Abstract
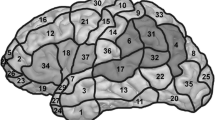
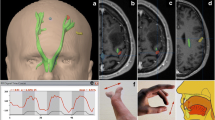
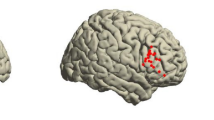
In preoperative planning, fMRI and repetitive navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) repeatedly revealed differences in the detected language sites, which can be attributed to tumor-induced oxygenation changes impairing the accuracy of fMRI. We therefore compared the accordance of those techniques in healthy subjects using exactly the same tasks in both investigations. 19 healthy right-handed subjects performed object naming, pseudoword reading, verb generation, and action naming during fMRI at 3 T and rTMS. For rTMS language mapping, we stimulated 46 cortical spots over the left hemisphere; each site was stimulated for three times. Language positive points during rTMS for one, two, or three errors out the three stimulations per spot (1/3, 2/3, 3/3) were exported via DICOM, and compared to the positive fMRI clusters. As a result of this comparison, the best correlation was observed between 3/3 errors and fMRI for pseudoword reading and verb generation with t-values of pu < 0.001, uncorrected for multiple comparisons, on average across the whole rTMS-spot map. We found a close spatial agreement between several rTMS-spots (2/3 and 3/3 errors) and fMRI clusters accentuated in the frontal lobe, followed by the parietal lobe and less in the temporal lobe. Compared to the fMRI clusters, there was a higher congruence for 2/3 and 3/3 errors than for 1/3 errors. Overall, results of language mapping in healthy subjects by fMRI and rTMS correspond well yet depending on the used language task.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- aMTG:
-
Anterior middle temporal gyrus
- CPS:
-
Cortical parcellation system
- DCS:
-
Direct cortical stimulation
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalography
- EPI:
-
Echo planar imaging
- fMRI:
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
- GLM:
-
General linear model
- ITG:
-
Inferior temporal gyrus
- MEG:
-
Magnetoencephalography
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- nTMS:
-
Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation
- orIFG:
-
Orbital part of the inferior frontal gyrus
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- polIFG:
-
Polar inferior frontal gyrus
- polMFG:
-
Polar middle frontal gyrus
- polMTG:
-
Polar middle temporal gyrus
- polSFG:
-
Polar superior frontal gyrus
- polSTG:
-
Polar superior temporal gyrus
- PTI:
-
Picture to trigger interval
- RMT:
-
Resting Motor Threshold
- rTMS:
-
Repetitive navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation
- SEM:
-
Standard error of mean
- VAS:
-
Visual analogue scale
References
Alario, F. X., Chainay, H., Lehericy, S., & Cohen, L. (2006). The role of the supplementary motor area (SMA) in word production. Brain Research, 1076(1), 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.11.104.
Allendorfer, J. B., Kissela, B. M., Holland, S. K., & Szaflarski, J. P. (2012). Different patterns of language activation in post-stroke aphasia are detected by overt and covert versions of the verb generation fMRI task. Medical Science Monitor, 18(3), CR135–CR137.
Aziz-Zadeh, L., Cattaneo, L., Rochat, M., & Rizzolatti, G. (2005). Covert speech arrest induced by rTMS over both motor and nonmotor left hemisphere frontal sites. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(6), 928–938. https://doi.org/10.1162/0898929054021157.
Bak, T. H., O'Donovan, D. G., Xuereb, J. H., Boniface, S., & Hodges, J. R. (2001). Selective impairment of verb processing associated with pathological changes in Brodmann areas 44 and 45 in the motor neurone disease-dementia-aphasia syndrome. Brain, 124(Pt 1), 103–120.
Barker, A. T., Jalinous, R., & Freeston, I. L. (1985). Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet, 1(8437), 1106–1107.
Binder, J. R., & Desai, R. H. (2011). The neurobiology of semantic memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(11), 527–536, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.7001.
Binder, J. R., Frost, J. A., Hammeke, T. A., Bellgowan, P. S., Rao, S. M., & Cox, R. W. (1999). Conceptual processing during the conscious resting state. A functional MRI study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 11(1), 80–95.
Binder, J. R., Desai, R. H., Graves, W. W., & Conant, L. L. (2009). Where is the semantic system? A critical review and meta-analysis of 120 functional neuroimaging studies. Cerebral Cortex, 19(12), 2767–2796. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp055.
Bookheimer, S. (2002). Functional MRI of language: New approaches to understanding the cortical organization of semantic processing. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 25, 151–188. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142946.
Bookheimer, S. (2007). Pre-surgical language mapping with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropsychology Review, 17(2), 145–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-007-9026-x.
Buckner, R. L., Raichle, M. E., & Petersen, S. E. (1995). Dissociation of human prefrontal cortical areas across different speech production tasks and gender groups. Journal of Neurophysiology, 74(5), 2163–2173.
Chang, E. F., Clark, A., Smith, J. S., Polley, M. Y., Chang, S. M., Barbaro, N. M., et al. (2011). Functional mapping-guided resection of low-grade gliomas in eloquent areas of the brain: Improvement of long-term survival. Clinical article. Journal of Neurosurgery, 114(3), 566–573. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.6.JNS091246.
Corina, D. P., Gibson, E. K., Martin, R., Poliakov, A., Brinkley, J., & Ojemann, G. A. (2005). Dissociation of action and object naming: evidence from cortical stimulation mapping. Human Brain Mapping, 24(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20063.
Corina, D. P., Loudermilk, B. C., Detwiler, L., Martin, R. F., Brinkley, J. F., & Ojemann, G. (2010). Analysis of naming errors during cortical stimulation mapping: implications for models of language representation. Brain and Language, 115(2), 101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2010.04.001.
Crescentini, C., Shallice, T., & Macaluso, E. (2010). Item retrieval and competition in noun and verb generation: an FMRI study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(6), 1140–1157. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21255.
Crosson, B., Sadek, J. R., Maron, L., Gokcay, D., Mohr, C. M., Auerbach, E. J., et al. (2001). Relative shift in activity from medial to lateral frontal cortex during internally versus externally guided word generation. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 13(2), 272–283.
de Zubicaray, G., McMahon, K., Eastburn, M., Pringle, A., & Lorenz, L. (2006). Classic identity negative priming involves accessing semantic representations in the left anterior temporal cortex. Neuroimage, 33(1), 383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.06.024.
Demonet, J. F., Chollet, F., Ramsay, S., Cardebat, D., Nespoulous, J. L., Wise, R., et al. (1992). The anatomy of phonological and semantic processing in normal subjects. Brain, 115(Pt 6), 1753–1768.
Epstein, C. M., Lah, J. J., Meador, K., Weissman, J. D., Gaitan, L. E., & Dihenia, B. (1996). Optimum stimulus parameters for lateralized suppression of speech with magnetic brain stimulation. Neurology, 47(6), 1590–1593.
Felty, R. A. (2007). Context effects in spoken word recognition of English and German by native and non-native listeners. East Lansing: Michigan State University.
FitzGerald, D. B., Cosgrove, G. R., Ronner, S., Jiang, H., Buchbinder, B. R., Belliveau, J. W., et al. (1997). Location of language in the cortex: A comparison between functional MR imaging and electrocortical stimulation. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 18(8), 1529–1539.
Friston, K. J., Williams, S., Howard, R., Frackowiak, R. S., & Turner, R. (1996). Movement-related effects in fMRI time-series. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 35(3), 346–355.
Gaillard, W. D., Balsamo, L., Xu, B., McKinney, C., Papero, P. H., Weinstein, S., et al. (2004). fMRI language task panel improves determination of language dominance. Neurology, 63(8), 1403–1408.
Giussani, C., Roux, F. E., Ojemann, J., Sganzerla, E. P., Pirillo, D., & Papagno, C. (2010). Is preoperative functional magnetic resonance imaging reliable for language areas mapping in brain tumor surgery? Review of language functional magnetic resonance imaging and direct cortical stimulation correlation studies. Neurosurgery, 66(1), 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000360392.15450.C9.
Gold, B. T., & Buckner, R. L. (2002). Common prefrontal regions coactivate with dissociable posterior regions during controlled semantic and phonological tasks. Neuron, 35(4), 803–812.
Haglund, M. M., Berger, M. S., Shamseldin, M., Lettich, E., & Ojemann, G. A. (1994). Cortical localization of temporal lobe language sites in patients with gliomas. Neurosurgery, 34(4), 567–576 discussion 576.
Hagoort, P., Indefrey, P., Brown, C., Herzog, H., Steinmetz, H., & Seitz, R. J. (1999). The neural circuitry involved in the reading of German words and pseudowords: a PET study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 11(4), 383–398.
Hauck, T., Tanigawa, N., Probst, M., Wohlschlaeger, A., Ille, S., Sollmann, N., et al. (2015a). Stimulation frequency determines the distribution of language positive cortical regions during navigated transcranial magnetic brain stimulation. BMC Neuroscience, 16, 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-015-0143-9.
Hauck, T., Tanigawa, N., Probst, M., Wohlschlaeger, A., Ille, S., Sollmann, N., et al. (2015b). Task type affects location of language-positive cortical regions by repetitive navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation mapping. PLoS One, 10(4), e0125298. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125298.
Hervey-Jumper, S. L., Li, J., Lau, D., Molinaro, A. M., Perry, D. W., Meng, L., et al. (2015). Awake craniotomy to maximize glioma resection: methods and technical nuances over a 27-year period. Journal of Neurosurgery, 123(2), 325–339. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.JNS141520.
Ille, S., Sollmann, N., Hauck, T., Maurer, S., Tanigawa, N., Obermueller, T., et al. (2015a). Impairment of preoperative language mapping by lesion location: a functional magnetic resonance imaging, navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation, and direct cortical stimulation study. Journal of Neurosurgery, 123(2), 314–324. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.JNS141582.
Ille, S., Sollmann, N., Hauck, T., Maurer, S., Tanigawa, N., Obermueller, T., et al. (2015b). Impairment of preoperative language mapping by lesion location: a functional magnetic resonance imaging, navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation, and direct cortical stimulation study. J Neurosurg, 1–11, https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.JNS141582.
Ille, S., Sollmann, N., Hauck, T., Maurer, S., Tanigawa, N., Obermueller, T., et al. (2015c). Combined noninvasive language mapping by navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and functional MRI and its comparison with direct cortical stimulation. [Comparative Study. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. Journal of Neurosurgery, 123(1), 212–225. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.9.JNS14929.
Ille, S., Sollmann, N., Hauck, T., Maurer, S., Tanigawa, N., Obermueller, T., et al. (2015d). Combined noninvasive language mapping by navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and functional MRI and its comparison with direct cortical stimulation. Journal of Neurosurgery, 1–14, https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.9.JNS14929.
Ilmoniemi, R. J., Ruohonen, J., & Karhu, J. (1999). Transcranial magnetic stimulation--a new tool for functional imaging of the brain. Critical Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 27(3–5), 241–284.
Indefrey, P. (2011). The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components: A critical update. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 255. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00255.
Indefrey, P., & Levelt, W. J. (2004). The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components. Cognition, 92(1–2), 101–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2002.06.001.
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage, 17(2), 825–841.
Kim, S. G., & Ogawa, S. (2012). Biophysical and physiological origins of blood oxygenation level-dependent fMRI signals. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 32(7), 1188–1206. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.23.
Kiyosawa, M., Inoue, C., Kawasaki, T., Tokoro, T., Ishii, K., Ohyama, M., et al. (1996). Functional neuroanatomy of visual object naming: a PET study. Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 234(2), 110–115.
Kononen, M., Tamsi, N., Saisanen, L., Kemppainen, S., Maatta, S., Julkunen, P., et al. (2015). Non-invasive mapping of bilateral motor speech areas using navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 248, 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.03.030.
Krieg, S. M., Shiban, E., Buchmann, N., Meyer, B., & Ringel, F. (2013a). Presurgical navigated transcranial magnetic brain stimulation for recurrent gliomas in motor eloquent areas. Clinical Neurophysiology, 124(3), 522–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2012.08.011.
Krieg, S. M., Sollmann, N., Hauck, T., Ille, S., Foerschler, A., Meyer, B., et al. (2013b). Functional language shift to the right hemisphere in patients with language-eloquent brain tumors. PLoS One, 8(9), e75403. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075403.
Krieg, S. M., Sollmann, N., Hauck, T., Ille, S., Meyer, B., & Ringel, F. (2014a). Repeated mapping of cortical language sites by preoperative navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation compared to repeated intraoperative DCS mapping in awake craniotomy. BMC Neuroscience, 15, 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-15-20.
Krieg, S. M., Tarapore, P. E., Picht, T., Tanigawa, N., Houde, J., Sollmann, N., et al. (2014b). Optimal timing of pulse onset for language mapping with navigated repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neuroimage, 100C, 219–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.06.016.
Krieg, S. M., Sollmann, N., Tanigawa, N., Foerschler, A., Meyer, B., & Ringel, F. (2015). Cortical distribution of speech and language errors investigated by visual object naming and navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Structure and Function. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1042-7.
Kuchcinski, G., Mellerio, C., Pallud, J., Dezamis, E., Turc, G., Rigaux-Viode, O., et al. (2015). Three-tesla functional MR language mapping: Comparison with direct cortical stimulation in gliomas. Neurology, 84(6), 560–568. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001226.
Lioumis, P., Zhdanov, A., Makela, N., Lehtinen, H., Wilenius, J., Neuvonen, T., et al. (2012). A novel approach for documenting naming errors induced by navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 204(2), 349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.11.003.
Logothetis, N. K., Pauls, J., Augath, M., Trinath, T., & Oeltermann, A. (2001). Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal. Nature, 412(6843), 150–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/35084005.
Lubrano, V., Filleron, T., Demonet, J. F., & Roux, F. E. (2014). Anatomical correlates for category-specific naming of objects and actions: a brain stimulation mapping study. Human Brain Mapping, 35(2), 429–443. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22189.
Martin, A., Wiggs, C. L., Ungerleider, L. G., & Haxby, J. V. (1996). Neural correlates of category-specific knowledge. Nature, 379(6566), 649–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/379649a0.
Matzig, S., Druks, J., Masterson, J., & Vigliocco, G. (2009). Noun and verb differences in picture naming: past studies and new evidence. Cortex, 45(6), 738–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2008.10.003.
Moore, C. J., & Price, C. J. (1999). Three distinct ventral occipitotemporal regions for reading and object naming. Neuroimage, 10(2), 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1999.0450.
Moseley, R. L., & Pulvermuller, F. (2014). Nouns, verbs, objects, actions, and abstractions: local fMRI activity indexes semantics, not lexical categories. Brain and Language, 132, 28–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2014.03.001.
Murtha, S., Chertkow, H., Beauregard, M., & Evans, A. (1999). The neural substrate of picture naming. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 11(4), 399–423.
Neggers, S. F., Langerak, T. R., Schutter, D. J., Mandl, R. C., Ramsey, N. F., Lemmens, P. J., et al. (2004). A stereotactic method for image-guided transcranial magnetic stimulation validated with fMRI and motor-evoked potentials. Neuroimage, 21(4), 1805–1817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.12.006.
Ogawa, S., Lee, T. M., Kay, A. R., & Tank, D. W. (1990). Brain magnetic resonance imaging with contrast dependent on blood oxygenation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 87(24), 9868–9872.
Ojemann, J. G., Ojemann, G. A., & Lettich, E. (2002). Cortical stimulation mapping of language cortex by using a verb generation task: effects of learning and comparison to mapping based on object naming. Journal of Neurosurgery, 97(1), 33–38. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.97.1.0033.
Oldfield, R. C. (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia, 9(1), 97–113.
Pascual-Leone, A., Gates, J. R., & Dhuna, A. (1991). Induction of speech arrest and counting errors with rapid-rate transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology, 41(5), 697–702.
Pascual-Leone, A., Bartres-Faz, D., & Keenan, J. P. (1999). Transcranial magnetic stimulation: studying the brain-behaviour relationship by induction of 'virtual lesions'. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 354(1387), 1229–1238. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1999.0476.
Paus, T. (1999). Imaging the brain before, during, and after transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neuropsychologia, 37(2), 219–224.
Pei, X., Leuthardt, E. C., Gaona, C. M., Brunner, P., Wolpaw, J. R., & Schalk, G. (2011). Spatiotemporal dynamics of electrocorticographic high gamma activity during overt and covert word repetition. Neuroimage, 54(4), 2960–2972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.029.
Perani, D., Cappa, S. F., Schnur, T., Tettamanti, M., Collina, S., Rosa, M. M., et al. (1999). The neural correlates of verb and noun processing. A PET Study, 122(12), 2337–2344. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/122.12.2337.
Peschke, C., Ziegler, W., Kappes, J., & Baumgaertner, A. (2009). Auditory-motor integration during fast repetition: the neuronal correlates of shadowing. Neuroimage, 47(1), 392–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.03.061.
Petrovich Brennan, N. M., Whalen, S., de Morales Branco, D., O'Shea, J. P., Norton, I. H., & Golby, A. J. (2007). Object naming is a more sensitive measure of speech localization than number counting: converging evidence from direct cortical stimulation and fMRI. Neuroimage, 37(Suppl 1), S100–S108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.052.
Picht, T., Mularski, S., Kuehn, B., Vajkoczy, P., Kombos, T., & Suess, O. (2009). Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation for preoperative functional diagnostics in brain tumor surgery. Neurosurgery, 65(6 Suppl), 93–98.
Picht, T., Schulz, J., Hanna, M., Schmidt, S., Suess, O., & Vajkoczy, P. (2012). Assessment of the influence of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation on surgical planning for tumors in or near the motor cortex. Neurosurgery, 70(5), 1248–1256; discussion 1256-1247. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e318243881e.
Picht, T., Krieg, S. M., Sollmann, N., Rosler, J., Niraula, B., Neuvonen, T., et al. (2013). A comparison of language mapping by preoperative navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and direct cortical stimulation during awake surgery. Neurosurgery, 72(5), 808–819. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182889e01.
Poldrack, R. A., Wagner, A. D., Prull, M. W., Desmond, J. E., Glover, G. H., & Gabrieli, J. D. (1999). Functional specialization for semantic and phonological processing in the left inferior prefrontal cortex. Neuroimage, 10(1), 15–35. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1999.0441.
Price, C. J. (2012). A review and synthesis of the first 20 years of PET and fMRI studies of heard speech, spoken language and reading. Neuroimage, 62(2), 816–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.04.062.
Price, C. J., Wise, R. J., Warburton, E. A., Moore, C. J., Howard, D., Patterson, K., et al. (1996). Hearing and saying. The functional neuro-anatomy of auditory word processing. Brain, 119(Pt 3), 919–931.
Riecker, A., Ackermann, H., Wildgruber, D., Dogil, G., & Grodd, W. (2000). Opposite hemispheric lateralization effects during speaking and singing at motor cortex, insula and cerebellum. Neuroreport, 11(9), 1997–2000.
Rosler, J., Niraula, B., Strack, V., Zdunczyk, A., Schilt, S., Savolainen, P., et al. (2014). Language mapping in healthy volunteers and brain tumor patients with a novel navigated TMS system: evidence of tumor-induced plasticity. Clinical Neurophysiology, 125(3), 526–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2013.08.015.
Rossi, S., Hallett, M., Rossini, P. M., & Pascual-Leone, A. (2009). Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clinical Neurophysiology, 120(12), 2008–2039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.08.016.
Roux, F. E., Boulanouar, K., Lotterie, J. A., Mejdoubi, M., LeSage, J. P., & Berry, I. (2003). Language functional magnetic resonance imaging in preoperative assessment of language areas: correlation with direct cortical stimulation. Neurosurgery, 52(6), 1335–1345 discussion 1345-1337.
Ruohonen, J., & Ilmoniemi, R. J. (1999). Modeling of the stimulating field generation in TMS. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. Supplement, 51, 30–40.
Ruohonen, J., & Karhu, J. (2010). Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurophysiologie Clinique, 40(1), 7–17.
Saccuman, M. C., Cappa, S. F., Bates, E. A., Arevalo, A., Della Rosa, P., Danna, M., et al. (2006). The impact of semantic reference on word class: an fMRI study of action and object naming. Neuroimage, 32(4), 1865–1878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.04.179.
Sack, A. T., Cohen Kadosh, R., Schuhmann, T., Moerel, M., Walsh, V., & Goebel, R. (2009). Optimizing functional accuracy of TMS in cognitive studies: A comparison of methods. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(2), 207–221. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21126.
Salmelin, R., Helenius, P., & Service, E. (2000). Neurophysiology of fluent and impaired reading: a magnetoencephalographic approach. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology, 17(2), 163–174.
Sanai, N., & Berger, M. S. (2008). Mapping the horizon: techniques to optimize tumor resection before and during surgery. Clinical Neurosurgery, 55, 14–19.
Shapiro, K. A., Moo, L. R., & Caramazza, A. (2006). Cortical signatures of noun and verb production. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(5), 1644–1649. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504142103.
Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2005). Dyslexia (specific reading disability). Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1301–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.01.043.
Shaywitz, B. A., Shaywitz, S. E., Pugh, K. R., Mencl, W. E., Fulbright, R. K., Skudlarski, P., et al. (2002). Disruption of posterior brain systems for reading in children with developmental dyslexia. Biological Psychiatry, 52(2), 101–110.
Shepherd, F. A., Domerg, C., Hainaut, P., Janne, P. A., Pignon, J. P., Graziano, S., et al. (2013). Pooled analysis of the prognostic and predictive effects of KRAS mutation status and KRAS mutation subtype in early-stage resected non-small-cell lung cancer in four trials of adjuvant chemotherapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 31(17), 2173–2181. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.48.1390.
Simos, P. G., Breier, J. I., Fletcher, J. M., Foorman, B. R., Castillo, E. M., & Papanicolaou, A. C. (2002). Brain mechanisms for reading words and pseudowords: an integrated approach. Cerebral Cortex, 12(3), 297–305.
Siri, S., Tettamanti, M., Cappa, S. F., Della Rosa, P., Saccuman, C., Scifo, P., et al. (2008). The neural substrate of naming events: effects of processing demands but not of grammatical class. Cerebral Cortex, 18(1), 171–177. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhm043.
Snodgrass, J. G., & Vanderwart, M. (1980). A standardized set of 260 pictures: Norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity, and visual complexity. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning and Memory, 6(2), 174–215.
Sollmann, N., Hauck, T., Hapfelmeier, A., Meyer, B., Ringel, F., & Krieg, S. M. (2013a). Intra- and interobserver variability of language mapping by navigated transcranial magnetic brain stimulation. BMC Neuroscience, 14, 150. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-14-150.
Sollmann, N., Picht, T., Makela, J. P., Meyer, B., Ringel, F., & Krieg, S. M. (2013b). Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation for preoperative language mapping in a patient with a left frontoopercular glioblastoma. Journal of Neurosurgery, 118(1), 175–179. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.9.JNS121053.
Sollmann, N., Tanigawa, N., Ringel, F., Zimmer, C., Meyer, B., & Krieg, S. M. (2014). Language and its right-hemispheric distribution in healthy brains: An investigation by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neuroimage, 102(Pt 2), 776–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.09.002.
Sollmann, N., Ille, S., Obermueller, T., Negwer, C., Ringel, F., Meyer, B., et al. (2015a). The impact of repetitive navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation coil positioning and stimulation parameters on human language function. European Journal of Medical Research, 20, 47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-015-0138-0.
Sollmann, N., Tanigawa, N., Tussis, L., Hauck, T., Ille, S., Maurer, S., et al. (2015b). Cortical regions involved in semantic processing investigated by repetitive navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and object naming. Neuropsychologia, 70, 185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.02.035.
Stark, C. E., & Squire, L. R. (2001). When zero is not zero: the problem of ambiguous baseline conditions in fMRI. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(22), 12760–12766. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.221462998.
Tarapore, P. E., Tate, M. C., Findlay, A. M., Honma, S. M., Mizuiri, D., Berger, M. S., et al. (2012). Preoperative multimodal motor mapping: a comparison of magnetoencephalography imaging, navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation, and direct cortical stimulation. Journal of Neurosurgery, 117(2), 354–362. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.5.JNS112124.
Tarapore, P. E., Findlay, A. M., Honma, S. M., Mizuiri, D., Houde, J. F., Berger, M. S., et al. (2013). Language mapping with navigated repetitive TMS: proof of technique and validation. Neuroimage, 82, 260–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.018.
Taylor, J. S., Rastle, K., & Davis, M. H. (2013). Can cognitive models explain brain activation during word and pseudoword reading? A meta-analysis of 36 neuroimaging studies. Psychological Bulletin, 139(4), 766–791. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030266.
Tsapkini, K., Frangakis, C. E., & Hillis, A. E. (2011). The function of the left anterior temporal pole: evidence from acute stroke and infarct volume. Brain, 134(Pt 10), 3094–3105. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr050.
Van Westen, D., Skagerberg, G., Olsrud, J., Fransson, P., & Larsson, E. M. (2005). Functional magnetic resonance imaging at 3T as a clinical tool in patients with intracranial tumors. Acta Radiologica, 46(6), 599–609.
Vigliocco, G., Vinson, D. P., Druks, J., Barber, H., & Cappa, S. F. (2011). Nouns and verbs in the brain: a review of behavioural, electrophysiological, neuropsychological and imaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35(3), 407–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.04.007.
Viswanathan, A., & Freeman, R. D. (2007). Neurometabolic coupling in cerebral cortex reflects synaptic more than spiking activity. Nature Neuroscience, 10(10), 1308–1312. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1977.
Wassermann, E. M., Blaxton, T. A., Hoffman, E. A., Berry, C. D., Oletsky, H., Pascual-Leone, A., et al. (1999). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the dominant hemisphere can disrupt visual naming in temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Neuropsychologia, 37(5), 537–544.
Wise, R., Chollet, F., Hadar, U., Friston, K., Hoffner, E., & Frackowiak, R. (1991). Distribution of cortical neural networks involved in word comprehension and word retrieval. Brain, 114(Pt 4), 1803–1817.
Funding
The study was financed by institutional grants from the Department of Neurosurgery and the Section of Neuroradiology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
SK, FR, and BM are consultants for Brainlab AG (Munich, Germany). SK is consultant for Nexstim Plc (Helsinki, Finland).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hauck, T., Probst, M., Zimmer, C. et al. Language function shows comparable cortical patterns by functional MRI and repetitive nTMS in healthy volunteers. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 1071–1092 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9921-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9921-1