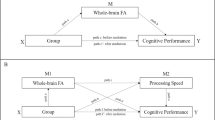
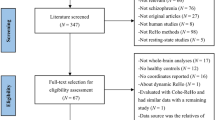
Abstract
This meta-analysis evaluated the extent to which executive function can be understood with structural and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Studies included structural in schizophrenia (k = 8; n = 241) and healthy controls (k = 12; n = 1660), and functional in schizophrenia (k = 4; n = 104) and healthy controls (k = 12; n = 712). Results revealed a positive association in the brain behavior relationship when pooled across schizophrenia and control samples for structural (pr = 0.27) and functional (pr = 0.29) modalities. Subgroup analyses revealed no significant difference for functional neuroimaging (pr = .43, 95%CI = -.08-.77, p = .088) but with structural neuroimaging (pr = .37, 95%CI = -.08-.69, p = .015) the association to executive functions is lower in the control group. Subgroup analyses also revealed no significant differences in the strength of the brain-behavior relationship in the schizophrenia group (pr = .59, 95%CI = .58-.61, p = .881) or the control group (pr = 0.19, 95%CI = 0.18–0.19, p = 0.920), suggesting concordance.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
*References marked with an asterisk indicate studies that were included in the meta-analysis
*Baare, W. F. C., Hulshoff Pol, H. E., Hijman, R., Mali, W. P. T., Viergever, M. A., & Kahn, R. S. (1999). Volumetric analysis of frontal lobe regions in schizophrenia: Relation to cognitive function and symptomatology. Society of Biological Psychiatry, 45, 1597-1605.
Basak, C., Voss, M. W., Erickson, K. I., Boot, W. R., & Kramer, A. F. (2011). Regional differences in brain volume predict the acquisition of skill in a complex real-time videogame. Brain and Cognition, 76(3), 407–414.
Berg, E. A. (1948). A simple objective technique for measuring flexibility in thinking. The Journal of General Psychology, 39(1), 15–22.
Bigler, E. D. (1995). Aging, brain size, and IQ. Intelligence, 21(1), 109–119.
Birur, B., Kraguljac, N. V., Shelton, R. C., & Lahti, A. C. (2017). Brain structure, function, and neurochemistry in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder – a systematic review of the magnetic resonance neuroimaging literature. Schizophrenia, 3(15), e1-15.
Bjork, J. M., Grant, S. J., & Homer, D. W. (2003). Cross-sectional volumetric analysis of brain atrophy in alcohol dependence: Effects of drinking history and comorbid substance use disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 2038–2045.
*Bonila, L., Molnar, C., Horner, M. D., Anderson, B., Forster, L., George, M. S., & Nahas, Z. (2008). Neurocognitive deficits and prefrontal cortical atrophy in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 101, 142-151.
Brown, R. R., & Partington, J. E. (1942). The intelligence of the narcotic drug addict. Journal of General Psychology, 26, 175–179.
Burgess, P. W., & Stuss, D. T. (2017). Fifty years of prefrontal cortex research: Impact on assessment. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 23, 755–767.
Carney, R., Yung, A. R., Amminger, G. P., Gradshaw, T., Glozier, N., Hermens, I. B., Killackey, E., McGorry, P., Pentelis, C., Wood, S. J., & Purcell, R. (2017). Substance use in youth at risk for psychosis. Schizophrenia Research, 181, 23–29.
Chand, G. B., Wu, J., Hajjar, I., & Qiu, D. (2017). Interactions of the salience network and its subsystems with the default-mode and the central-executive networks in normal aging and mild cognitive impairment. Brain Connectivity, 7(7), 401–412.
Chen, Y., Meng, X., Hu, Q., Cui, H., Ding, Y., Kang, L., Juhas, M., Greenshaw, A. J., Zhao, A., Wang, Y., Cui, G., & Li, P. (2016). Altered resting-state functional organization within the central executive network in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 70, 448–456.
*Chen, Y., Qi, D., Qin, T., Chen, K., Ai, M., Li, X., Li, H., Zhang, J., Mao, H., Yang, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Brain network connectivity mediates education-related cognitive performance in healthy elderly adults. Current Alzheimer’s Research, 16, 1-10.
Chow, E. W. C., Mikulis, D. J., Zipursky, R. B., Scutt, L. E., Weksberg, R., & Bassett, A. S. (1999). Qualitative MRI findings in adults with 22q11 deletion syndrome and schizophrenia. Society of Biological Psychiatry, 46, 1436–1442.
Clark, L. R., Schiehser, D. M., Weissberger, G. H., Salmon, D. P., Delis, D. C., & Bondi, M. W. (2012). Specific measures of executive function predict cognitive decline in older adults. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 18(1), 118–127.
*Colom, R., Burgaleta, M., Roman, F. J., Karama, S., Alvarez-Linera, J., Abad, F. J., Martinez, K., Quiroga, M. A., & Haier, R. J. (2013). Neuroanatomic overlap between intelligence and cognitive factors: Morphometry methods provide support for the key role of the frontal lobes. NeuroImage, 72, 143-152.
*Cox, S. R., MacPherson, S. E., Ferguson, K. J., Nissan, J., Royle, N. A., MacLullich, A. M. J., Wardlaw, J. M., & Deary, I. J. (2014). Correlational structure of ‘frontal’ tests and intelligence tests indicates two components with asymmetrical neurostructural correlates in old age. Intelligence, 46, 94-106.
Darby, R. R., Joutsa, J., & Fox, M. D. (2019). Network localization of heterogeneous neuroimaging findings. Brain, 142, 70–79.
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 135–168.
*Drobetz, R., Hanggi, J., Maeker, A., Kaufmann, K., Jancke, L., & Forstmeier, S. (2014). Structural brain correlates of delay of gratification in the elderly. Behavioral Neuroscience, 128(2), 134-145.
Eisenberg, D. P., & Berman, K. F. (2010). Executive function neural circuitry, and genetic mechanisms in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35, 258–277.
Emul, M., & Kalelioglu, T. (2015). Etiology of cardiovascular disease in patients with schizophrenia: Current perspectives. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 11, 2493.
Ersche, K. D., Turton, A. J., Chamberlain, S. R., Müller, U., Bullmore, E. T., & Robbins, T. W. (2012). Cognitive dysfunction and anxious-impulsive personality traits are endophenotypes for drug dependence. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 169, 926–936.
Foong, J., Quaghbeur, R. G., Davie, C. A., Kartsounis, L. D., Thompson, A. J., Miller, D. H., & Ron, M. A. (1997). Executive function in multiple sclerosis: The role of frontal lobe pathology. Brain, 120, 15–26.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., McAvoy, M. P., Barch, D. M., & Raichle, M. E. (2005). The BOLD onset transient: Identification of novel functional differences in schizophrenia. NeuroImage, 25, 771–782.
*Fuentes-Claramonte, P., Avila, C., Rodriguez-Pujadas, A., Costumero, V., Ventura-Campos, N., Bustamante, J. C., Rosell-Negre, P., & Barros-Loscertales, A. (2016). Inferior frontal cortex activity is modulated by reward sensitivity and performance variability. Biological Psychology, 114, 127-137.
*Garlinghouse, M. A., Roth, R. M., Isquith, P. K., Flashman, L. A., & Saykin, A. J. (2010). Subjective rating of working memory is associated with frontal lobe volume in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 120, 71-75.
Gattaz, W. F., Mayer, S., Ziegler, P., Platz, M., & Gasser, T. (1992). Hypofrontality on topographic EEG in schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 241, 328–332.
Geerligs, L., Maurits, N. M., Renken, R. J., & Lorist, M. M. (2014). Reduced specificity of functional connectivity in the aging brain during task performance. Human Brain Mapping, 35, 319–330.
*Gold, B. T. Brown, C. A., Hakun, J. G., Shaw, L. M, Trojanowski, J. Q., & Smith, C. D. (2017). Clinically silent Alzheimer’s and vascular pathologies influence brain networks supporting executive function in healthy older adults. Neurobiology of Aging, 58, 102-111.
*Gordon, E. M., Devaney, J. M., Bean, S., Vaidya, C. J. (2015). Resting-state striato-frontal functional connectivity is sensitive to DAT1 genotype and predicts executive function. Cerebral Cortex, 25, 336-345.
Guye, M., Bettus, G., Bartolomei, F., & Cozzone, P. J. (2010). Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional connectivity MRI in normal and pathological brain networks. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, 23, 409–421.
Hackman, D. A., Gallop, R., Evans, G. W., & Farah, M. J. (2015). Socioeconomic status and executive function: Developmental trajectories and mediation. Developmental Science, 18(5), 686–702.
He, Y., Wang, L., Zang, Y., Tian, L., Zhang, X., Li, K., & Jiang, T. (2007). Regional coherence changes in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease: A combined structural and resting-state functional MRI study. NeuroImage, 35(2), 488–500.
*Henseler, I., Falkai, P., & Gruber, O. (2009). A systematic fMRI investigation of the brain systems subserving different working memory components in schizophrenia. European Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 693-702.
*Hu, S., Ide, J. S., Chao, H. H., Castagna, B., Fischer, K. A., Zhang, S., & Li, C. R. (2018). Structural and functional cerebral bases of diminished inhibitory control during healthy aging. Human Brain Mapping, 39, 5085-5096.
Huizinga, M., Dolan, C. V., & van der Molen, M. W. (2006). Age-related change in executive function: Developmental trends and a latent variable analysis. Neuropsychologia, 44, 2017–2036.
Iturria-Medina, Y., Sotero, R. C., Canales-Rodriguez, E. J., Aleman-Gomez, Y., & Melie-Garcia, L. (2008). Studying the human brain anatomical network via diffusion-weighted MRI and graph theory. NeuroImage, 40, 1064–1076.
Ivleva, E. I., Clementz, B. A., Dutcher, A. M., Arnold, S. J. M., Jeon-Slaughter, H., Aslan, S., … Sweeney, J. A. (2017). Brain structure biomarkers in the psychosis biotypes: Findings from the bipolar-schizophrenia network for intermediate phenotypes. Biological Psychiatry, 82(1), 26-39.
*Jalbrzikowski, M., Murty, V. P., Stan, P. L., Saifullan, J., Simmonds, D., Foran, W., & Luna, B. (2018). Differentiating between clinical and behavioral phenotypes in first-episode psychosis during maintenance of visuospatial working memory. Schizophrenia Research, 197, 357-364.
*Jansma, J. M., Ramsey, N. F., Coppola, R., & Kahn, R. S. (2000). Specific versus nonspecific braina activity in a parametric N-back task. NeuroImage, 12, 688-697.
Jurado, M. B., & Rosselli, M. (2007). The elusive nature of executive functions: A review of our current understanding. Neuropsychology Review, 17, 213–233.
Kambeitz, J., Kambeitz-Ilankovic, L., Leucht, S., Wood, S., Davatzikos, C., Malchow, B., Falkai, P., & Koutsouleris, N. (2015). Detecting neuroimaging biomarkers for schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of multivariate pattern recognition studies. Neuropsychopharmacology, 40, 1742–1751.
Keefe, R. S. E., & Harvey, P. D. (2012). Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, 213, 11–37.
Keshavan, M. S., Morris, D. W., Sweeney, J. A., Pearlson, G., Thaker, G., Siedman, L. J., … Tamminga, C. (2011). A dimensional approach to the psychosis spectrum between bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: The Schizo-Bipolar Scale. Schizophrenia Research, 133, 250-254.
*Knochel, C., Oertel-Knochel, V., Bittner, R., Stablein, M., Heselhaus, V., Prvulovic, D., Fuber, F., Karakaya, T., Pantel, J., Maurer, K., & Linden, D. E. J. (2015). Consolidation time affects performance and neural activity during visual working memory. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 231, 33-41.
Kokkonen, S., Nikkinen, J., Remes, J., Kantola, J., Starck, T., Haapea, M., Tuominen, J., Tervonen, O., & Kiviniemi, V. (2009). Preoperative localization of the sensorimotor area using independent component analysis of resting-state MRI. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 27(6), 733–740.
*La Corte, V., Sperduti, M., Malherbe, C., Vialatte, F., Lion, S., Gallarda, T., Oppenheim, C., & Piolino, P. (2016). Cognitive decline and reorganization of functional connectivity in healthy aging: The pivotal role of the salience network in the predication of age and cognitive performances. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 8, e1-12.
Larsen, I. U., Vinther-Jensen, T., Gade, A., Nielsen, J. E., & Vogel, A. (2015). Assessing impairment of executive function and psychomotor speed in premanifest and manifest Huntington’s disease gene-expansion carriers. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 21, 193–202.
Lezak, M. D. (1993). Newer contributions to the neuropsychological assessment of executive functions. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 8(1), 24–31.
Lezak, M. D. (2012). The behavioral geography of the brain. In M. D. Lezak, D. B. Howieson, E. D. Bigler, & D. Tranel (Eds.), Neuropsychological Assessment (pp. 41–100). Oxford University Press.
Lindsey, D. T., Holzman, P. S., Haberman, S., & Yasillo, N. J. (1978). Smooth-pursuit eye movements: A comparison of two measurement techniques for studying schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 87(5), 491–496.
Liu, C. H. (2015). Anatomical, functional, and molecular biomarker applications of magnetic resonance neuroimaging. Future Neurology, 10(1), 49–65.
Mace, R. A., Waters, A. B., Sawyer, K. S., Turrisi, T., & Gansler, D. A. (2019). Components of executive functioning predict regional prefrontal volumes. Neuropsychology, 33(7), 1007–1019.
McCabe, D. P., Roediger, H. L., McDaniel, M. A., Balota, D. A., & Hambrick, D. Z. (2010). The relationship between working memory capacity and executive functioning: Evidence for a common executive attention construct. Neuropsychology, 24, 222–243.
McHugh, M.L. (2012). Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochemia Medica, 22(3), 276–282.
McKenna, R., Rushe, T., & Woodcock, K. A. (2017). Informing the structure of executive function in children: A meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging data. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, e1-17.
Menon, V., & Uddin, L. Q. (2010). Saliency, switching, attention and control: A network model of insula function. Brain Structure & Function, 214, 655–667.
*Methqal, I., Provost, J., Wilson, M. A., Monchi, O., Amiri, M., Pinsard, B., Ansado, J., & Joanette, Y. (2017). Age-related shift in neuro-action during a word-matching task. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, e1-18.
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Rettinger, D. A., Shah, P., & Hegarty, M. (2001). How are visuospatial working memory, executive functioning, and spatial abilities related? A latent-variable analysis. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 130(4), 621–640.
Miyake, A., & Friedman, N. P. (2012). The nature and organization of individual differences in executive functions: For general conclusions. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21(1), 8–14.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med, 6(7): e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed1000097
*Muller-Oehring, E. M., Schulte, T., Rohlfing, T., Pfefferbaum, A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2013). Visual search and the aging brain: Discerning the effects of age-related brain volume shrinkage on alertness, feature binding, and attentional control. Neuropsychology, 27(1), 48-59.
*Newman, L. M., Trivedi, M. A., Bendlin, B. B., Ries, M. L., & Johnson, S. C. (2007). The relationship between gray mater morphometry and neuropsychological performance in a large sample of cognitively healthy adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 1, 3-10.
Nowrangi, M. A., Lyketsos, C., Rao, V., & Munro, C. A. (2014). Systematic review of neuroimaging correlates of executive functioning: Converging evidence from different clinical populations. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 26(2), 114–125.
Ogden, L. P. (2014). “Waiting to go home”: Narratives of homelessness, housing and home among older adults with schizophrenia. Journal of Aging Studies, 29, 53–65.
Olabi, B., Ellison-Wright, I., McIntosh, A. M., Wood, S. J., Bullmore, E., & Lawrie, S. M. (2011). Are there progressive brain changes in schizophrenia? A meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging studies. Biological Psychiatry, 70, 88–96.
Palmer, B. W., Heaton, R. K., Paulsen, J. S., Kuck, J., Braff, D., Harris, M. J., Zisook, S., & Jeste, D. V. (1997). Is it possible to be schizophrenic yet neuropsychologically normal? Neuropsychology, 11(3), 437–446.
Peterson, R. A., & Brown, S. P. (2005). On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(1), 175–181.
Pietschnig, J., Penke, L., Wicherts, J. M., Ziler, M., & Voracek, M. (2015). Meta-analysis of associations between human brain volume and intelligence differences: How strong are they and what do they mean? Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 57, 411–432.
Rabin, L. A., Paolillo, E., & Barr, W. B. (2016). Stability in test-usage practices of clinical neuropsychologists in the United States and Canada over a 10-year period: A follow-up survey of INS and NAN members. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 31(3), 206–230.
Raichle, M. E. (2009). A brief history of human brain mapping. Review Historical Perspective, 32(2), 118–126.
Rashid, B., Damaraju, E., Pearlson, G. D., & Calhoun, V. D. (2014). Dynamic connectivity states estimated from resting fMRI identify differences among schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and healthy control subjects. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 1–13.
*Raz, N., Briggs, S. D., Marks, W., & Acker, J. D. (1999). Age-related deficits in generation and manipulation of mental images: II. The role of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Psychology and Aging, 14(3), 436–444.
Reichenberg, A., Harvey, P. D., Bowie, C. R., Mojtabai, R., Rabinowitz, J., Heaton, R. K., & Evelyn, B. (2009). Neuropsychological function and dysfunction in schizophrenia and psychotic affective disorders. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 35(5), 1022–1029.
Reineberg, A. E., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Depue, B. E., Friedman, N. P., & Banich, M. T. (2015). Resting-state networks predict individual differences in common and specific aspects of executive function. NeuroImage, 104, 69–78.
Remy, F., Mirrashed, F., Campbell, B., & Richter, W. (2005). Verbal episodic memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: A combined structural and functional MRI study. NeuroImage, 25(1), 253–266.
*Riekmann, A., Karlsson, S., Fischer, H., & Backman, L. (2011). Caudate dopamine D1 receptor density is associated with individual differences in frontoparietal connectivity during working memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(40), 14284-14290.
Ringo, J. L., Doty, R. W., Demeter, S., & Simard, P. Y. (1994). Time is of the essence: A conjecture that hemispheric specialization arises from interhemispheric conduction delay. Cerebral Cortex, 4, 331–343.
Robinson, G., Shallice, T., Bozzali, M., & Cipolotti, L. (2012). The differing roles of the frontal cortex in fluency tests. Brain, 135(7), 2202–2214.
Rodriguez-Jimenez, R., Bagney, A., Martinez-Gras, I., Ponce, G., Sanchez-Morla, E. M., Argues, M., Rubio, G., Jimenez-Arriero, M. A., Santos, J. L., & Palomo, T. (2010). Executive function in schizophrenia: Influence of substance use disorder history. Schizophrenia Research, 118(1–3), 34–40.
Rosenberg, M. D., Finn, E. S., Scheinost, D., Papademetris, X., Shen, X., Constable, R. T., & Chun, M. M. (2015). A neuromarker of sustained attention from whole-brain functional connectivity. Nature Neuroscience, 19(1), 165–171.
Rubinov, M., & Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. NeuroImage, 52(3), 1059–1069.
*Rusch, N., Spoletini, I., Wilke, M., Bria, P., Di Paola, M., Di Iulio, F., Martinotti, G., Caltagirone, C., & Spalletta, G. (2007). Prefrontal-thalamic-cerebellar gray matter networks and executive functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 93, 79-89.
*Rusch, N., van Elst, L. T., Valerius, G., Buchert, M., Thiel, T., Ebert, D., Hennig, J., & Olbrich, H. (2008). Neurochemical and structural correlates of executive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 99, 155-163.
Ruscheweyh, R., Deppe, M., Lohmann, H., Wersching, H., Koruskewitz, C., Duning, T., Bluhm, S., Stehling, C., Keller, S. S., & Knecht, S. (2013). Executive performance is related to regional gray matter volume in healthy older adults. Human Brain Mapping, 34, 3333–3346.
*Schobel, S. A., Kelly, M. A., Corcoran, C. M., van Heertum, K., Seckinger, R., Goetz, R., Harkavy-Friedman, J., & Malaspina, D. (2009). Anterior hippocampal and orbitofrontal cortical structural brain abnormalities in association with cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 114, 110-118.
Seeley, W. W., Menon, V., Schatzberg, A. F., Keller, J., Glover, G. H., Kenna, H., ... & Greicius, M. D. (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(9), 2349-2356.
*Seidman, L. J., Yurgelun-Todd, D., Kremen, W. S., Woods, B. T., Goldstein, J. M., Faraone, S. V., & Tsuang, M. T. (1994). Relationship of prefrontal and temporal lobe MRI measures to neuropsychological performance in chronic schizophrenia. Society of Biological Psychiatry, 35, 235-246.
Semplicini, A., Inverso, G., Realdi, A., Macchini, L., Maraffon, M., Puato, M., Zanardo, M., Tirrito, C., Amodio, P., Schiff, S., Mapelli, D., & Manara, R. (2011). Blood pressure control have distinct effects on executive function, attention, memory and markers of cerebrovascular damage. Journal of Human Hypertension, 25, 80–87.
*Shafritz, K. M., Ikuta, T., Greene, A., Robinson, D. G., Gallego, J., Lencz, T., DeRosse, P., Kingsley, P. B., & Szeszko, P. R. (2019). Frontal lobe functioning during a simple response conflict task in first-episode psychosis and its relationship to treatment response. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 13, 541-553.
*Shaked, D., Katzel, L. I., Seliger, S. L., Gullapalli, R. P., Davatzikos, C., Erus, G., Evans, M. K., Zonderman, A. B., & Waldstein, S. R. (2018). Neuropsychology, 32(8), 985-995.
*Smolker, H. R., Depue, B. E., Reineberg, A. E., Orr, J. M., & Banich, M. T. (2015). Individual differences in regional prefrontal gray matter morphometry and fractional anisotropy are associated with different constructs of executive function. Brain Structure & Function, 220, 1291-1306.
Steen, R. G., Mull, C., McClure, R., Hamer, R. M., & Lieberman, J. A. (2006). Brain volume in first-episode schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry, 188, 510–518.
Stergiopoulos, V., Burra, T., Rourke, S., & Hwang, S. (2011). Housing status as an independent predictor of functional capacity in patients with schizophrenia. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 199(11), 854–860.
Stopford, C. L., Thompson, J. C., Neary, D., Richardson, A. M. T., & Snowden, J. S. (2012). Working memory, attention, and executive function in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Cortex, 48, 429–446.
Stroop, J. R. (1935). Studies of the interference in serial verbal reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 18, 643–662.
Sui, J., He, H., Yu, Q., Chen, J., Rogers, J., Pearlson, G. D., Mayer, A., Bustillo, J., Canive, J., & Calhoun, V. D. (2013). Combination of resting state fMRI, DTI, and sMRI data to discriminate schizophrenia by N-way MCAA + jICA. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7(235), e1-14.
Stuss, D. T. (2011). Functions of the frontal lobes: Relation to executive functions. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 17, 759–765.
Stuss, D. T., & Alexander, M. P. (2000). Executive functions and the frontal lobes: A conceptual view. Psychological Research Psychologische Forschung, 63, 289–298.
Sutherland, M. T., McHugh, M. J., Pariyadath, V., & Stein, E. A. (2012). Resting state functional connectivity in addiction: Lessons learned and a road ahead. NeuroImage, 62(4), 2281–2295.
Suurmond, R., van Rhee, H., & Hak, T. (2017). Introduction, comparison and validation of Meta-Essentials: A free and simple tool for meta-analysis. Research Synthesis Methods. Vol. 8. Iss., 4, 537–553. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1260
Topolovec-Vranic, J., Schuler, A., Gozdzik, A., Somers, J., Bourque, P. É., Frankish, C. J., ... & Hwang, S. W. (2017). The high burden of traumatic brain injury and comorbidities amongst homeless adults with mental illness. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 87, 53-60.
Van Rhee, H.J., Suurmond, R., & Hak, T. (2015). User manual for Meta-Essentials: Workbooks for meta-analysis (Version 1.2) Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Erasmus Research Institute of Management. Retrieved from www.erim.eur.nl/research-support/meta-essentials
*Visintin, E., De Panfilis, C., Antonucci, C., Capecci, C., Marchesi, C., & Sambataro, F. (2015). Parsing the intrinsic networks underlying attention: A resting-state study. Behavioural Brain Research, 278, 315-322.
Vita, A., De Peri, L., & Sacchetti, E. (2012). Progressive loss of cortical gray matter in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis and meta-regression of longitudinal MRI studies. Translational Psychiatry, 2, e190.
Voltz, H., Gaser, C., Hager, F., Rzanny, R., Mentzel, H., Kreitschmann-Andermahr, I., Kaiser, W. A., & Sauer, H. (1997). Brain activation during cognitive stimulation with the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test – a functional MRI study on healthy volunteers and schizophrenics. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging Section, 75, 145–157.
*Vonk, J. M. J., Rizvi, B., Lao, P. J., Budge, M., Manly, J. J., Mayeux, R., & Brickman, A. M. (2019). Letter and category fluency performance correlates with distinct patterns of cortical thickness in older adults. Cerebral Cortex, 29, 2694-2700.
*Weinstein, A. M., Voss, M. W., Prakash, R. S., Chaddock, L., Szabo, A., White, S. M., Wojcicki, T. R., Mailey, E., McAuley, E., Kramer, A. F., & Erickson, K. I. (2012). The association between aerobic fitness and executive function is mediated by prefrontal cortex volume. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 26, 811-819.
*Wojtalik, J. A., Eack, S. M., Pollock, B. G., & Keshavan, M. S. (2012). Prefrontal gray matter morphology mediates the association between serum anticholinergicity and cognitive functioning in early course schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 204, 61-67.
Woodward, L. J., Clark, C. A. C., Pritchard, V. E., Anderson, P. J., & Inder, T. E. (2011). Neonatal white matter abnormalities predict global executive function impairment in children born very preterm. Developmental Neuropsychology, 36(1), 22–41.
*Yin, X., Zhao, L., Evans, A. C., Fan, L., Ge, H., Tang, Y., Khundrakpam, B., Wang, J., & Liu, S. (2012). Anatomical substrates of the alerting, orienting and executive control components of attention: Focus on the posterior parietal lobe. PLoS ONE, 7(11), e50590.
Yuan, P., & Raz, N. (2014). Prefrontal cortex and executive functions in healthy adults: a meta-analysis of structural neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience & biobehavioral. Reviews, 42, 180-192.
*Zanbelt, B. B., van Buuren, M., Kahn, R. S., & Vink, M. (2011). Reduced proactive inhibition in schizophrenia is related to corticostriatal dysfunction and poor working memory. Biological Psychiatry, 70(12), 1151-1158.
*Zhang, H., Sachdev, P. S., Thalamuthu, A., He, Y., Xia, M., Kochan, N. A., Crawford, J. D., Trollor, J. N., Brodaty, H., & Wen, W. (2018). The relationship between voxel-based metrics of resting state functional connectivity and cognitive performance in cognitively healthy elderly adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 12, 1742-1758.
*Zhu, W., Chen, Q., Xia, L., Beaty, R. E., Yang, W., Tian, F., Sun, J., Cao, G., Zhang, Q., Chen, X., & Qiu, J. (2017). Common and distinct brain networks underlying verbal and visual creativity. Human Brain Mapping, 38, 2094-2111.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Suffolk University Psychology Department for their support of doctoral students and David Gansler’s Clinical Neuroscience of Cognitive Control Lab.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions included conception and study design (KMD, ABW, DAG), data collection (KMD, MOP, ABW), statistical analysis (MOP, KMD, ABW), interpretation of results (MOP, KMD, ABW, LPS, DAG), drafting the manuscript work or revising it critically for important intellectual content (MOP), and approval of final version to be published and agreement to be accountable for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work (all authors).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest to declare.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pietrzykowski, M.O., Daigle, K.M., Waters, A.B. et al. The central executive network and executive function in healthy and persons with schizophrenia groups: a meta-analysis of structural and functional MRI. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 1451–1464 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00589-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00589-3