Abstract
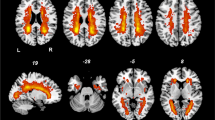
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is common in the end-stage renal disease (ESRD) population; however, their interrelationship remains largely unclear. In the current study, we aimed to investigate the brain structure variation in ESRD patients with RLS (ERSD-RLS) and its potential relation with the severity of RLS. Diffusion tensor imaging and T1-weighted imaging were obtained from 64 ERSD-RLS and 64 matched healthy controls. Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis and tractography atlas-based analysis (TABS) were used to detect the alteration of gray matter (GM) volume and white matter (WM) microstructural characterization. The corticospinal tract (CST), which is a main motor-pathway, was selected as a fiber bundle of interest in the TABS analysis. The severity of RLS was evaluated by using the International RLS Study Group scale. Lastly, a correlation analysis was performed to explore the interrelationship between RLS rating scores and brain structure measurements. For the results, ERSD-RLS showed abnormal GM volume of motor-related brain regions located in the bilateral superior frontal gyri, precentral gyrus, and putamen. Significant differences in the diffusion properties were found at the posterior limb of the internal capsule. Furthermore, the severity of RLS was only significantly associated with the diffusion properties, which was not found in the motor-related regions of GM. Our results suggest that the motor-related brain structure was altered in ERSD-RLS. The abnormal WM microstructure of the CST may serve as an imaging marker correlated with the severity of motor dysfunction in ERSD-RLS, indicating that WM neuroprotection should be considered when improving motor function in ERSD-RLS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R. P., Picchietti, D. L., Garcia-Borreguero, D., Ondo, W. G., Walters, A. S., Winkelman, J. W., et al. (2014). Restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: Updated international restless legs syndrome study group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria--history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Medicine, 15(8), 860–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2014.03.025.
Bonnet, M. H., & Arand, D. L. (2010). Hyperarousal and insomnia: State of the science. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 14(1), 9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2009.05.002.
Chavoshi, F., Einollahi, B., Sadeghniat Haghighi, K., Saraei, M., & Izadianmehr, N. (2015). Prevalence and sleep related disorders of restless leg syndrome in hemodialysis patients. Nephro-Urology Monthly, 7(2), e24611. https://doi.org/10.5812/numonthly.24611.
Chen, Y. J., Lo, Y. C., Hsu, Y. C., Fan, C. C., Hwang, T. J., Liu, C. M., et al. (2015). Automatic whole brain tract-based analysis using predefined tracts in a diffusion spectrum imaging template and an accurate registration strategy. Human Brain Mapping, 36(9), 3441–3458. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22854.
Chou, M. C., Hsieh, T. J., Lin, Y. L., Hsieh, Y. T., Li, W. Z., Chang, J. M., et al. (2013). Widespread white matter alterations in patients with end-stage renal disease: A voxelwise diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 34(10), 1945–1951. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3511.
Duque, J., Greenhouse, I., Labruna, L., & Ivry, R. B. (2017). Physiological markers of motor inhibition during human behavior. Trends in Neurosciences, 40(4), 219–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.02.006.
Einollahi, B., & Izadianmehr, N. (2014). Restless leg syndrome: A neglected diagnosis. Nephro-Urology Monthly, 6(5), e22009. https://doi.org/10.5812/numonthly.22009.
Espie, C. A., Broomfield, N. M., MacMahon, K. M., Macphee, L. M., & Taylor, L. M. (2006). The attention-intention-effort pathway in the development of psychophysiologic insomnia: A theoretical review. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 10(4), 215–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2006.03.002.
Fornito, A., Zalesky, A., & Breakspear, M. (2015). The connectomics of brain disorders. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 16(3), 159–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3901.
Geng, X., Gouttard, S., Sharma, A., Gu, H., Styner, M., Lin, W., et al. (2012). Quantitative tract-based white matter development from birth to age 2years. Neuroimage, 61(3), 542–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.057.
Goodlett, C. B., Fletcher, P. T., Gilmore, J. H., & Gerig, G. (2009). Group analysis of DTI fiber tract statistics with application to neurodevelopment. Neuroimage, 45(1 Suppl), S133–S142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.060.
Guo, C. N., Yang, W. J., Zhan, S. Q., Yang, X. F., Chen, M. C., Fuller, P. M., & Lu, J. (2017). Targeted disruption of supraspinal motor circuitry reveals a distributed network underlying restless legs syndrome (RLS)-like movements in the rat. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 9905. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10284-3.
Guye, M., Parker, G. J., Symms, M., Boulby, P., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., Salek-Haddadi, A., et al. (2003). Combined functional MRI and tractography to demonstrate the connectivity of the human primary motor cortex in vivo. Neuroimage, 19(4), 1349–1360.
Imfeld, A., Oechslin, M. S., Meyer, M., Loenneker, T., & Jancke, L. (2009). White matter plasticity in the corticospinal tract of musicians: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroimage, 46(3), 600–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.025.
Jang, S. H. (2009). The role of the corticospinal tract in motor recovery in patients with a stroke: A review. NeuroRehabilitation, 24(3), 285–290. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-2009-0480.
Lanza, G., Cantone, M., Lanuzza, B., Pennisi, M., Bella, R., Pennisi, G., & Ferri, R. (2015). Distinctive patterns of cortical excitability to transcranial magnetic stimulation in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, restless legs syndrome, insomnia, and sleep deprivation. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 19, 39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2014.04.001.
Lindemann, K., Muller, H. P., Ludolph, A. C., Hornyak, M., & Kassubek, J. (2016). Microstructure of the midbrain and cervical spinal cord in idiopathic restless legs syndrome: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Sleep, 39(2), 423–428. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.5456.
Liu, J., Liu, H., Mu, J., Xu, Q., Chen, T., Dun, W., et al. (2017). Altered white matter microarchitecture in the cingulum bundle in women with primary dysmenorrhea: A tract-based analysis study. Human Brain Mapping, 38(9), 4430–4443. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23670.
Lu, R., Kiernan, M. C., Murray, A., Rosner, M. H., & Ronco, C. (2015). Kidney-brain crosstalk in the acute and chronic setting. Nature Reviews. Nephrology, 11(12), 707–719. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2015.131.
Marshall, R. S., Perera, G. M., Lazar, R. M., Krakauer, J. W., Constantine, R. C., & DeLaPaz, R. L. (2000). Evolution of cortical activation during recovery from corticospinal tract infarction. Stroke, 31(3), 656–661.
Meier, J. D., Aflalo, T. N., Kastner, S., & Graziano, M. S. (2008). Complex organization of human primary motor cortex: A high-resolution fMRI study. Journal of Neurophysiology, 100(4), 1800–1812. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.90531.2008.
Meng, Y., & Zhang, X. (2014). In vivo diffusion spectrum imaging of non-human primate brain: Initial experience in transcallosal fiber examination. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery, 4(2), 129–135. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2014.04.05.
Merlino, G., Piani, A., Dolso, P., Adorati, M., Cancelli, I., Valente, M., et al. (2006). Sleep disorders in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing dialysis therapy. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 21(1), 184–190. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfi144.
Molnar, M. Z., Novak, M., Ambrus, C., Szeifert, L., Kovacs, A., Pap, J., et al. (2005). Restless legs syndrome in patients after renal transplantation. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 45(2), 388–396.
Mucsi, I., Molnar, M. Z., Ambrus, C., Szeifert, L., Kovacs, A. Z., Zoller, R., et al. (2005). Restless legs syndrome, insomnia and quality of life in patients on maintenance dialysis. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 20(3), 571–577. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfh654.
Murray, A. M. (2008). Cognitive impairment in the aging dialysis and chronic kidney disease populations: An occult burden. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease, 15(2), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2008.01.010.
O'Donnell, L. J., Westin, C. F., & Golby, A. J. (2009). Tract-based morphometry for white matter group analysis. Neuroimage, 45(3), 832–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.12.023.
Oldenburg, I. A., & Sabatini, B. L. (2015). Antagonistic but not symmetric regulation of primary motor cortex by basal ganglia direct and indirect pathways. Neuron, 86(5), 1174–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.05.008.
Qiu, M. H., Yao, Q. L., Vetrivelan, R., Chen, M. C., & Lu, J. (2016). Nigrostriatal dopamine acting on globus pallidus regulates sleep. Cerebral Cortex, 26(4), 1430–1439. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu241.
Riemann, D., Spiegelhalder, K., Feige, B., Voderholzer, U., Berger, M., Perlis, M., & Nissen, C. (2010). The hyperarousal model of insomnia: A review of the concept and its evidence. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 14(1), 19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2009.04.002.
Rizzo, G., Manners, D., Testa, C., Tonon, C., Vetrugno, R., Marconi, S., et al. (2013). Low brain iron content in idiopathic restless legs syndrome patients detected by phase imaging. Movement Disorders, 28(13), 1886–1890. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25576.
Schaechter, J. D., Perdue, K. L., & Wang, R. (2008). Structural damage to the corticospinal tract correlates with bilateral sensorimotor cortex reorganization in stroke patients. Neuroimage, 39(3), 1370–1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.071.
Schattschneider, J., Bode, A., Wasner, G., Binder, A., Deuschl, G., & Baron, R. (2004). Idiopathic restless legs syndrome: Abnormalities in central somatosensory processing. Journal of Neurology, 251(8), 977–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-0475-3.
Stocco, A., Lebiere, C., & Anderson, J. R. (2010). Conditional routing of information to the cortex: A model of the basal ganglia's role in cognitive coordination. Psychological Review, 117(2), 541–574. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019077.
Thomason, M. E., & Thompson, P. M. (2011). Diffusion imaging, white matter, and psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 7, 63–85. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104507.
Zaaimi, B., Edgley, S. A., Soteropoulos, D. S., & Baker, S. N. (2012). Changes in descending motor pathway connectivity after corticospinal tract lesion in macaque monkey. Brain, 135(Pt 7), 2277–2289. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws115.
Zhang, L., Wang, F., Wang, L., Wang, W., Liu, B., Liu, J., et al. (2012). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet, 379(9818), 815–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60033-6.
Zhang, L. J., Wen, J., Ni, L., Zhong, J., Liang, X., Zheng, G., et al. (2013). Predominant gray matter volume loss in patients with end-stage renal disease: A voxel-based morphometry study. Metabolic Brain Disease, 28(4), 647–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9438-7.
Zhang, R., Liu, K., Yang, L., Zhou, T., Qian, S., Li, B., et al. (2015). Reduced white matter integrity and cognitive deficits in maintenance hemodialysis ESRD patients: A diffusion-tensor study. European Radiology, 25(3), 661–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3466-5.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81471737, 81571640, 81473603, and 81501547; the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JB171201); and the Science and Technology Planning Program of Henan Province under Grant Nos. 172106000074 and 162102210218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Junya Mu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Xiaohui Liu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Shaohui Ma declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Tao Chen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Xueying Ma declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Peng Li declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Dun Ding declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Jixin Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Ming Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, J., Liu, X., Ma, S. et al. The variation of motor-related brain structure and its relation to abnormal motor behaviors in end-stage renal disease patients with restless legs syndrome. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 42–50 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9968-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9968-z