Abstract
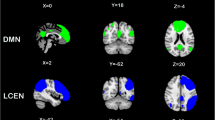
An association has been shown between chronic cigarette smoking and structural abnormalities in the brain areas related to several functions relevant to addictive behavior. However, few studies have focused on the structural alternations of chronic smoking by using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Also, it remains unclear how structural alternations are associated with tobacco-dependence severity and the positive/negative outcome expectances. The q-sampling imaging (GQI) is an advanced diffusion MRI technique that can reconstruct more precise and consistent images of complex oriented fibers than other methods. We aimed to use GQI to evaluate the impact of the neurological structure caused by chronic smoking. Sixty-seven chronic smokers and 43 nonsmokers underwent a MRI scan. The tobacco dependence severity and the positive/negative outcome expectancies were assessed via self-report. We used GQI with voxel-based statistical analysis (VBA) to evaluate structural brain and connectivity abnormalities. Graph theoretical analysis (GTA) and network-based statistical (NBS) analysis were also performed to identify the structural network differences among groups. Chronic smokers had smaller GM and WM volumes in the bilateral frontal lobe and bilateral frontal region. The GM/WM volumes correlated with dependence severity and outcome expectancies in the brain areas involving high-level functions. Chronic smokers had shape changes in the left hippocampal head and tail and the inferior brain stem. Poorer WM integrity in chronic smokers was found in the left middle frontal region, the right superior fronto-occipital fasciculus, the right temporal region, the left parahippocampus, the left anterior internal capsule, and the right inferior parietal region. WM integrity correlated with dependence severity and outcome expectancies in brain areas involving high-level functions. Chronic smokers had decreased local segregation and global integration among the brain regions and networks. Our results provide further evidence indicating that chronic smoking may be associated with brain structure and connectivity changes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the ethical approval and requirements of the data protection legislation. The data set will only be made available on a restricted basis according to the data sharing policies at Chang Gung University and Chung Shan Medical University Hospital. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to Jun-Cheng Weng, jcweng@mail.cgu.edu.tw.
References
Aminoff, E. M., Kveraga, K., & Bar, M. (2013). The role of the parahippocampal cortex in cognition. Trends in cognitive sciences, 17(8), 379–390
Andrejević, M., Meshi, D., van den Bos, W., & Heekeren, H. R. (2017). Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience17(6):1255–1264
Bagga, D., Sharma, A., Kumari, A., Kaur, P., Bhattacharya, D., Garg, M. L., Singh, N. (2014). “Decreased white matter integrity in fronto-occipital fasciculus bundles: relation to visual information processing in alcohol-dependent subjects. " Alcohol, 48(1), 43–53
Bandura, A., & Walters, R. H. (1977). Social learning theory, Prentice-hall Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Battelli, L., Alvarez, G. A., Carlson, T., & Pascual-Leone, A. (2009). The role of the parietal lobe in visual extinction studied with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(10), 1946–1955
Berridge, K. C., & Robinson, T. E. (2016). Liking, wanting, and the incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. American Psychologist, 71(8), 670–679
Bigler, E. D., Mortensen, S., Neeley, E. S., Ozonoff, S., Krasny, L., Johnson, M., Lainhart, J. E. (2007). Superior temporal gyrus, language function, and autism. Developmental neuropsychology, 31(2), 217–238
Binkofski, F. C., Klann, J., & Caspers, S. (2016). On the neuroanatomy and functional role of the inferior parietal lobule and intraparietal sulcus.Neurobiology of language, Elsevier:35–47
Brandon, T. H., Juliano, L. M., & Copeland, A. L. (Eds.). (1999). Expectancies for tobacco smoking. How expectancies shape experience. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association
Brody, A. L., Mandelkern, M. A., Jarvik, M. E., Lee, G. S., Smith, E. C., Huang, J. C., London, E. D. (2004). “Differences between smokers and nonsmokers in regional gray matter volumes and densities.“ Biological psychiatry, 55(1), 77–84
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2009). Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci, 10(3), 186–198
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2012). The economy of brain network organization. Nat Rev Neurosci, 13(5), 336–349
Bullmore, E. T., & Bassett, D. S. (2011). Brain graphs: graphical models of the human brain connectome. Annu Rev Clin Psychol, 7, 113–140
Chapleau, M., Bedetti, C., Devenyi, G. A., Sheldon, S., Rosen, H. J., Miller, B. L., Brambati, S. M. (2020). “Deformation-based shape analysis of the hippocampus in the semantic variant of primary progressive aphasia and Alzheimer’s disease.“ NeuroImage: Clinical, 27, 102305
Chase, H. W., Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., & Hogarth, L. (2011). “The neural basis of drug stimulus processing and craving: an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis.“ Biological psychiatry, 70(8), 785–793
Chica, A. B., Bartolomeo, P., & Lupiáñez, J. (2013). Two cognitive and neural systems for endogenous and exogenous spatial attention. Behavioural brain research, 237, 107–123
Cohen, L. M., McCarthy, D. M., Brown, S. A., & Myers, M. G. (2002). Negative affect combines with smoking outcome expectancies to predict smoking behavior over time. Psychology of addictive behaviors, 16(2), 91–97
Conti, A. A., McLean, L., Tolomeo, S., Steele, J., & Baldacchino, A. (2019). Chronic tobacco smoking and neuropsychological impairments: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 96, 143–154
de Kloet, S. F., Mansvelder, H. D., & De Vries, T. J. (2015). “Cholinergic modulation of dopamine pathways through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.“ Biochemical pharmacology, 97(4), 425–438
Du Boisgueheneuc, F., Levy, R., Volle, E., Seassau, M., Duffau, H., Kinkingnehun, S., Dubois, B. (2006). Functions of the left superior frontal gyrus in humans: a lesion study. Brain, 129(12), 3315–3328
Durazzo, T. C., Meyerhoff, D. J., & Nixon, S. J. (2010). Chronic cigarette smoking: implications for neurocognition and brain neurobiology. International journal of environmental research and public health, 7(10), 3760–3791
Ernst, M., Heishman, S. J., Spurgeon, L., & London, E. D. (2001).“Smoking history and nicotine effects on cognitive performance.“ Neuropsychopharmacology 25(3):313–319
Ersche, K. D., Jones, P. S., Williams, G. B., Turton, A. J., Robbins, T. W., & Bullmore, E. T. (2012).“Abnormal brain structure implicated in stimulant drug addiction.“ Science335(6068):601–604
Ersche, K. D., Williams, G. B., Robbins, T. W., & Bullmore, E. T. (2013). Meta-analysis of structural brain abnormalities associated with stimulant drug dependence and neuroimaging of addiction vulnerability and resilience. Current opinion in neurobiology, 23(4), 615–624
Everitt, B. J., & Robbins, T. W. (2005). Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nature neuroscience, 8(11), 1481–1489
Garza-Villarreal, E. A., Chakravarty, M. M., Hansen, B., Eskildsen, S. F., Devenyi, G. A., Castillo-Padilla, D., Perez-Palacios, P. (2017). “The effect of crack cocaine addiction and age on the microstructure and morphology of the human striatum and thalamus using shape analysis and fast diffusion kurtosis imaging.“ Translational psychiatry, 7(5), e1122–e1122
Gerritsen, L., Rijpkema, M., van Oostrom, I., Buitelaar, J., Franke, B., Fernandez, G., & Tendolkar, I. (2012). “Amygdala to hippocampal volume ratio is associated with negative memory bias in healthy subjects.“ Psychol Med, 42(2), 335–343
Hamid, H. (2014). Networks in Mood and Anxiety Disorders. Neuronal Networks in Brain Function, CNS Disorders, and Therapeutics, Elsevier: 327-334
Health Promotion Administration (2019). Taiwan Tocacco Control Annual Report 2019. Taipei, Taiwan, Ministry of Health and Welfare
Heatherton, T. F., Kozlowski, L. T., Frecker, R. C., & Fagerström, K. O. (1991). “The Fagerström test for nicotine dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire.“ British Journal of Addiction, 86(9), 1119–1127
Herath, P., Kinomura, S., & Roland, P. E. (2001). Visual recognition: evidence for two distinctive mechanisms from a PET study. Human brain mapping, 12(2), 110–119
Hosseini, S. M., Hoeft, F., & Kesler, S. R. (2012). “GAT: a graph-theoretical analysis toolbox for analyzing between-group differences in large-scale structural and functional brain networks.“ PLoS One, 7(7), e40709
Hudkins, M., O’Neill, J., Tobias, M. C., Bartzokis, G., & London, E. D. (2012).“Cigarette smoking and white matter microstructure.“ Psychopharmacology 221(2):285–295
Hughes, T. (2003). Neurology of swallowing and oral feeding disorders: assessment and management. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 74(suppl 3), iii48–iii52
Jacobsen, L. K., Krystal, J. H., Mencl, W. E., Westerveld, M., Frost, S. J., & Pugh, K. R. (2005). Effects of smoking and smoking abstinence on cognition in adolescent tobacco smokers. Biological psychiatry, 57(1), 56–66
Jacobsen, L. K., Picciotto, M. R., Heath, C. J., Frost, S. J., Tsou, K. A., Dwan, R. A., Mencl, W. E. (2007). Prenatal and adolescent exposure to tobacco smoke modulates the development of white matter microstructure. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(49), 13491–13498
Japee, S., Holiday, K., Satyshur, M. D., Mukai, I., & Ungerleider, L. G. (2015). A role of right middle frontal gyrus in reorienting of attention: a case study. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 9, 1–16
Jasinska, A. J., Zorick, T., Brody, A. L., & Stein, E. A. (2014). Dual role of nicotine in addiction and cognition: a review of neuroimaging studies in humans. Neuropharmacology, 84, 111–122
Johnson, K. A., Zvolensky, M. J., Marshall, E. C., Gonzalez, A., Abrams, K., & Vujanovic, A. A. (2008). Linkages between cigarette smoking outcome expectancies and negative emotional vulnerability. Addictive behaviors, 33(11), 1416–1424
Jou, R. J., Minshew, N. J., Keshavan, M. S., Vitale, M. P., & Hardan, A. Y. (2010). Enlarged right superior temporal gyrus in children and adolescents with autism. Brain research, 1360, 205–212
Kelemen, W. L., & Kaighobadi, F. (2007). Expectancy and pharmacology influence the subjective effects of nicotine in a balanced-placebo design. Experimental and clinical psychopharmacology, 15(1), 93–101
Kim, J. S., & Pope, A. (2005). “Somatotopically located motor fibers in corona radiata: evidence from subcortical small infarcts. " Neurology, 64(8), 1438–1440
Koob, G. F., & Volkow, N. D. (2010).“Neurocircuitry of addiction.“ Neuropsychopharmacology 35(1):217–238
Kouimtsidis, C., Stahl, D., West, R., & Drummond, C. (2014). “Can outcome expectancies be measured across substances? Development and validation of a questionnaire for populations in treatment. " Drugs and Alcohol Today
Kringelbach, M. L. (2005). “The human orbitofrontal cortex: linking reward to hedonic experience.“ Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 6(9), 691–702
Kutlu, M. G., & Gould, T. J. (2016). Effects of drugs of abuse on hippocampal plasticity and hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: contributions to development and maintenance of addiction. Learning & memory, 23(10), 515–533
Lee, K. H., Bowen, S., & An-Fu, B. (2011). Psychosocial outcomes of mindfulness-based relapse prevention in incarcerated substance abusers in Taiwan: A preliminary study. Journal of Substance Use, 16(6), 476–483
Li, S., Shi, F., Pu, F., Li, X., Jiang, T., Xie, S., & Wang, Y. (2007). Hippocampal shape analysis of Alzheimer disease based on machine learning methods. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 28(7), 1339–1345
Liao, Y., Tang, J., Deng, Q., Deng, Y., Luo, T., Wang, X., Brody, A. L. (2011). “Bilateral fronto-parietal integrity in young chronic cigarette smokers: a diffusion tensor imaging study.“ PloS one, 6(11), e26460
Liao, Y., Tang, J., Liu, T., Chen, X., & Hao, W. (2012). Differences between smokers and non-smokers in regional gray matter volumes: a voxel‐based morphometry study. Addiction biology, 17(6), 977–980
Lin, F., Wu, G., Zhu, L., & Lei, H. (2015). Altered brain functional networks in heavy smokers. Addiction biology, 20(4), 809–819
Machielsen, W., Rombouts, S. A., Barkhof, F., Scheltens, P., & Witter, M. P. (2000). “FMRI of visual encoding: reproducibility of activation.“ Human brain mapping, 9(3), 156–164
McCarthy, D. M., & Thompsen, D. M. (2006). Implicit and explicit measures of alcohol and smoking cognitions. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 20(4), 436
McClernon, F. J., Kozink, R. V., Lutz, A. M., & Rose, J. E. (2009). 24-h smoking abstinence potentiates fMRI-BOLD activation to smoking cues in cerebral cortex and dorsal striatum. Psychopharmacology, 204(1), 25–35
Mithani, K., Davison, B., Meng, Y., & Lipsman, N. (2020). “The anterior limb of the internal capsule: Anatomy, function, and dysfunction.“Behavioural Brain Research:112588
Moerel, M., De Martino, F., & Formisano, E. (2014). An anatomical and functional topography of human auditory cortical areas. Frontiers in neuroscience, 8, 225
Noël, X., Brevers, D., & Bechara, A. (2013). A neurocognitive approach to understanding the neurobiology of addiction. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 23, 632–638
Öberg, M., Jaakkola, M. S., Woodward, A., Peruga, A., & Prüss-Ustün, A. (2011). “Worldwide burden of disease from exposure to second-hand smoke: a retrospective analysis of data from 192 countries.“ The Lancet, 377(9760), 139–146
Pan, P., Shi, H., Zhong, J., Xiao, P., Shen, Y., Wu, L., He, G. (2013). “Chronic smoking and brain gray matter changes: evidence from meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies.“ Neurological Sciences, 34(6), 813–817
Park, S. E., Choi, D. S., Shin, H. S., Baek, H. J., Choi, H. C., Kim, J. E., Park, M. J. (2017). “Splenial lesions of the corpus callosum: disease spectrum and MRI findings.“ Korean Journal of Radiology, 18(4), 710–721
Paul, R. H., Grieve, S. M., Niaura, R., David, S. P., Laidlaw, D. H., Cohen, R., Pogun, S. (2008). Chronic cigarette smoking and the microstructural integrity of white matter in healthy adults: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 10(1), 137–147
Peng, P., Li, M., Liu, H., Tian, Y. R., Chu, S. L., Halm-Lutterodt, V., Jiang, T. (2018). Brain structure alterations in respect to tobacco consumption and nicotine dependence: A comparative voxel-based morphometry study. Frontiers in neuroanatomy, 12, 43
Ramnani, N. (2006). The primate cortico-cerebellar system: anatomy and function. Nature reviews neuroscience, 7(7), 511–522
Renier, L. A., Anurova, I., De Volder, A. G., Carlson, S., VanMeter, J., & Rauschecker, J. P. (2010). Preserved functional specialization for spatial processing in the middle occipital gyrus of the early blind. Neuron, 68(1), 138–148
Rose, J. E., McClernon, F. J., Froeliger, B., Behm, F. M., Preud’homme, X., & Krystal, A. D. (2011). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the superior frontal gyrus modulates craving for cigarettes. Biological psychiatry, 70(8), 794–799
Rose, J. S., Chassin, L., Presson, C. C., & Sherman, S. J. (1996). “Prospective predictors of quit attempts and smoking cessation in young adults.“ Health Psychology, 15(4), 261–268
Roussotte, F., Soderberg, L., Warner, T., Narr, K., Lebel, C., Behnke, M., Sowell, E. (2012). Adolescents with prenatal cocaine exposure show subtle alterations in striatal surface morphology and frontal cortical volumes. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 4(1), 22
Scher, A. I., Xu, Y., Korf, E., White, L. R., Scheltens, P., Toga, A. W., Valentino, D. J. (2007). “Hippocampal shape analysis in Alzheimer’s disease: a population-based study. " Neuroimage, 36(1), 8–18
Schmahmann, J. D., & Pandya, D. N. (2007). The complex history of the fronto-occipital fasciculus. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences, 16(4), 362–377
Silvanto, J., Schwarzkopf, D., Gilaie-Dotan, S., & Rees, G. (2010). “Differing causal roles for lateral occipital cortex and occipital face area in invariant shape recognition.“ European Journal of Neuroscience, 32(1), 165–171
Sutherland, M. T., Riedel, M. C., Flannery, J. S., Yanes, J. A., Fox, P. T., Stein, E. A., & Laird, A. R. (2016). Chronic cigarette smoking is linked with structural alterations in brain regions showing acute nicotinic drug-induced functional modulations. Behavioral and Brain Functions, 12(1), 1–15
The Health Promotion Administration (2018). “Adult smoking behavior surveillance system.“ from https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/List.aspx?nodeid=1710
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., Joliot, M. (2002). “Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. " Neuroimage, 15(1), 273–289
Ungerleider, L. G., & Haxby, J. V. (1994). ‘What’and ‘where’in the human brain. Current opinion in neurobiology, 4(2), 157–165
Vňuková, M., Ptáček, R., Raboch, J., & Stefano, G. B. (2017). “Decreased central nervous system grey matter volume (GMV) in smokers affects cognitive abilities: a systematic review.“ Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research, 23: 1907
Volkow, N. D., Wang, G. J., Fowler, J. S., & Tomasi, D. (2012). Addiction circuitry in the human brain. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 52, 321–336
Walton, M. E., Behrens, T. E., Buckley, M. J., Rudebeck, P. H., & Rushworth, M. F. (2010).“Separable learning systems in the macaque brain and the role of orbitofrontal cortex in contingent learning.“ Neuron65(6):927–939
Wang, C., Xu, X., Qian, W., Shen, Z., & Zhang, M. (2015). Altered human brain anatomy in chronic smokers: a review of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Neurological Sciences, 36(4), 497–504
Wang, X., Pathak, S., Stefaneanu, L., Yeh, F. C., Li, S., & Fernandez-Miranda, J. C. (2016). Subcomponents and connectivity of the superior longitudinal fasciculus in the human brain. Brain Structure and Function, 221(4), 2075–2092
Weng, J. C., Huang, S. Y., Lee, M. S., & Ho, M. C. (2021). “Association between functional brain alterations and neuropsychological scales in male chronic smokers using resting-state fMRI. " Psychopharmacology (Berl), 238(5), 1387–1399
Wetter, D. W., Kenford, S. L., Welsch, S. K., Smith, S. S., Fouladi, R. T., Fiore, M. C., & Baker, T. B. (2004). Prevalence and predictors of transitions in smoking behavior among college students. Health psychology, 23(2), 168–177
Wonnacott, S., Sidhpura, N., & Balfour, D. J. (2005). Nicotine: from molecular mechanisms to behaviour. Current opinion in pharmacology, 5(1), 53–59
World Health Organization. (2018). WHO global report on trends in prevalence of tobacco smoking 2000-2025. World Health Organization
Yeh, F. C., Wedeen, V. J., & Tseng, W. Y. (2010). Generalized q-sampling imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 29(9), 1626–1635
Yoshida, T., & Tuder, R. M. (2007). “Pathobiology of Cigarette Smoke-Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. " Physiological Reviews, 87(3), 1047–1082
Yu, R., Zhao, L., & Lu, L. (2011). Regional grey and white matter changes in heavy male smokers. PloS one, 6(11), e27440
Zalesky, A., Fornito, A., & Bullmore, E. T. (2010). “Network-based statistic: identifying differences in brain networks. " Neuroimage, 53(4), 1197–1207
Zhang, X., Salmeron, B. J., Ross, T. J., Geng, X., Yang, Y., & Stein, E. A. (2011).“Factors underlying prefrontal and insula structural alterations in smokers.“ Neuroimage54(1):42–48
Zhang, Y., Li, M., Wang, R., Bi, Y., Li, Y., Yi, Z., Yuan, K. (2018). Abnormal brain white matter network in young smokers: a graph theory analysis study. Brain imaging and behavior, 12(2), 345–356
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Oishi, K., Faria, A. V., Jiang, H., Li, X., Evans, A. (2010). “Atlas-guided tract reconstruction for automated and comprehensive examination of the white matter anatomy. " Neuroimage, 52(4), 1289–1301
Funding
This study was supported by the research program MOST105-2410-H-040-001-MY3 and MOST110-2221-E-182-027, which were sponsored by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taipei, Taiwan. This study was also supported by grants NMRPD1L0311of Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan. The funders had no role in the conduct of the study nor the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, M-C. H. and J-C. W.; methodology, J-C. W. and M-C. H.; software, Y-C. C. and L-B. Z.; validation, J-C. W.; formal analysis, Y-C. C. and L-B. Z.; investigation, M-C. H. and J-C. W.; resources, M-C. H. and M-S. L.; data curation, M-C. H. and M-S. L.; writing—original draft preparation, M-C. H. and J-C. W.; writing—review and editing, M-S. L.; visualization, Y-C. C. and L-B. Z.; supervision, J-C. W.; project administration, M-C. H. and J-C. W.; funding acquisition, M-C. H. and J-C. W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This research was approved by the institutional review board of Chung Shan Medical University Hospital (CMUH No: CS2-14059). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all of the individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Written informed consent was obtained from all of the individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, JC., Chuang, YC., Zheng, LB. et al. Assessment of brain connectome alterations in male chronic smokers using structural and generalized q-sampling MRI. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 1761–1775 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00647-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00647-4