Abstract
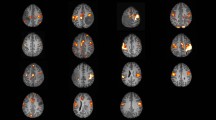
Brain metastases are the most prevalent cerebral tumors. Resting state networks (RSNs) are involved in multiple perceptual and cognitive functions. Therefore, precisely localizing multiple RSNs may be extremely valuable before surgical resection of metastases, to minimize neurocognitive impairments. Here we aimed to investigate the reliability of independent component analysis (ICA) for localizing multiple RSNs from resting-state functional MRI (rs-fMRI) data in individual patients, and further evaluate lesion-related spatial shifts of the RSNs. Twelve patients with brain metastases and 14 healthy controls were recruited. Using an improved automatic component identification method, we successfully identified seven common RSNs, including: the default mode network (DMN), executive control network (ECN), dorsal attention network (DAN), language network (LN), sensorimotor network (SMN), auditory network (AN) and visual network (VN), in both individual patients and controls. Moreover, the RSNs in the patients showed a visible spatial shift compared to those in the controls, and the spatial shift of some regions was related to the tumor location, which may reflect a complicated functional mechanism - functional disruptions and reorganizations - caused by metastases. Besides, higher cognitive networks (DMN, ECN, DAN and LN) showed significantly larger spatial shifts than perceptual networks (SMN, AN and VN), supporting a functional dichotomy between the two network groups even in pathologic alterations associated with metastases. Overall, our findings provide evidence that ICA is a promising approach for presurgical localization of multiple RSNs from rs-fMRI data in individual patients. More attention should be paid to the spatial shifts of the RSNs before surgical resection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, S. M., Rapcsak, S. Z., & Beeson, P. M. (2010). Cost function masking during normalization of brains with focal lesions: still a necessity? NeuroImage, 53, 78–84.
Beckmann, C. F., DeLuca, M., Devlin, J. T., & Smith, S. M. (2005). Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 360, 1001–1013.
Bell, A. J., & Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Computation, 7, 1129–1159.
Brett, M., Leff, A. P., Rorden, C., & Ashburner, J. (2001). Spatial normalization of brain images with focal lesions using cost function masking. NeuroImage, 14, 486–500.
Briganti, C., Sestieri, C., Mattei, P. A., Esposito, R., Galzio, R. J., Tartaro, A., et al. (2012). Reorganization of functional connectivity of the language network in patients with brain gliomas. AJNR - American Journal of Neuroradiology, 33, 1983–1990.
Brownsett, S. L., Warren, J. E., Geranmayeh, F., Woodhead, Z., Leech, R., & Wise, R. J. (2014). Cognitive control and its impact on recovery from aphasic stroke. Brain : a Journal of Neurology, 137, 242–254.
Chang, E. L., Wefel, J. S., Maor, M. H., Hassenbusch 3rd, S. J., Mahajan, A., Lang, F. F., et al. (2007). A pilot study of neurocognitive function in patients with one to three new brain metastases initially treated with stereotactic radiosurgery alone. Neurosurgery, 60, 277–283 discussion 283–274.
Charras, P., Herbet, G., Deverdun, J., de Champfleur, N. M., Duffau, H., Bartolomeo, P., et al. (2015). Functional reorganization of the attentional networks in low-grade glioma patients: a longitudinal study. Cortex; a Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior, 63, 27–41.
Corbetta, M., & Shulman, G. L. (2002). Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3, 201–215.
Damoiseaux, J. S., Rombouts, S. A., Barkhof, F., Scheltens, P., Stam, C. J., Smith, S. M., et al. (2006). Consistent resting-state networks across healthy subjects. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 13848–13853.
Delattre, J. Y., Krol, G., Thaler, H. T., & Posner, J. B. (1988). Distribution of brain metastases. Archives of Neurology, 45, 741–744.
Ding, J. R., Liao, W., Zhang, Z., Mantini, D., Xu, Q., Wu, G. R., et al. (2011). Topological fractionation of resting-state networks. PLoS One, 6, e26596.
Duffau, H. (2001). Acute functional reorganisation of the human motor cortex during resection of central lesions: a study using intraoperative brain mapping. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 70, 506–513.
Esposito, R., Mattei, P. A., Briganti, C., Romani, G. L., Tartaro, A., & Caulo, M. (2012). Modifications of default-mode network connectivity in patients with cerebral glioma. PLoS One, 7, e40231.
Fox, M. D., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8, 700–711.
Gavrilovic, I. T., & Posner, J. B. (2005). Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 75, 5–14.
Gooijers, J., Beets, I. A., Albouy, G., Beeckmans, K., Michiels, K., Sunaert, S., et al. (2016). Movement preparation and execution: differential functional activation patterns after traumatic brain injury. Brain : a Journal of Neurology, 139, 2469–2485.
Hacker, C. D., Laumann, T. O., Szrama, N. P., Baldassarre, A., Snyder, A. Z., Leuthardt, E. C., et al. (2013). Resting state network estimation in individual subjects. NeuroImage, 82, 616–633.
Huang, H., Ding, Z., Mao, D., Yuan, J., Zhu, F., Chen, S., et al. (2016). PreSurgMapp: a MATLAB toolbox for presurgical mapping of eloquent functional areas based on task-related and resting-state functional MRI. Neuroinformatics, 14, 421–438.
Jann, K., Kottlow, M., Dierks, T., Boesch, C., & Koenig, T. (2010). Topographic electrophysiological signatures of FMRI Resting State Networks. PLoS One, 5, e12945.
Kokkonen, S. M., Nikkinen, J., Remes, J., Kantola, J., Starck, T., Haapea, M., et al. (2009). Preoperative localization of the sensorimotor area using independent component analysis of resting-state fMRI. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 27, 733–740.
Lee, M. H., Smyser, C. D., & Shimony, J. S. (2013). Resting-state fMRI: a review of methods and clinical applications. AJNR - American Journal of Neuroradiology, 34, 1866–1872.
Li, Y. O., Adali, T., & Calhoun, V. D. (2007). Estimating the number of independent components for functional magnetic resonance imaging data. Human Brain Mapping, 28, 1251–1266.
Liao, W., Chen, H., Feng, Y., Mantini, D., Gentili, C., Pan, Z., et al. (2010a). Selective aberrant functional connectivity of resting state networks in social anxiety disorder. NeuroImage, 52, 1549–1558.
Liao, W., Mantini, D., Zhang, Z., Pan, Z., Ding, J., Gong, Q., et al. (2010b). Evaluating the effective connectivity of resting state networks using conditional Granger causality. Biological Cybernetics, 102, 57–69.
Lin, X., & DeAngelis, L. M. (2015). Treatment of brain metastases. Journal of Clinical Oncology: Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 33, 3475–3484.
Liu, H., Buckner, R. L., Talukdar, T., Tanaka, N., Madsen, J. R., & Stufflebeam, S. M. (2009). Task-free presurgical mapping using functional magnetic resonance imaging intrinsic activity. Journal of Neurosurgery, 111, 746–754.
Martino, J., Honma, S. M., Findlay, A. M., Guggisberg, A. G., Owen, J. P., Kirsch, H. E., et al. (2011). Resting functional connectivity in patients with brain tumors in eloquent areas. Annals of Neurology, 69, 521–532.
Mesulam, M. M. (1998). From sensation to cognition. Brain : a Journal of Neurology, 121(Pt 6), 1013–1052.
Mitchell, T. J., Hacker, C. D., Breshears, J. D., Szrama, N. P., Sharma, M., Bundy, D. T., et al. (2013). A novel data-driven approach to preoperative mapping of functional cortex using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery, 73, 969–982 discussion 982–963.
Price, C. J., & Friston, K. J. (1999). Scanning patients with tasks they can perform. Human Brain Mapping, 8, 102–108.
Qi, R., Zhang, L. J., Xu, Q., Zhong, J., Wu, S., Zhang, Z., et al. (2012). Selective impairments of resting-state networks in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS One, 7, e37400.
Qiu, T. M., Yan, C. G., Tang, W. J., Wu, J. S., Zhuang, D. X., Yao, C. J., et al. (2014). Localizing hand motor area using resting-state fMRI: validated with direct cortical stimulation. Acta Neurochirurgica, 156, 2295–2302.
Rosazza, C., & Minati, L. (2011). Resting-state brain networks: literature review and clinical applications. Neurological Sciences : Official Journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology, 32, 773–785.
Sair, H. I., Yahyavi-Firouz-Abadi, N., Calhoun, V. D., Airan, R. D., Agarwal, S., Intrapiromkul, J., et al. (2016). Presurgical brain mapping of the language network in patients with brain tumors using resting-state fMRI: comparison with task fMRI. Human Brain Mapping, 37, 913–923.
Schwarzkopf, D. S., De Haas, B., & Rees, G. (2012). Better ways to improve standards in brain-behavior correlation analysis. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 200.
Shimony, J. S., Zhang, D., Johnston, J. M., Fox, M. D., Roy, A., & Leuthardt, E. C. (2009). Resting-state spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity: a new paradigm for presurgical planning using fMRI. Academic Radiology, 16, 578–583.
Shinoura, N., Suzuki, Y., Yamada, R., Kodama, T., Takahashi, M., & Yagi, K. (2006). Restored activation of primary motor area from motor reorganization and improved motor function after brain tumor resection. AJNR - American Journal of Neuroradiology, 27, 1275–1282.
Shirer, W. R., Ryali, S., Rykhlevskaia, E., Menon, V., & Greicius, M. D. (2012). Decoding subject-driven cognitive states with whole-brain connectivity patterns. Cerebral Cortex, 22, 158–165.
Sills, A. K. (2005). Current treatment approaches to surgery for brain metastases. Neurosurgery, 57, S24–S32 discusssion S21–24.
Smith, S. M., Fox, P. T., Miller, K. L., Glahn, D. C., Fox, P. M., Mackay, C. E., et al. (2009). Correspondence of the brain's functional architecture during activation and rest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 13040–13045.
Smith, S. M., Vidaurre, D., Beckmann, C. F., Glasser, M. F., Jenkinson, M., Miller, K. L., et al. (2013). Functional connectomics from resting-state fMRI. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17, 666–682.
Stippich, C., Blatow, M., & Karkow, K. (2007). Presurgical functional MRI in patients with brain tumors. In C. Stippich (Ed.), Clinical functional MRI: Presurgical functional neuroimaging (pp. 87–134). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Sunaert, S. (2006). Presurgical planning for tumor resectioning. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging : JMRI, 23, 887–905.
Tie, Y., Rigolo, L., Norton, I. H., Huang, R. Y., Wu, W., Orringer, D., et al. (2014). Defining language networks from resting-state fMRI for surgical planning--a feasibility study. Human Brain Mapping, 35, 1018–1030.
Tieleman, A., Deblaere, K., Van Roost, D., Van Damme, O., & Achten, E. (2009). Preoperative fMRI in tumour surgery. European Radiology, 19, 2523–2534.
Vargo, M. M. (2017). Brain tumors and metastases. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America, 28, 115–141.
Vlieger, E. J., Majoie, C. B., Leenstra, S., & Den Heeten, G. J. (2004). Functional magnetic resonance imaging for neurosurgical planning in neurooncology. European Radiology, 14, 1143–1153.
Wood, J. M., Kundu, B., Utter, A., Gallagher, T. A., Voss, J., Nair, V. A., et al. (2011). Impact of brain tumor location on morbidity and mortality: a retrospective functional MR imaging study. AJNR - American Journal of Neuroradiology, 32, 1420–1425.
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14, 339–351.
Yu, Q., Plis, S. M., Erhardt, E. B., Allen, E. A., Sui, J., Kiehl, K. A., et al. (2011). Modular organization of functional network connectivity in healthy controls and patients with Schizophrenia during the resting state. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 5, 103.
Zhang, D., Johnston, J. M., Fox, M. D., Leuthardt, E. C., Grubb, R. L., Chicoine, M. R., et al. (2009). Preoperative sensorimotor mapping in brain tumor patients using spontaneous fluctuations in neuronal activity imaged with functional magnetic resonance imaging: initial experience. Neurosurgery, 65, 226–236.
Zhang, H., Zuo, X. N., Ma, S. Y., Zang, Y. F., Milham, M. P., & Zhu, C. Z. (2010). Subject order-independent group ICA (SOI-GICA) for functional MRI data analysis. NeuroImage, 51, 1414–1424.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81401482) and the Educational Commission of Sichuan Province of China (No. 17ZA0269). P. Thompson is funded in part by the NIH, under grant U54 EB020403 from the Big Data to Knowledge (BD2K) program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6518 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, JR., Zhu, F., Hua, B. et al. Presurgical localization and spatial shift of resting state networks in patients with brain metastases. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 408–420 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9864-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9864-6