Abstract
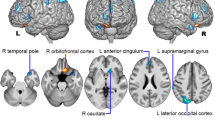
Neuroimaging studies have implicated abnormal brain microstructure in episodic migraine (EM), but whether the pattern is altered during migraine chronification is not well known. Fifty-six patients with migraine without aura, including 39 EM patients and 17 chronic migraine (CM) patients, and 35 healthy controls (HCs) were enrolled. Voxel-based morphometry analysis was performed to assess gray matter (GM) volume differences among groups and their association with clinical feature was examined. Compared with the HC group, both migraine groups showed increased GM volume in the periaqueductal grey matter (PAG) and decreased GM volume in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). The left hippocampus/parahippocampal gyrus (PHG) volume of the HC group was smaller than that of the EM group, but was larger than that of the CM group. For the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC), the EM group showed the smallest GM volume while the CM group had the largest volume. Higher headache frequency was associated with greater GM volume in the PAG and dlPFC, but was associated with smaller GM volume in the ACC and hippocampus/PHG across all patients. GM volume changes in regions involved in pain generation and control are potential neural mechanism underlying migraine, and are associated with migraine types and headache frequency.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apkarian, A. V., Baliki, M. N., & Geha, P. Y. (2009). Towards a theory of chronic pain. Progress in Neurobiology, 87(2), 81–97.
Arnold, M. (2018). Headache classification committee of the international headache society (ihs) the international classification of headache disorders. Cephalalgia, 38(1), 1–211.
Chen, Z., Chen, X., Liu, M., Liu, S., Ma, L., & Yu, S. (2016). Nonspecific periaqueductal gray lesions on T2WI in episodic migraine. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 17(1), 101.
Chen, Z., Chen, X., Liu, M., Liu, S., Ma, L., & Yu, S. (2017a). Disrupted functional connectivity of periaqueductal gray subregions in episodic migraine. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 18(1), 36.
Chen, Z., Chen, X., Liu, M., Liu, S., Ma, L., & Yu, S. (2017b). Volume expansion of periaqueductal gray in episodic migraine: A pilot MRI structural imaging study. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 18(1), 83.
Chenwang, J., Kai, Y., Limei, Z., Ling, Z., Dahua, Y., Deneen, K. M., Von, et al. (2013). Structural and functional abnormalities in migraine patients without aura. NMR in Biomedicine, 26(1), 58–64.
Chong, C. D., Dumkrieger, G. M., & Schwedt, T. J. (2017). Structural co-variance patterns in migraine: A cross-sectional study exploring the role of the Hippocampus. Headache.
Chong, C. D., Schwedt, T. J., & Dodick, D. W. (2016). Migraine: What imaging reveals. Current Neurology & Neuroscience Reports, 16(7), 1–10.
Coppola, G., Petolicchio, B., Di Renzo, A., Tinelli, E., Di Lorenzo, C., Parisi, V., et al. (2017). Cerebral gray matter volume in patients with chronic migraine: Correlations with clinical features. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 18(1), 115.
Dai, Z., Zhong, J., Xiao, P., Zhu, Y., Chen, F., Pan, P., & Shi, H. (2015). Gray matter correlates of migraine and gender effect: A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Neuroscience, 299, 88–96.
Ellerbrock, I., Engel, A. K., & May, A. (2013). Microstructural and network abnormalities in headache. Current Opinion in Neurology, 26(4), 353–359.
Gianluca, C., Antonio, D. R., Emanuele, T., Elisa, I., Chiara, L., Cherubino, D. L., et al. (2015). Evidence for brain morphometric changes during the migraine cycle: A magnetic resonance-based morphometry study. Cephalalgia, 35(9), 783–791.
Hubbard, C. S., Khan, S. A., Keaser, M. L., Mathur, V. A., Goyal, M., & Seminowicz, D. A. (2014). Altered brain structure and function correlate with disease severity and pain catastrophizing in migraine patients. eNeuro, 1(1).
Jin, C., Yuan, K., Zhao, L., Yu, D., von Deneen, K. M., Zhang, M., et al. (2013). Structural and functional abnormalities in migraine patients without aura. NMR in Biomedicine, 26(1), 58–64.
Kim, J., Suh, S. I., Seol, H., Oh, K., Seo, W. K., Yu, S. W., Park, K. W., & Koh, S. B. (2008). Regional grey matter changes in patients with migraine: A voxel-based morphometry study. Cephalalgia, 28(6), 598–604.
Liu, H.-Y., Chou, K.-H., & Chen, W.-T. (2018). Migraine and the Hippocampus. Current Pain and Headache Reports, 22(2), 13.
Liu, H.-Y., Chou, K.-H., Lee, P.-L., Fuh, J.-L., Niddam, D. M., Lai, K.-L., Hsiao, F. J., Lin, Y. Y., Chen, W. T., Wang, S. J., & Lin, C. P. (2017). Hippocampus and amygdala volume in relation to migraine frequency and prognosis. Cephalalgia, 37(14), 1329–1336.
Liu, J., Lan, L., Li, G., Yan, X., Nan, J., Xiong, S., et al. (2013). Migraine-related gray matter and white matter changes at a 1-year follow-up evaluation. Journal of Pain Official Journal of the American Pain Society, 14(12), 1703–1708.
Liu, J., Zhao, L., Li, G., Xiong, S., Nan, J., Li, J., Yuan, K., von Deneen, K., Liang, F., Qin, W., & Tian, J. (2012). Hierarchical alteration of brain structural and functional networks in female migraine sufferers. PLoS One, 7(12), e51250.
Liu, M.-G., & Chen, J. (2009). Roles of the hippocampal formation in pain information processing. Neuroscience Bulletin, 25(5), 237–266.
Ma, M., Zhang, J., Chen, N., Guo, J., Zhang, Y., & He, L. (2018). Exploration of intrinsic brain activity in migraine with and without comorbid depression. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 19(1), 48.
Maleki, N., Becerra, L., Brawn, J., Bigal, M., Burstein, R., & Borsook, D. (2012). Concurrent functional and structural cortical alterations in migraine. Cephalalgia, 32(8), 607–620.
Maleki, N., Becerra, L., Brawn, J., McEwen, B., Burstein, R., & Borsook, D. (2013). Common hippocampal structural and functional changes in migraine. Brain Structure and Function, 218(4), 903–912.
Maleki, N., & Gollub, R. L. (2016). What have we learned from brain functional connectivity studies in migraine headache? Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain, 56(3), 453–461.
Matharu, M. S., Good, C. D., May, A., Bahra, A., & Goadsby, P. J. (2015). No change in the structure of the brain in migraine: A voxel-based morphometric study. European Journal of Neurology, 10(1), 53–57.
Neeb, L., Bastian, K., Villringer, K., Israel, H., Reuter, U., & Fiebach, J. B. (2017). Structural gray matter alterations in chronic migraine: Implications for a progressive disease? Headache, 57(3), 400–416.
Peyron, R., Laurent, B., & Garcia-Larrea, L. (2000). Functional imaging of brain responses to pain. A review and meta-analysis (2000). Neurophysiologie Clinique/Clinical Neurophysiology, 30(5), 263–288.
Rocca, M. A., Ceccarelli, A., Falini, A., Colombo, B., Tortorella, P., Bernasconi, L., Comi, G., Scotti, G., & Filippi, M. (2006). Brain gray matter changes in migraine patients with T2-visible lesions: A 3-T MRI study. Stroke, 37(7), 1765–1770.
Russo, A., Silvestro, M., Tedeschi, G., & Tessitore, A. (2017). Physiopathology of migraine: What have we learned from functional imaging? Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports, 17(12), 95.
Russo, A., Silvestro, M., Tessitore, A., & Tedeschi, G. (2018). Advances in migraine neuroimaging and clinical utility: From the MRI to the bedside. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 18(7), 533–544.
Russo, A., Tessitore, A., Giordano, A., Corbo, D., Marcuccio, L., De Stefano, M., et al. (2012). Executive resting-state network connectivity in migraine without aura. Cephalalgia, 32(14), 1041–1048.
Schwedt, T. J., & Dodick, D. W. (2009). Advanced neuroimaging of migraine. The Lancet Neurology, 8(6), 560–568.
Schwedt, T. J., Larson-Prior, L., Coalson, R. S., Nolan, T., Mar, S., Ances, B. M., Benzinger, T., & Schlaggar, B. L. (2014). Allodynia and descending pain modulation in migraine: A resting state functional connectivity analysis. Pain Medicine, 15(1), 154–165.
Schwedt, T. J., Schlaggar, B. L., Mar, S., Nolan, T., Coalson, R. S., Nardos, B., et al. (2013). Atypical resting-state functional connectivity of affective pain regions in chronic migraine. Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain, 53(5), 737–751.
Steiner, T. J., Stovner, L. J., & Birbeck, G. L. (2013). Migraine: The seventh disabler. Journal of Headache & Pain, 53(2), 227–229.
Valfre, W., Rainero, I., Bergui, M., & Pinessi, L. (2008). Voxel-based morphometry reveals gray matter abnormalities in migraine. Headache, 48(1), 109–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00723.x.
Wöber-Bingöl, Ç. (2013). Epidemiology of migraine and headache in children and adolescents. Current Pain and Headache Reports, 17(6), 341.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China [grant number 81701669, 81701667]; the Nature Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province [grant number BK20170368, BK20170367]; the Scientific Research Program of Jiangsu Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission [H201621].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yang Yu, Hongru Zhao, Lingling Dai, Yunyan Su, Ximing Wang, Can Chen, Yalei Shang, Jun Ke, Chunhong Hu declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki, and were approved by the ethics committee of the first affiliated hospital of Soochow university.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Zhao, H., Dai, L. et al. Headache frequency associates with brain microstructure changes in patients with migraine without aura. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 60–67 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00232-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00232-2