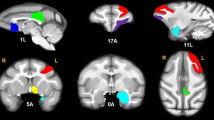
Abstract
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has been used to study the influence of opioids on neural circuitry implicated in opioid use disorder, such as the cortico-striatal-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) circuit. Given the increase in fentanyl-related deaths, this study was conducted to characterize the effects of fentanyl on patterns of brain activation in awake nonhuman primates. Four squirrel monkeys were acclimated to awake scanning procedures conducted at 9.4 Tesla. Subsequently, test sessions were conducted in which a dose of fentanyl that reliably maintains intravenous (IV) self-administration behavior in monkeys, 1 μg/kg, was administered and the effects on patterns of brain activity were assessed using: (1) a pharmacological regressor to elucidate fentanyl-induced patterns of neural activity, and (2) seed-based approaches targeting bilateral anterior cingulate, thalamus, or nucleus accumbens (NAc) to determine alterations in CSTC functional connectivity. Results showed a functional inhibition of BOLD signal in brain regions that mediate behavioral effects of opioid agonists, such as cingulate cortex, striatum and midbrain. Functional connectivity between each of the seed regions and areas involved in motoric, sensory and cognition-related behavior generally decreased. In contrast, NAc functional connectivity with other striatal regions increased. These results indicate that fentanyl produces changes within CSTC circuitry that may reflect key features of opioid use disorder (e.g. persistent drug-taking/seeking) and thereby contribute to long-term disruptions in behavior and addiction. They also indicate that fMRI in alert nonhuman primates can detect drug-induced changes in neural circuits and, in turn, may be useful for investigating the effectiveness of medications to reverse drug-induced dysregulation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alimohammadi, H., Baratloo, A., Abdalvand, A., Rouhipour, A., & Safari, S. (2014). Effects of pain relief on arterial blood o2 saturation. Trauma Monthly, 19(1), E14034.
Alkire, M. T. (2008). Probing the mind: Anesthesia and neuroimaging. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 84(1), 149–152.
Atlas, L. Y., Whittington, R. A., Lindquist, M. A., Wielgosz, J., Sonty, N., & Wager, T. D. (2012). Dissociable influences of opiates and expectations on pain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 32(23), 8053–8064.
Becerra, L., Harter, K., Gonzalez, R. G., & Borsook, D. (2006). Functional magnetic resonance imaging measures of the effects of morphine on central nervous system circuitry in opioid-naive healthy volunteers. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 103(1), 208–216.
Berke, J. D., & Human, S. E. (2000). Addiction, dopamine and the molecular mechanisms of memory. Neuron., 25(3), 515–532.
Berke, J. D., Okatan, M., Skurski, J. & Eichenbaum, H. B. (2004). Oscillatory entrainment of striatal neurons in freely moving rats. Neuron (Cambridge, Mass.), 43(6), 883-896.
Connor, M. A., Vaughan, C. W., Ingram, S. L., & Christie, M. J. (1997). How opioids inhibit GABA-mediated neurotransmission. Nature (London), 390(6660), 611–614.
Dahan, A., Yassen, A., Bijl, H., Romberg, R., Sarton, E., Teppema, L., et al. (2005). Comparison of the respiratory effects of intravenous buprenorphine and fentanyl in humans and rats. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 94(6), 825–834.
de Wit, H. (2009). Impulsivity as a determinant and consequence of drug use: A review of underlying processes. Addiction Biology, 14(1), 22–31 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1369-1600.2008.00129.x
Emmers, R., & Akert, K. (1963). A stereotaxic atlas of the brain of the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). Univ. of Wisconsin Press.
Ersche, K. D., Barnes, A., Jones, P. S., Morein-Zamir, S., Robbins, T. W., & Bullmore, E. T. (2011). Abnormal structure of frontostriatal brain systems is associated with aspects of impulsivity and compulsivity in cocaine dependence. Brain, 134(Pt 7), 2013–2024.
Esteban, O., Birman, D. S., Marie, K., Oluwasanmi, O., Poldrack, R. A., & Gorgolewski, K. J. (2017). MRIQC: Advancing the automatic prediction of image quality in MRI from unseen sites. PLoS One, 12(9), E0184661.
Ezeomah, C., Cunningham, K. A., Stutz, S. J., Fox, R. G., Bukreyeva, N., Dineley, K. T., et al. (2020). Fentanyl self-administration impacts brain immune responses in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 87, 725–738.
Fox, M. D., Halko, M. A., Eldaief, M. C., & Pascual-Leone, A. (2012). Measuring and manipulating brain connectivity with resting state functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging (fcMRI) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). NeuroImage (Orlando, Fla.), 62(4), 2232–2243.
Gao, Y., Schilling, K. G., Khare, S. P., Panda, S., Choe, A. S., Stepniewska, I. et al. (2014). A brain MRI atlas of the common squirrel monkey, Saimiri sciureus. Proceedings of SPIE, the International Society for Optical Engineering 9038: 90380C-90380C-9.
Gergen, J. A., & Maclean, P. D. (1962). A stereotaxic atlas of the squirrel monkey’s brain (Saimiri sciureus)
Goldberg, S. R. (1973). Comparable behavior maintained under fixed-ratio and second-order schedules of food presentation, cocaine injection or d-amphetamine injection in the squirrel monkey. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 186(1), 18–30.
Gorka, S. M., Fitzgerald, D. A., De Wit, H., Angstadt, M., & Phan, K. L. (2014). Opioid modulation of resting-state anterior cingulate cortex functional connectivity. Journal of Psychopharmacology (Oxford), 28(12), 1115–1124.
Gradin, V. B., Baldacchino, A., Balfour, D., Mattews, K., & Steele, J. D. (2014). Abnormal brain activity during a reward and loss task in opiate-dependent patients receiving methadone maintenance therapy. Neuropsychopharmacology (New York, N.Y.), 39(4), 885–894.
Hill, R. S., Dewey, W., Kelly, E., & Henderson, G. (2020). Fentanyl depression of respiration: Comparison with heroin and morphine. British Journal of Pharmacology, 177(2), 254–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14860.
Huang, A. S., Mitchell, J. A., Haber, S. N., Alia-Klein, N., & Goldstein, R. Z. (2018). The thalamus in drug addiction: From rodents to humans. Philosophical transactions. Biological Sciences, 373(1742), 20170028.
Hyman, S. E., Malenka, R. C., & Nestler, E. J. (2006). Neural mechanisms of addiction: The role of reward-related learning and memory. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 29(1), 565–598.
Janczewski, W. A., & Feldman, J. L. (2006). Novel data supporting the two respiratory rhythm oscillator hypothesis. Focus on "respiration-related rhythmic activity in the rostral medulla of newborn rats". Journal of Neurophysiology, 96(1), 1–2.
Kaufman, M. J., Janes, A. C., Frederick, B. B., Brimson-Théberge, M., Tong, Y., McWilliams, S. B., et al. (2013). A method for conducting functional MRI studies in alert nonhuman primates: Initial results with opioid agonists in male cynomolgus monkeys. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 21(4), 323–331.
Ko, M. C., Terner, J., Hursh, S., Woods, J. H., & Winger, G. (2002). Relative reinforcing effects of three opioids with different durations of action. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 301(2), 698–704.
Koob, G. F., & Le Moal, M. (1997). Drug abuse: Hedonic homeostatic dysregulation. Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science), 278(5335), 52–58.
Koob, G. F., & Volkow, N. D. (2010). Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology (New York, N.Y.), 35(4), 1051.
Koob, G. F., & Volkow, N. D. (2016). Neurobiology of addiction: A neurocircuitry analysis. The Lancet, Psychiatry, 3(8), 760–773.
Kuhar, J. R., Bedini, A., Melief, E. J., Chiu, Y., Striegel, H. N., & Chavkin, C. (2015). Mu opioid receptor stimulation activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 by distinct arrestin-dependent and independent mechanisms. Cellular Signalling, 27(9), 1799–1806.
Kühn, S., & Gallinat, J. (2011). Common biology of craving across legal and illegal drugs - a quantitative meta-analysis of cue-reactivity brain response. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 33(7), 1318–1326.
Kuo, A., Wyse, B. D., Meutermans, W., & Smith, M. T. (2015). In vivo profiling of seven common opioids for antinociception, constipation and respiratory depression: No two opioids have the same profile. British Journal of Pharmacology, 172(2), 532–548.
Lanciego, J. L., Luquin, N., & Obeso, J. A. (2012). Functional neuroanatomy of the basal ganglia. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 2(12), A009621.
Langleben, D. D., Ruparel, K., Elman, I., Loughead, J. W., Busch, E. L., Cornish, J., et al. (2014). Extended-release naltrexone modulates brain response to drug cues in abstinent heroin-dependent patients. Addiction Biology, 19(2), 262–271.
Liu, J. V., Hirano, Y., Nascimento, G. C., Stefanovic, B., Leopold, D. A., & Silva, A. C. (2013). FMRI in the awake marmoset: Somatosensory-evoked responses, functional connectivity, and comparison with propofol anesthesia. NeuroImage (Orlando, Fla.), 78, 186–195.
Maguma, H. T., Dewey, W. L., & Akbarali, H. I. (2012). Differences in the characteristics of tolerance to μ-opioid receptor agonists in the colon from wild type and β-arrestin2 knockout mice. European Journal of Pharmacology, 685(1–3), 133–140.
Mandeville, J. B., Liu, C. H., Vanduffel, W., Marota, J. J., & Jenkins, B. G. (2014). Data collection and analysis strategies for phMRI. Neuropharmacology, 84, 65–78.
Martuzzi, R., Ramani, R., Qiu, M., Rajeevan, N., & Constable, R. T. (2010). Functional connectivity and alterations in baseline brain state in humans. NeuroImage (Orlando, Fla.), 49(1), 823–834.
Mather, L. (1983). Clinical pharmacokinetics of fentanyl and its newer derivatives. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 8(5), 422–446.
Mattson, C. L., Tanz, L. J., Quinn, K., Kariisa, M., Patel, P., & Davis, N. L. (2021). Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths – United States, 2013-2019. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 70, 202–207.
Melief, E. J., Miyatake, M., Bruchas, M. R., & Chavkin, C. (2010). Ligand-directed c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation disrupts opioid receptor signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – PNAS, 107(25), 11608–11613.
Mercadante, S., Villari, P., Ferrera, P., Casuccio, A., & Gambaro, V. (2007). Opioid plasma concentrations during a switch from transdermal fentanyl to methadone. Journal of Palliative Medicine, 10(2), 338–344.
Mhuircheartaigh, R., Rosenorn-Lanng, D., Wise, R., Jbabdi, S., Rogers, R., & Tracey, I. (2010). Cortical and subcortical connectivity changes during decreasing levels of consciousness in humans: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study using propofol. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(27), 9095–9102.
Moningka, H., Lichenstein, S., Worhunsky, P. D., DeVito, E. E., Scheinost, D., & Yip, S. W. (2019). Can neuroimaging help combat the opioid epidemic? A systematic review of clinical and pharmacological challenge fMRI studies with recommendations for future research. Neuropsychopharmacology (New York, N.Y.), 44(2), 259–273.
Montandon, G., Qin, W., Liu, H., Ren, J., Greer, J. J., & Horner, R. L. (2011). PreBotzinger complex neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing neurons mediate opioid-induced respiratory depression. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(4), 1292–1301.
Moreno-López, L., Stamatakis, E. A., Fernández-Serrano, M., Gómez-Río, M., Rodríguez-Fernández, A., Pérez-García, M., & Verdejo-García, A. (2012). Neural correlates of the severity of cocaine, heroin, alcohol, MDMA and cannabis use in polysubstance abusers: A resting-PET brain metabolism study. PLoS One, 7(6), E39830.
Murnane, K. S., & Howell, L. L. (2010). Development of an apparatus and methodology for conducting functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) with pharmacological stimuli in conscious rhesus monkeys. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 191(1), 11–20.
Naqvi, N. H., & Bechara, A. (2008). The hidden island of addiction: The insula. Trends in Neurosciences (Regular Ed.), 32(1), 56–67.
Peltier, S. J., Kerssens, C., Hamann, S. B., Sebel, P. S., Byas-Smith, M., & Hu, X. (2005). Functional connectivity changes with concentration of sevoflurane anesthesia. Neuroreport, 16(3), 285–288.
Peper, J. S., Mandl, R. C. W., Braams, B. R., de Water, E., Heijboer, A. C., Koolschijn, P. C. M. P., et al. (2013). Delay discounting and frontostriatal fiber tracts: A combined DTI and MTR study on impulsive choices in healthy young adults. Cerebral Cortex, 23, 1695–1702.
Peters, J., & Büchel, C. (2011). The neural mechanisms of inter-temporal decision-making: Understanding variability. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15, 227–239.
Peters, S. K., Dunlop, K., & Downar, J. (2016). Cortico-striatal-thalamic loop circuits of the salience network: A central pathway in psychiatric disease and treatment. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 10, 104.
Rădulescu, A., Herron, J., Kennedy, C., & Scimemi, A. (2017). Global and local excitation and inhibition shape the dynamics of the cortico-striatal-thalamo-cortical pathway. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 7608–7621.
Schmidt, A., Denier, N., Magon, S., Radue, E. W., Huber, C. G., Riecher-Rossler, A., et al. (2015). Increased functional connectivity in the resting-state basal ganglia network after acute heroin substitution. Translational Psychiatry, 5(3), E533.
Seah, S., Asad, A., Baumgartner, R., Feng, D., Williams, D., Manigbas, E., et al. (2014). Investigation of cross-species translatability of pharmacological MRI in awake nonhuman primate - a buprenorphine challenge study. PLoS One, 9(10), E110432.
Shah, Y. B., Haynes, L., Prior, M. J. W., Marsden, C. A., Morris, P. G., & Chapman, V. (2005). Functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of opioid receptor-mediated modulation of noxious-evoked BOLD contrast in rats. Psychopharmacology, 180(4), 761–773.
Stevens, F. L., Hurley, R. A., Taber, K. H., Hayman, L. A., Hurley, R. A., & Taber, K. H. (2011). Anterior cingulate cortex: Unique role in cognition and emotion. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 23(2), 121–125.
Ting, J. T., & Feng, G. (2011). Neurobiology of obsessive–compulsive disorder: Insights into neural circuitry dysfunction through mouse genetics. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 21(6), 842–848.
Ting-A-Kee, R., & Van der Kooy, D. (2012). The neurobiology of opiate motivation. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 2(10), A012096.
Upadhyay, J., Maleki, N., Potter, J., Elman, I., Rudrauf, D., Knudsen, J., et al. (2010). Alterations in brain structure and functional connectivity in prescription opioid-dependent patients. Brain (London, England : 1878), 133(7), 2098–2114.
Vargas-Perez, H., Ting-A-Kee, R. A., Heinmiller, A., Sturgess, J. E., & Van Der Kooy, D. (2007). A test of the opponent-process theory of motivation using lesions that selectively block morphine reward. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 25(12), 3713–3718.
Virk, M. S., & Williams, J. T. (2008). Agonist-specific regulation of mu-opioid receptor desensitization and recovery from desensitization. Molecular Pharmacology, 73(4), 1301–1308.
Volkow, N. D., Fowler, J. S., & Wang, G. (2004). The addicted human brain viewed in the light of imaging studies: Brain circuits and treatment strategies. Neuropharmacology, 47, 3–13.
Volkow, N. D., Fowler, J. S., Wang, G., Swanson, J. M., & Telang, F. (2007). Dopamine in drug abuse and addiction: Results of imaging studies and treatment implications. Archives of Neurology (Chicago), 64(11), 1575–1579.
Walter, M., Denier, N., Gerber, H., Schmid, O., Lanz, C., Brenneisen, R., et al. (2015). Orbitofrontal response to drug-related stimuli after heroin administration. Addiction Biology, 20(3), 570–579.
Wardle, M. C., Fitzgerald, D. A., Angstadt, M., Rabinak, C. A., De Wit, H., & Phan, K. L. (2014). Effects of oxycodone on brain responses to emotional images. Psychopharmacology, 231(22), 4403–4415.
Xu, T., Falchier, A., Sullivan, E. L., Linn, G., Ramirez, J. S. B., Ross, D., et al. (2018). Delineating the macroscale areal Organization of the Macaque Cortex in Vivo. Cell Reports (Cambridge), 23(2), 429–441.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Walid Yassine for his valuable input and thoughtful discussions during manuscript preparation.
Funding
This work was supported by a Pathways Research Awards® grant, an independent competitive grants program sponsored by Alkermes, Inc. and NIDA/NIH grants K01 DA039306, T32DA015036, and R01 DA047130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions included conception and study design (SLW, JB and SJK), data collection or acquisition (SLW, FBM, KRC and MLR), statistical analysis (SLW, LC and SJK), interpretation of results.
(SLW and SJK), drafting the manuscript or revising it critically for important intellectual content (SLW, LC, FBM, JB and SJK) and approval of final version to be published and agreement to be accountable for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work (All authors).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at McLean Hospital in a facility licensed by the US Department of Agriculture and in accordance with guidelines provided by the Committee on Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Institute of Laboratory Animals Resources, Commission on Life Sciences.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Withey, S.L., Cao, L., de Moura, F.B. et al. Fentanyl-induced changes in brain activity in awake nonhuman primates at 9.4 Tesla. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 1684–1694 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00639-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00639-4