., Phillips, M. L., McInnis, M., Fava, M., Trivedi, M. H., McGrath, P., Parsey, R., Weissman, M. M., & Sheline, Y. I. (2019). Childhood trauma history is linked to abnormal brain connectivity in major depression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116, 8582–8590.
Zhang, R., Geng, X., & Lee, T. (2017). Large-scale functional neural network correlates of response inhibition: an fMRI meta-analysis. Brain Structure & Function, 222, 3973–3990.
Zhang, J., Cui, H., Yang, H., Li, Y., Xu, D., Zhao, T., Wu, H., Du, Z., Huang, W., Wang, C., Chen, A., & Wang, J. (2021). Dynamic changes of large-scale resting-state functional networks in major depressive disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 111, 110369.
Zhu, J., Lowen, S. B., Anderson, C. M., Ohashi, K., Khan, A., & Teicher, M. H. (2019). Association of Prepubertal and Postpubertal Exposure to Childhood Maltreatment With Adult Amygdala Function. JAMA Psychiatry, 76, 843–853.
Acknowledgment
We thank our participants for their readiness to engage in this study. We thank Sydney Koke, MFA, from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
The Guangdong Natural Science Foundation, China (2015A030313800 to HP) supported the design of the study. The Guangzhou municipal key discipline in medicine for Guangzhou Brain Hospital (GBH2014-ZD04 to HP) supported the data collection of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP, HW and QL designed the study and drafted the primary manuscript. HW, ZW, and QL supervised the recruitment and made statistical analyses. JC, LQ and YL took part in recruitment and data management. HP and HW made further revisions of the manuscript. All the authors had read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All participants consent to participate and provided written informed consents in the study.
Human or animal subjects
The authors verified that written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Availability of data and materials
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Q., Chen, J., Li, Y. et al. Aberrant brain connectivity is associated with childhood maltreatment in individuals with major depressive disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 2021–2036 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00672-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00672-3